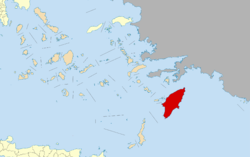
Rhodes
Rhodes Ρόδος | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Island and Municipality | |||
 Palace of the Grand Master in the city of Rhodes | |||
| |||
 | |||
| Coordinates: 36°10′N 27°56′E / 36.167°N 27.933°E / 36.167; 27.933Coordinates: 36°10′N 27°56′E / 36.167°N 27.933°E / 36.167; 27.933 | |||
| Country | |||
| Administrative region | |||
| Regional unit | Rhodes | ||
| Highest elevation | 1,216 m (3,990 ft) | ||
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) | ||
| Population (2011) | |||
| • Total | 115,490 | ||
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) | ||
| Postal code | 851 00 | ||
| Telephone | 2241, 2244, 2246 | ||
| Website | www.rhodes.gr | ||

General view of the village of Lindos, with the acropolis and the beaches, island of Rhodes, Greece
Rhodes (Greek: Ρόδος, Ródos [ˈroðos]) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece in terms of land area and also the island group's historical capital. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the South Aegean administrative region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Rhodes.[1] The city of Rhodes had 50,636 inhabitants in 2011. It is located northeast of Crete, southeast of Athens and just off the Anatolian coast of Turkey. Rhodes' nickname is The island of the Knights, named after the Knights of Saint John of Jerusalem, who once conquered the land.[2]
Historically, Rhodes was famous worldwide for the Colossus of Rhodes, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The Medieval Old Town of the City of Rhodes has been declared a World Heritage Site. Today, it is one of the most popular tourist destinations in Europe.[3][4][5][6] The name of the U.S. state of Rhode Island is based on these islands.
Contents
1 Name
2 Geography
2.1 Flora
2.2 Fauna
2.3 Earthquakes
2.4 Climate
3 History
3.1 Early and classical antiquity
3.2 Prehistory
3.3 Minoan Era
3.4 Mycenaean Era
3.5 Archaic Era
3.6 Classical Era
3.7 Hellenistic age
3.8 Byzantine period
3.9 Crusader and Islamic rule
3.10 Modern history
4 Archaeology
5 Religion
5.1 Christianity
5.2 Islam
5.3 Judaism
6 Government
6.1 Towns and villages
7 Economy
8 Transportation
8.1 Air
8.2 Sea
8.3 Road network
8.4 Bus
8.5 Cars and motorbikes
9 Sports
10 Culture
11 Notable people
12 Tourism
13 Panoramas
14 See also
15 References
16 Sources
17 External links
Name
The island has been known as Ρόδος in Greek throughout its history. In addition, the island has been called Rodi in Italian, Rodos in Turkish, and Rodi or Rodes in Ladino.
The Travels of Sir John Mandeville incorrectly reports that Rhodes was formerly called "Collosus", through a conflation of the Colossus of Rhodes and Paul's Epistle to the Colossians, which refers to Colossae.[7]
The island's name might be derived from erod, Phoenician for snake, since the island was infested with snakes in antiquity.[8]
Geography

Topographic map of Rhodes

Akramitis mountain
The island of Rhodes is shaped like a spearhead, 79.7 km (49.5 mi) long and 38 km (24 mi) wide, with a total area of approximately 1,400 square kilometres (541 sq mi) and a coastline of approximately 220 km (137 mi). Limestone is the main bedrock.[9] The city of Rhodes is located at the northern tip of the island, as well as the site of the ancient and modern commercial harbours. The main air gateway (Diagoras International Airport, IATA code: RHO) is located 14 km (9 mi) to the southwest of the city in Paradisi. The road network radiates from the city along the east and west coasts.
Outside of the city of Rhodes, the island is dotted with small villages and spa resorts, among them Faliraki, Lindos, Kremasti, Haraki, Pefkos, Archangelos, Afantou, Ixia, Koskinou, Embona (Attavyros), Paradisi, and Trianta (Ialysos). There are mineral-rich spring water (and sometimes sea water) used to give medicinal baths and the spa resorts offer various health treatments.
Rhodes is situated 363 km (226 mi) east-south-east from the Greek mainland, and 18 km (11 mi) from the southern shore of Turkey.
Flora
The interior of the island is mountainous, sparsely inhabited and covered with forests of pine (Pinus brutia) and cypress (Cupressus sempervirens). While the shores are rocky, the island has arable strips of land where citrus fruit, wine grapes, vegetables, olives and other crops are grown.
Fauna
The Rhodian population of fallow deer was found to be genetically distinct in 2005, and to be of urgent conservation concern.[10] In Petaloudes Valley (Greek for "Valley of the Butterflies"), large numbers of tiger moths gather during the summer months. Mount Attavyros, at 1,216 metres (3,990 ft), is the island's highest point of elevation.
Earthquakes
Earthquakes include the 226 BC earthquake that destroyed the Colossus of Rhodes; one on 3 May 1481 which destroyed much of the city of Rhodes;[11] and one on 26 June 1926.[12]
On 15 July 2008, Rhodes was struck by a 6.3 magnitude earthquake causing minor damage to a few old buildings and one death.[13]
Climate
Rhodes has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate (Csa in the Köppen climate classification).
| Climate data for Rhodes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.0 (71.6) | 22.0 (71.6) | 27.4 (81.3) | 30.6 (87.1) | 34.8 (94.6) | 36.2 (97.2) | 39.0 (102.2) | 41.2 (106.2) | 35.4 (95.7) | 33.2 (91.8) | 28.4 (83.1) | 22.8 (73) | 41.2 (106.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 15.1 (59.2) | 15.2 (59.4) | 16.8 (62.2) | 20.0 (68) | 24.2 (75.6) | 28.4 (83.1) | 30.5 (86.9) | 30.7 (87.3) | 28.2 (82.8) | 24.5 (76.1) | 20.1 (68.2) | 16.6 (61.9) | 22.5 (72.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 12.0 (53.6) | 12.0 (53.6) | 13.5 (56.3) | 16.3 (61.3) | 20.0 (68) | 24.2 (75.6) | 26.4 (79.5) | 26.7 (80.1) | 24.4 (75.9) | 20.7 (69.3) | 16.7 (62.1) | 13.5 (56.3) | 18.9 (66) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 8.8 (47.8) | 8.8 (47.8) | 10.1 (50.2) | 12.5 (54.5) | 15.8 (60.4) | 19.9 (67.8) | 22.3 (72.1) | 22.7 (72.9) | 20.5 (68.9) | 16.9 (62.4) | 13.2 (55.8) | 10.4 (50.7) | 15.2 (59.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −4.0 (24.8) | −1.6 (29.1) | 0.2 (32.4) | 5.2 (41.4) | 8.6 (47.5) | 12.6 (54.7) | 16.8 (62.2) | 17.0 (62.6) | 10.6 (51.1) | 7.2 (45) | 2.4 (36.3) | 1.2 (34.2) | −4.0 (24.8) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 149.6 (5.89) | 105.7 (4.161) | 75.6 (2.976) | 27.8 (1.094) | 18.6 (0.732) | 2.3 (0.091) | 0.4 (0.016) | 0.2 (0.008) | 5.8 (0.228) | 65.5 (2.579) | 94.1 (3.705) | 157.4 (6.197) | 703 (27.677) |
| Average rainy days | 15.5 | 12.7 | 10.5 | 7.6 | 4.6 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 6.7 | 9.5 | 15.4 | 85.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 70.1 | 69.1 | 68.7 | 66.5 | 64.4 | 58.5 | 57.6 | 59.9 | 61.4 | 67.5 | 71.4 | 72.4 | 65.6 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 5.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 9.0 | 11.0 | 13.0 | 14.0 | 13.0 | 11.0 | 8.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 50 | 55 | 58 | 69 | 79 | 87 | 100 | 100 | 92 | 73 | 60 | 50 | 73 |
| Source #1: Hellinic National Meteorological Service [14] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: NOAA (Record temperature),[15] Weather Atlas (sunshine data)[16] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Rhodes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average sea temperature °C (°F) | 17.9 (64.2) | 17.0 (62.6) | 17.1 (62.8) | 17.6 (63.7) | 20.1 (68.2) | 23.4 (74.1) | 25.9 (78.6) | 27.2 (81.0) | 26.7 (80.1) | 23.8 (74.8) | 20.9 (69.6) | 18.8 (65.8) | 21.4 (70.5) |
| Mean daily daylight hours | 10.0 | 11.0 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 14.0 | 15.0 | 14.0 | 13.0 | 12.0 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 12.1 |
| Average Ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 5.9 |
| Source: Weather Atlas [16] | |||||||||||||

Ixia beach, Rhodes

Valley of Petaloudes
History
Early and classical antiquity

Mycenean necklace of carnelian found in Kattavia

Silver drachma of Rhodes, 88/42 BC. Obverse: radiate head of Helios. Reverse: rose, "rhodon" (ῥόδον), the symbol of Rhodes.

Temple of Apollo at the Acropolis of Rhodes
Prehistory
The island was inhabited in the Neolithic period, although little remains of this culture.
Minoan Era
In the 16th century BC, the Minoans came to Rhodes. Later Greek mythology recalled a Rhodian race called the Telchines and associated the island of Rhodes with Danaus; it was sometimes nicknamed Telchinis.
Mycenaean Era
In the 15th century BC, Mycenaean Greeks invaded. After the Bronze Age collapse, the first renewed outside contacts were with Cyprus.[17]
Homer mentions that Rhodes participated in the Trojan War under the leadership of Tlepolemus.[18]
Archaic Era
In the 8th century BC, the island's settlements started to form, with the coming of the Dorians, who built the three important cities of Lindos, Ialyssos and Kameiros, which together with Kos, Cnidus and Halicarnassus (on the mainland) made up the so-called Dorian Hexapolis (Greek for six cities).
In Pindar's ode, the island was said to be born of the union of Helios the sun god and the nymph Rhodos, and the cities were named for their three sons. The rhoda is a pink hibiscus native to the island. Diodorus Siculus added that Actis, one of the sons of Helios and Rhode, travelled to Egypt. He built the city of Heliopolis and taught the Egyptians astrology.[19]
In the second half of the 8th century, the sanctuary of Athena received votive gifts that are markers for cultural contacts: small ivories from the Near East and bronze objects from Syria. At Kameiros on the northwest coast, a former Bronze Age site, where the temple was founded in the 8th century, there is another notable contemporaneous sequence of carved ivory figurines. The cemeteries of Kameiros and Ialyssos yielded several exquisite exemplars of the Orientalizing Rhodian jewellery, dated in the 7th and early 6th centuries BC.[20] Phoenician presence on the island at Ialysos is attested in traditions recorded much later by Rhodian historians.[citation needed]
Classical Era
The Persians invaded and overran the island, but they were in turn defeated by forces from Athens in 478 BC. The Rhodian cities joined the Athenian League. When the Peloponnesian War broke out in 431 BC, Rhodes remained largely neutral, although it remained a member of the League. The war lasted until 404 BC, but by this time Rhodes had withdrawn entirely from the conflict and decided to go her own way.[citation needed]
In 408 BC, the cities united to form one territory. They built the city of Rhodes, a new capital on the northern end of the island. Its regular plan was, according to Strabo, superintended by the Athenian architect Hippodamus.
In 357 BC, the island was conquered by the king Mausolus of Caria, then it fell again to the Persians in 340 BC. Their rule was also short.
Hellenistic age
Rhodes then became a part of the growing empire of Alexander the Great in 332 BC, after he defeated the Persians.[citation needed]

The Colossus of Rhodes, as depicted in an artist's impression of 1880
Following the death of Alexander, his generals vied for control of the kingdom. Three—Ptolemy, Seleucus, and Antigonus—succeeded in dividing the kingdom among themselves. Rhodes formed strong commercial and cultural ties[21] with the Ptolemies in Alexandria, and together formed the Rhodo-Egyptian alliance that controlled trade throughout the Aegean in the 3rd century BC.
The city developed into a maritime, commercial and cultural center; its coins circulated nearly everywhere in the Mediterranean. Its famous schools of philosophy, science, literature and rhetoric shared masters with Alexandria: the Athenian rhetorician Aeschines, who formed a school at Rhodes; Apollonius of Rhodes;[22] the observations and works of the astronomers Hipparchus and Geminus, the rhetorician Dionysius Thrax. Its school of sculptors developed, under Pergamese influence, a rich, dramatic style that can be characterized as "Hellenistic Baroque". Agesander of Rhodes, with two other Rhodian sculptors, carved the famous Laocoön group, now in the Vatican Museums, and the large sculptures rediscovered at Sperlonga in the villa of Tiberius, probably in the early Imperial period.[23]
In 305 BC, Antigonus directed his son, Demetrius, to besiege Rhodes in an attempt to break its alliance with Egypt. Demetrius created huge siege engines, including a 180 ft (55 m) battering ram and a siege tower named Helepolis that weighed 360,000 pounds (163,293 kg). Despite this engagement, in 304 BC after only one year, he relented and signed a peace agreement, leaving behind a huge store of military equipment. The Rhodians sold the equipment and used the money to erect a statue of their sun god, Helios, the statue since called the Colossus of Rhodes.[citation needed]
Throughout the 3rd century BC, Rhodes attempted to secure her independence and her commerce, most especially her virtual control over the grain trade in the eastern Mediterranean. Both of these goals were dependent upon no one of the three great Hellenistic states achieving dominance, and consequently the Rhodians pursued a policy of maintaining a balance of power among the Antigonids, Seleucids and Ptolemies, even if that meant going to war with her traditional ally, Egypt. To this end they employed as leverage their economy and their excellent navy, which was manned by proverbially the finest sailors in the Mediterranean world: "If we have ten Rhodians, we have ten ships."[citation needed] The Rhodians also established their dominance on the shores of Caria across from their island, which became known as the "Rhodian Peraia". It extended roughly from the modern city of Muğla (ancient Mobolla) in the north and Kaunos bordering Lycia in the south, near the present-day Dalyan, Turkey.
Rhodes successfully carried on this policy through the course of the third century BC, an impressive achievement for what was essentially a democratic state. By the end of that period, however, the balance of power was crumbling, as declining Ptolemaic power made Egypt an attractive target for Seleucid ambitions. In 203/2 BC the young and dynamic kings of Antigonid Macedon and Seleucid Asia, Philip V and Antiochus III, agreed to accept—at least temporarily—their respective military ambitions, Philip's campaign in the Aegean and western Anatolia and Antiochus’ final solution of the Egyptian question. Heading a coalition of small states, the Rhodians checked Philip's navy, but not his superior army. Without a third power to which to turn, the Rhodians appealed in 201 BC to the Roman Republic.[citation needed]

Medieval gate at the Acropolis of Lindos
Despite being exhausted by the titanic struggle against Hannibal (218-201 BC) the Romans agreed to intervene, having already been stabbed in the back by Philip during the war against Carthage. The Senate saw the appeal from Rhodes and her allies as the opportunity to pressure Philip. The result was the Second Macedonian War (200-196 BC), which ended Macedon's role as a major player and preserved Rhodian independence.[citation needed] Rhodian influence in the Aegean was cemented through the organization of the Cyclades into the Second Nesiotic League under Rhodian leadership.
The Romans actually withdrew from Greece after the end of the conflict, but the resulting power vacuum quickly drew in Antiochus and subsequently the Romans, who defeated (192-188 BC) the last Mediterranean power that might even vaguely threaten their predominance. Having provided Rome with valuable naval help in her first foray into Asia, the Rhodians were rewarded with territory and enhanced status.[citation needed] The Romans once again evacuated the east – the Senate preferred clients to provinces – but it was clear that Rome now ruled the world and Rhodian autonomy was ultimately dependent upon good relations with them.[citation needed]
And those good graces soon evaporated in the wake of the Third Macedonian War (171-168 BC). In 169 BC, during the war against Perseus, Rhodes sent Agepolis as ambassador to the consul Quintus Marcius Philippus, and then to Rome in the following year, hoping to turn the Senate against the war.[24] Rhodes remained scrupulously neutral during the war, but in the view of hostile elements in the Senate she had been a bit too friendly with the defeated King Perseus. Some actually proposed declaring war on the island republic, but this was averted. In 164, Rhodes became a permanent ally of Rome, ending an independence that no longer had any meaning.[clarification needed] It was said that the Romans ultimately turned against the Rhodians because the islanders were the only people they had encountered who were more arrogant than themselves.[citation needed]
After surrendering its independence Rhodes became a cultural and educational center for Roman noble families and was especially noted for its teachers of rhetoric, such as Hermagoras and the unknown author of Rhetorica ad Herennium. At first, the state was an important ally of Rome and enjoyed numerous privileges, but these were later lost in various machinations of Roman politics. Cassius eventually invaded the island and sacked the city. In the early Imperial period Rhodes became a favorite place for political exiles.[25]
In the 1st century AD, the Emperor Tiberius spent a brief term of exile on Rhodes. Saint Paul brought Christianity to people on the island.[26] Rhodes reached her zenith in the 3rd century.
In ancient times there was a Roman saying: "hic Rhodus, hic salta!"—"Here is Rhodes, jump here", an admonition to prove one's idle boasts by deed rather than talk. It comes from an Aesop's fable called "The Boastful Athlete" and was cited by Hegel, Marx, and Kierkegaard.
Byzantine period
In 395 with the division of the Roman Empire, the long Byzantine period began for Rhodes. In Late Antiquity, the island was the capital of the Roman province of the Islands, headed by a praeses (hegemon in Greek), and encompassing most of the Aegean islands, with twenty cities. Correspondingly, the island was also the metropolis of the ecclesiastical province of Cyclades, with eleven suffragan sees.[27]
Beginning from ca. 600 AD, its influence in maritime issues was manifested in the collection of maritime laws known as "Rhodian Sea Law" (Nomos Rhodion Nautikos), accepted throughout the Mediterranean and in use throughout Byzantine times (and influencing the development of admiralty law up to the present).[citation needed] In 622/3, during the climactic Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628, Rhodes was captured by the Sasanian navy.[28][29][30]
Rhodes was occupied by the Islamic Umayyad forces of Caliph Muawiyah I in 654, who carried off the remains of the Colossus of Rhodes.[27][31] The island was again captured by the Arabs in 673 as part of their first attack on Constantinople. When their fleet was destroyed by Greek fire before Constantinople and by storms on its return trip, however, the island was evacuated in 679/80 as part of the Byzantine–Umayyad peace treaty.[32] In 715 the Byzantine fleet dispatched against the Arabs launched a rebellion at Rhodes, which led to the installation of Theodosios III on the Byzantine throne.[27][33]
From the early 8th to the 12th centuries, Rhodes belonged to the Cibyrrhaeot Theme of the Byzantine Empire, and was a centre for shipbuilding and commerce.[27] In c. 1090, it was occupied by the forces of the Seljuk Turks, not long after the Battle of Manzikert.[34] Rhodes was recaptured by the Emperor Alexios I Komnenos during the First Crusade.

Part of the late medieval fortifications of Rhodes
As Byzantine central power weakened under the Angeloi emperors (1185–1204), in the first half of the 13th century, Rhodes became the centre of an independent domain under Leo Gabalas and his brother John,[27] until it was occupied by the Genoese in 1248–1250. The Genoese were evicted by the Empire of Nicaea, after which the island became a regular province of the Nicaean state (and after 1261 of the restored Byzantine Empire). In 1305, the island was given as a fief to Andrea Morisco, a Genoese adventurer who had entered Byzantine service. But, Rhodes was controlled by Menteşe, was one of Anatolian beyliks between 1300 and 1314.
Crusader and Islamic rule

Ottoman Janissaries and defending Knights of Saint John at the Siege of Rhodes in 1522, from an Ottoman manuscript

Rhodes in the 19th century
In 1306–1310, the Byzantine era of the island's history came to an end when the island was occupied by the Knights Hospitaller.[27] Under the rule of the newly named "Knights of Rhodes", the city was rebuilt into a model of the European medieval ideal. Many of the city's famous monuments, including the Palace of the Grand Master, were built during this period.
The strong walls which the knights had built withstood the attacks of the Sultan of Egypt in 1444, and a siege by the Ottomans under Mehmed II in 1480. Eventually, however, Rhodes fell to the large army of Suleiman the Magnificent in December 1522. The Sultan deployed 400 ships delivering 100,000 men to the island (200,000 in other sources). Against this force the Knights, under Grand Master Philippe Villiers de L'Isle-Adam, had about 7,000 men-at-arms and their fortifications. The siege lasted six months, at the end of which the surviving defeated Hospitallers were allowed to withdraw to the Kingdom of Sicily. Despite the defeat, both Christians and Muslims seem to have regarded the conduct of Villiers de L'Isle-Adam as extremely valiant, and the Grand Master was proclaimed a Defender of the Faith by Pope Adrian VI (see Knights of Cyprus and Rhodes). The knights would later move their base of operations to Malta.
Rhodes was thereafter a possession of the Ottoman Empire (see Sanjak of Rhodes) for nearly four centuries.
Modern history

5 soldi Austrian Levant stamp cancelled in brown RHODUS.[35]

Palazzo Governale (today the offices of the Prefecture of the Dodecanese), built during the Italian period
The island was populated by ethnic groups from the surrounding nations, including Jews. Under Ottoman rule, they generally did fairly well, but discrimination and bigotry occasionally arose. In February 1840, the Jews of Rhodes were falsely accused of ritually murdering a Christian boy. This became known as the Rhodes blood libel.
Austria opened a post-office at RHODUS (Venetian name) before 1864,[36] as witnessed by stamps with Franz-Josef head.
In 1912, Italy seized Rhodes from the Turks during the Italo-Turkish War. The island's population was spared the "exchange of the minorities" between Greece and Turkey Rhodes and the rest of the Dodecanese Islands were assigned to Italy in the Treaty of Ouchy and were supposed to be given back but were not. Turkey ceded them officially in the 1923 Treaty of Lausanne. It then became the core of their possession of the Isole Italiane dell'Egeo.
Following the Italian Armistice of 8 September 1943, the British attempted to get the Italian garrison on Rhodes to change sides. This was anticipated by the German Army, which succeeded in occupying the island with the Battle of Rhodes. In great measure, the German occupation caused the British failure in the subsequent Dodecanese Campaign.
The Turkish Consul Selahattin Ülkümen succeeded, at considerable risk to himself and his family, in saving 42 Jewish families, about 200 persons in total, who had Turkish citizenship or were members of Turkish citizens' families.
On 8 May 1945 the Germans under Otto Wagener surrendered Rhodes as well as the Dodecanese as a whole to the British, who soon after then occupied the islands as a military protectorate.
In 1947, Rhodes, together with the other islands of the Dodecanese, was united with Greece.
In 1949, Rhodes was the venue for negotiations between Israel and Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, and Syria, concluding with the 1949 Armistice Agreements.
The name of the US state of Rhode Island is based on a reference to Rhodes by Italian explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano. In a 1524 letter detailing his excursion into the waters around either Block Island or Aquidneck Island Verrazano wrote that he "discovered an Ilande in the form of a triangle, distant from the maine lande 3 leagues, about the bignesse of the Ilande of the Rodes".
Archaeology

Fountain square at the ancient site of Kameiros

Medieval castle of Monolithos
The Colossus of Rhodes was considered to be one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. This giant bronze statue was documented as once standing at the harbour. It was completed in 280 BC and destroyed in an earthquake in 224 BC. No trace of the statue remains today.
Historical sites on the island of Rhodes include the Acropolis of Lindos, the Acropolis of Rhodes with the Temple of Pythian Apollo and an ancient theatre and stadium,[37] ancient Ialysos, ancient Kamiros, the Governor's Palace, Rhodes Old Town (walled medieval city), the Palace of the Grand Masters, Kahal Shalom Synagogue in the Jewish Quarter, the Archeological Museum, the ruins of the castle of Monolithos, the castle of Kritinia, St. Catherine Hospice and Rhodes Footbridge.
Religion

Filerimos Monastery in Ialysos
Christianity
The predominant religion is Greek Orthodox; the island is the seat of the Metropolis of Rhodes.
There is a significant Latin Catholic[38] minority on the island of 2,000, many of whom are descendants of Italians who remained after the end of the Italian occupation, pastorally served by the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Rhodes.
Islam
Rhodes has a Turkish Muslim minority, a remnant from Ottoman Turkish times who were not required in the population exchange of 1923-24 to leave because the Dodecanese Islands were under Italian administration. They are organized around the Turkish Association of Rhodes (Turkish: Rodos Türk Derneği), which gives the figure 3,500 for the population they bring together and represent for the island.[39] The number of the Turks in Rhodes could be as many as 4,000.[40][41][42]
Judaism
The Jewish community of Rhodes[43] goes back to the first century AD. Kahal Shalom Synagogue, established in 1557, during the Ottoman era, is the oldest synagogue in Greece and still stands in the Jewish quarter of the old town of Rhodes. At its peak in the 1920s, the Jewish community was one-third of the town's total population.[44] In the 1940s, there were about 2000 Jews of various ethnic backgrounds. The Nazis deported and killed most of the community during the Holocaust. Kahal Shalom has been renovated with the help of foreign donors but few Jews live year-round in Rhodes today, so services are not held on a regular basis.[45]
The Jewish Museum of Rhodes was established in 1997 to preserve the Jewish history and culture of the Jews of Rhodes. It is adjacent to the Kahal Shalom Synagogue.
Government

View of Archangelos

View of Lindos with the Acropolis

St Paul's Bay, Lindos
The present municipality Rhodes was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 10 former municipalities, that became municipal units (constituent communities in parentheses):[1]
Afantou (Afantou, Archipoli)
Archangelos (Archangelos, Malonas, Masari)
Attavyros (Embonas, Kritinia, Monolithos, Siana, Agios Isidoros)- Ialysos
Kallithea (Kalythies, Koskinou, Psinthos)
Kameiros (Soroni, Apollona, Dimylia, Kalavarda, Platania, Salakos, Fanes)
Lindos (Lindos, Kalathos, Laerma, Lardos, Pylona)
Petaloudes (Kremasti, Pastida, Maritsa, Paradeisi, Theologos, Damatria)- Rhodes
South Rhodes (Gennadi, Apolakkia, Arnitha, Asklipieio, Vati, Istrios, Kattavia, Lachania,[46]Mesanagros, Profilia)
The municipality has an area of 1400.681 km2.[47] It covers the island of Rhodes and a few uninhabited offshore islets. Rhodes city was the capital of the former Dodecanese Prefecture. Rhodes is the most populated island of the South Aegean Region.
Towns and villages
Rhodes has 43 towns and villages:
| Town/Village | Population[48] | Municipal unit | Town/Village | Population | Municipal unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhodes City | 50,636 | Rhodes | Gennadi | 671 | South Rhodes |
| Ialysos | 11,331 | Ialysos | Salakos | 576 | Kameiros |
| Afantou | 6,329 | Afantou | Kritinia | 503 | Attavyros |
| Archangelos | 5,476 | Archangelos | Kattavia | 307 | South Rhodes |
| Kremasti | 5,396 | Petaloudes | Dimylia | 465 | Kameiros |
| Kalythies | 4,832 | Kallithea | Kalavarda | 502 | Kameiros |
| Koskinou | 3,679 | Kallithea | Pylona | 627 | Lindos |
| Pastida | 3,641 | Petaloudes | Istrios | 291 | South Rhodes |
| Paradeisi | 2,667 | Petaloudes | Damatria | 641 | Petaloudes |
| Maritsa | 1,808 | Petaloudes | Laerma | 361 | Lindos |
| Embonas | 1,242 | Attavyros | Apolakkia | 496 | South Rhodes |
| Soroni | 1,278 | Kameiros | Platania | 196 | Kameiros |
| Lardos | 1,380 | Lindos | Kalathos | 502 | Lindos |
| Psinthos | 853 | Kallithea | Lachania | 153 | South Rhodes |
| Malona | 1,135 | Archangelos | Monolithos | 181 | Attavyros |
| Lindos | 3,087 | Lindos | Mesanagros | 155 | South Rhodes |
| Apollona | 845 | Kameiros | Profilia | 304 | South Rhodes |
| Massari | 1,004 | Archangelos | Arnitha | 215 | South Rhodes |
| Fanes | 858 | Kameiros | Siana | 152 | Attavyros |
| Theologos | 809 | Petaloudes | Vati | 323 | South Rhodes |
| Archipoli | 582 | Afantou | Agios Isidoros | 355 | Attavyros |
| Asklipio | 646 | South Rhodes |
Economy

View of the market (Nea Agora) of Mandraki (Rhodes city), built during the Italian period
The economy is tourist-oriented, and the most developed sector is service. Tourism has elevated Rhodes economically, compared to the rest of Greece.[49]
Small industries process imported raw materials for local retail, though other industry includes agricultural goods production, stockbreeding, fishery and winery.
Transportation
Air

Diagoras Airport, arrivals terminal
Rhodes has three airports but only one is public. Diagoras Airport, one of the biggest in Greece, is the main entrance/exit point for both locals and tourists. The island is well connected with other major Greek cities and islands as well as with major European capitals and cities via charter flights.
Rhodes International Airport, "Diagoras": public airport, 14 km (9 mi) southwest of Rhodes City, third in international passenger volume and fourth in total passenger volume in Greece.
Rhodes Maritsa Airport: closed to public, near Maritsa village. Built in 1938 by the Italians, it was the first airport of the island and was the public airport until 1977. Nowadays, it serves the Hellenic Air Force and is sometimes used for car races.- Kalathos Airfield: inoperative, 7 km (4 mi) north of Lindos. Built by the Italians during World War II, was called Aeroporto di Gadurrà. Today only the runway is visible.
Kattavia Airstrip, located in the south of the island it was an emergency airstrip built by the Italians during World War II. Today it is abandoned.[clarification needed]
Two pilot schools offer aviation services (small plane rental and island hopping).
Sea

MS Thomson Majesty at the harbour of Rhodes

The Kameiros Skala Dock
Rhodes has five ports, three of them in Rhodes City, one in the west coast near Kamiros and one in east coast near Lardos.[citation needed]
- Central Port: located in the city of Rhodes serves exclusively international traffic consisting of scheduled services to/from Turkey, cruise ships and yachts. Since Summer 2012, the port is also a homeport for Costa Cruises during the summer period.
- Kolona Port: opposite and north of the central port, serves intra-Dodecanese traffic and all sizes yachts.
- Akandia Port: the new port of the island, south and next to the central port, being built since the 1960s, for domestic, cargo and general purpose traffic. Since 2017 summer a passenger terminal is finally in use hosting a cafe and waiting lounges.[50]
- Kamiros Skala Dock: 30 km (19 mi) south west of the city near Ancient Kamiros ruins serves mainly the island of Halki
- Lardos Dock: formerly servicing local industries, now under development as an alternative port for times when the central port is inaccessible due to weather conditions. It is situated in a rocky shore near the village of Lardos in south east Rhodes.
Road network
The road network of the island is mostly paved and consists of 3 national roads plus one planned, 40 provincial and numerous local. These are the four major island arteries:
Rhodes-Kamiros Province Avenue: Province road 2 till Kalavarda village and 21 from there till Kamiros with two lane that runs through the west coast north to south and connects Rhodes City with Diagoras Airport and Kamiros.[citation needed]
- Rhodes-Lindos National Avenue (Greek National Road 95): Four and two lane, runs mainly inland north to south and connects Rhodes City with Lindos.[citation needed] Part from Rhodes Town until Kolympia is now 4 lanes, the rest until Lindos is 2 lanes.
- Rhodes-Kallithea-Faliraki Province Avenue 4: Two lanes, runs through the east coast north to south and connects Rhodes City with Kallithea monument and Faliraki Resort.[citation needed]
- Tsairi-Airport National Avenue (Greek National Road 100): Four and two lane, runs inland east to west and connects the east coast with the west and the airport.[citation needed]
- Lindos-Katavia Province Road 1: Two lane, begins just before Lindos and though villages and resorts leads to Katavia village, the southernmost of the island, from where a further deviation leads to Prasonissi.[citation needed]
- Rhodes Town Ring Road (Phase 1): Beginning from the new marina and ending to Rhodes-Kallithea province avenue is a four lane expressway.
Future roads:[citation needed]
- Further widening of Rhodes-Lindos National Avenue (Greek National Road 95) from Kolympia to Lindos. This is to be four lane with a jersey barrier in the middle. A tender is expected to take place by end of 2019 so as constructions can begin.
- Ring Road phases 2, 3 and 4 pending; phase 2 will extend the expressway to Greek National Road 95 and then to Rhodes General Hospital where it supposedly will connect to also planned new Rhodes City-Airport expressway. In June 2018 Rhodes municipality stated that plans for the final 700 meters of the ring road leading to Akandia Port are pending approval.[51] Phases 3 and 4 which plan to run the ring road from hospital hill down to Ixia and then through Kritika back to the town will most probably never occur.
- Plans also exist for a new four lane express road connecting Rhodes Town with Diagoras Airport. The road, recognised as National back in 2014[52], will follow existing Provincial Road 3 routing with a total length of 8,6 km and including 3 main junctions and is intended to relieve congestion on the coastal west avenue. The so called Leoforos Mesogeion is vastly anticipated and is a top priority for local authorities.
Bus
Bus services are handled by two operators:[53]
- RODA: Municipal bus company that serves Rhodes city as well suburban areas (Koskinou, Faliraki, Ialysos, Kremasti, Airport, Pastida, Maritsa, Paradeisi) and the west coast of the island
- KTEL: Limited liability private transport company that serve villages and resorts in the east coast of the island
Cars and motorbikes
Families in Rhodes often own more than one car, along with a motorbike. Traffic jams are common particularly in the summer months as vehicles more than double while parking spots downtown and around the old town are limited and can't cope with demand. Moreover, the island is served by 450 taxis and some 200 public and private buses adding to the traffic burden.
Sports

Diagoras Stadium in the city of Rhodes
- Football: AS Rodos and Diagoras F.C. are the island's biggest teams and rivals. Both competed in 2017-18 season at the national level third tier (Gamma Ethniki) along with GAS Ialysos but at season end the former relegated while Diagoras and Ialysos remained. Kremasti town team, Foivos, will join them for 2018-19 season as it was promoted. Local football leagues (organized at the prefecture level) contain three divisions with more than 50 teams.[54] Many stadia are grass covered.[55]
- Basketball: Colossus BC sponsors professional basketball and currently plays in the top-level Greek Basket League. The local league includes a single division with two groups, one for Rhodes and the other for the rest islands, with 7 and 5 teams respectively.[56] Three indoor courts exist in Rhodes City, and one each in Ialysos, Kremasti and Faliraki. Archangelos town will also get an indoor court according to Rhodes municipality planned works and regional government's approved funds.[57]
- Volleyball: Rodion Athlisis managed to escape local obscurity and currently competes at national level second tier losing promotion to first level in play-offs for two consecutive seasons.[58]
- Water polo: mostly amateur based. There is not any single public indoor pool on the island.
- Rugby: introduced in 2007. Teams compete at the national level.[citation needed]
- Tennis: Rhodes Tennis Club (Ροδιακός Όμιλος Αντισφαίρισης) promotes officially tennis since 1949. Club operates on two separate locations, one downtown next to the casino and one next to Kallipateira National Athletic Centre.[59]
- Sailing: Island has competed at the international level[citation needed]
- Cycling: for a long period of time Rhodes had the only cycling track in Greece, producing Olympics-level competitors.[citation needed]
- Rhodes competes in the bi-annual Island Games, which it hosted in 2007.[60]
Culture

Pitaroudia, a traditional chickpea dumpling from Rhodes and Dodecanese
Local specialties of Rhodes include avranies, koulouria, pouggia, tsirigia, fanouropita, katimeria, melekouni, pouggakia, takakia, or mantinades, muchalebi and pitaroudia.[citation needed] The pitaroudia is a large chick pea fritter, and is a characteristic dish in Rhodes.[61]
Notable people

Diagoras of Rhodes carried in the stadium by his two sons
Agesander (1st century BC), sculptor
Apollonius (3rd century BC), epic poet
Chares of Lindos (3rd century BC), sculptor
Cleobulus of Lindos (6th century BC), philosopher and one of the Seven Sages of Ancient Greece
Diagoras (5th century BC), boxer, multiple Olympic winner
Dinocrates (4th century BC), architect and technical adviser for Alexander the Great
Hecato (c. 100 BC), Stoic philosopher
Hieronymus, (c.290-c.230 BC), Peripatetic philosopher
Hipparchus, (2nd century BC), astronomer, mathematician, geographer, founder of trigonometry
Leonidas (2nd century BC), athlete
Memnon (380–333 BC), commander of mercenary army
Mentor (385-340 BC), mercenary soldier, brother of Memnon
Panaetius (c. 185 - c. 110/109 BC), Stoic philosopher
Timocreon (5th century BC), poet
Joannicius II of Constantinople, Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople
Reşit Galip, Turkish politician, one of the first ministers of education of the Republic of Turkey
Niki Xanthou, long jumper
Nick Galis, basketball player, FIBA Hall of Fame and Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame member (his father was born in a small village called Agios Isidoros)
Braith Anasta, rugby league player and NRL premiership winner (ancestral ties to the island through his father, Petros ("Peter") Anastasakis)
Lawrence Durrell, writer and poet, author of the Alexandria Quartet, resided on Rhodes 1945-1947. In 1953 his travel book about Rhodes - Reflections on a Marine Venus - was published.
Tourism
Rhodes is one of the most attractive tourist destinations in Greece. After Crete the island is the most visited destination in Greece, with arrivals standing at 1.785.305 in 2013. In 2014 they stood at 1.931.005, while in 2015 the arrival number reduced slightly and stood at 1.901.000. The average length of stay is estimated at 8 days. Guests from Great Britain, Israel, France, Italy, Sweden and Norway are the ones that constitute the biggest portion in terms of the arrivals by country.[62] In Rhodes the supply of available rooms is high, since more than 550 hotels are operating in the island, the majority of which are 2 star hotels.[62] Additionally, in terms of competitiveness, the World Tourism Organization ranks Greece in the 31st position globally.[63]
Panoramas
Rhodes harbor 2017:

Rhodes panorama 2017:

See also
- Brygindara
- Ancient regions of Anatolia
References
^ ab Kallikratis law Greece Ministry of Interior (in Greek)
^ "Rhodes". Visit Greece..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Paul Hellander, Greece, 2008
^ Duncan Garwood, Mediterranean Europe, 2009
^ Ryan Ver Berkmoes, Oliver Berry, Geert Cole, David Else, Western Europe, 2009
^ Harry Coccossis, Alexandra Mexa, The challenge of tourism carrying capacity assessment: theory and practice, 2004
^ Anthony Bale, trans., The Book of Marvels and Travels, Oxford 2012,
ISBN 0199600600, p. 16 and footnote
^ Encyclopedia Britannica entry for Rhodes
^ "Geography and Geomorphology - South Aegean". www.aegeanislands.gr.
^ Marco, M; Cavallaro, A; Pecchioli, E & Vernesi, C (2006-11-11), "Artificial Occurrence of the Fallow Deer, Dama dama dama (L., 1758), on the Island of Rhodes (Greece): Insight from mtDNA Analysis", Human Evolution, 21, No. 2 (2): 167–175, doi:10.1007/s11598-006-9014-9
^ "Rhodes, Greece, 1481". Jan Kozak Collection: KZ13, The Earthquake Engineering Online Archive.
^ Ambraseys, N. N.; Adams, R. D. (1998). "The Rhodes earthquake of 26 June 1926". Journal of Seismology. 2 (3): 267–292. doi:10.1023/A:1009706415417.
^ "Earthquake's aftermath". Discover Rhodes. Retrieved 16 July 2008.
^ "Climatology - Rodos". Hellinic National Meteorological Service. Retrieved 24 March 2017.
^
"Rhodes Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved March 1, 2015.
^ ab "Rhodes, Greece - Climate data". Weather Atlas. Retrieved 24 March 2017.
^ B. d'Agostino, "Funerary customs and society on Rhodes in the Geometric Period: some observations", in E. Herring and I. Lemos, eds. Across Frontiers: Etruscans, Greeks, Phoenicians and Cypriots. Studies in Honour of D. Ridgway and F.R. Serra Ridgway 2006:57-69.
^ Iliad 2.653-654
^ The Historical Library of Diodorus Siculus, Book V, ch.III. Retrieved 2010-01-24.
^ Sideris A., "Orientalizing Rhodian Jewellery in the Aegean", Cultural Portal of the Aegean Archipelago, Athens 2007.
^ A. Agelarakis"Demographic Dynamics and Funerary Rituals as Reflected from Rhodian Handra Urns", Archival Report, Archaeological and Historical Institute of Rhodes, 2005
^ He wrote about Jason and Medea in the Argonautica.
^ Boardman, 199-201
^ Polybius (1889). Friedrich Otto Hultsch, ed. The Histories of Polybius. London: Macmillan & Co. pp. xxviii. 14, 15, xxix. 4, 7.
^ On Rhodes in antiquity see esp. R.M. Berthold, Rhodes in the Hellenistic Age Ithaca 1984.
^ See Acts 21.
^ abcdef Gregory, Timothy E. (1991). "Rhodes". In Kazhdan, Alexander. The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 1791–1792. ISBN 0-19-504652-8.
^ Kia 2016, p. 223.
^ Greatrex & Lieu 2005, p. 197.
^ Howard-Johnston 2006, p. 33.
^ Treadgold, Warren (1997). A History of the Byzantine State and Society. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press. p. 313. ISBN 0-8047-2630-2.
^ Treadgold, Warren (1997). A History of the Byzantine State and Society. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press. pp. 325, 327. ISBN 0-8047-2630-2.
^ Treadgold, Warren (1997). A History of the Byzantine State and Society. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press. p. 344. ISBN 0-8047-2630-2.
^ Brownworth, Lars (2009). Lost to the West: The Forgotten Byzantine Empire That Rescued Western Civilization. Crown. p. 233. ISBN 978-0-307-40795-5.... the Muslims captured Ephesus in 1090 and spread out to the Greek islands. Chios, Rhodes, and Lesbos fell in quick succession.
^ Mueller, Edwin (1930). Die Poststempel auf der Freimarken-Ausgabe 1867 von Österreich und Ungarn.
^ Mueller, Edwin (1961). Handbook of Austria and Lombardy-Venetia Cancellations on the Postage Stamp Issues 1850-1864. p. 217.
^ "Acropolis if Rhodes:Information". Retrieved 15 May 2013.
^ "Καθολικη Εκκλησια Τησ Ροδου". Catholicchurchrhodes.com. Retrieved 2009-03-22.
^ Turkish wedding in Rhodes attended by Abdullah Gül (in Turkish)
^ Ürkek bir siyasetin tarih önündeki ağır vebali: Oniki ada : hatalı kararlar, acı kayıplar at Google Books
^ "MUM GİBİ ERİYORLAR".
^ "T.C. Dışişleri Bakanlığı'ndan". Archived from the original on 3 September 2014. Retrieved 6 September 2014.
^ See Angel, Marc. The Jews of Rhodes: The History of a Sephardic Community. Sepher-Hermon Press Inc. and The Union of Sephardic Congregations. New York: 1978 (1st ed.), 1980 (2nd ed.), 1998 (3rd ed.).
^ "History of Jewish Greece". Jewishvirtuallibrary.org. Retrieved 2010-01-24.
^ "The Virtual Jewish History Tour — Greece". Jewishvirtuallibrary.org. Retrieved 2010-01-24.
^ F.Fornol: Lachania
^ "Population & housing census 2001 (incl. area and average elevation)" (PDF) (in Greek). National Statistical Service of Greece. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 September 2015.
^ Cite error: The named referencecensus11was invoked but never defined (see the help page).
^ "3comma14.gr".
^ http://www.dimokratiki.gr/02-09-2017/anamorfonete-telios-limani-tis-akantias/
^ http://www.dimokratiki.gr/15-06-2018/anaferthike-se-ola-ta-erga-poy-ektelei-trechontos-o-dimos/
^ http://www.et.gr/idocs-nph/search/pdfViewerForm.html?args=5C7QrtC22wEc63YDhn5AeXdtvSoClrL8lj0jDA0wBrh5MXD0LzQTLWPU9yLzB8V6dxiWmYHFUbmCiBSQOpYnTy36MacmUFCx2ppFvBej56Mmc8Qdb8ZfRJqZnsIAdk8Lv_e6czmhEembNmZCMxLMtXdfQOB6C00YZBnEysLAU6pj8keECmvdb6G_FckhY0ki
^ "Bus schedule" (PDF). Ministry of Economy, Development and Tourism.
^ http://www.epsdod.gr/
^ http://www.epsdod.gr/field/fields_map.php
^ http://www.12basket.gr/
^ https://www.rodiaki.gr/article/392771/kleisto-arxaggeloy-ena-oneiro-etoimo-na-parei-sarka-kai-osta
^ http://www.volleyball.gr/a2-andron/article/1717/a2-andron-mparaz-anodou-a-omilou-apollon-athhnon-rodion-athlhsis-3-1-photos
^ http://www.rhodestennis.gr/index.php?option=com_k2&view=itemlist&layout=category&task=&id=&Itemid=663
^ International Island Games Association website. Retrieved 27Jun08.
^ Summer, A. (2015). 100 Places in Greece Every Woman Should Go. 100 Places. Travelers' Tales. p. 182. ISBN 978-1-60952-108-0. Retrieved June 22, 2017.
^ ab sete.gr
^ world tourism organization competitiveness ranking
Sources
Boardman, John ed., The Oxford History of Classical Art, 1993, OUP,
ISBN 0198143869
Greatrex, Geoffrey; Lieu, Samuel N. C. (2005). The Roman Eastern Frontier and the Persian Wars AD 363-628. Routledge. ISBN 978-1134756469.
Howard-Johnston, J.D. (2006). East Rome, Sasanian Persia and the End of Antiquity: Historiographical and Historical Studies. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 978-0860789925.
Kia, Mehrdad (2016). he Persian Empire: A Historical Encyclopedia [2 volumes]: A Historical Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1610693912.
Nicolle, David (1996), Sassanian Armies: the Iranian Empire Early 3rd to Mid-7th Centuries AD, Stockport: Montvert, ISBN 978-1-874101-08-6
External links
- Official website
- Beaches in Rhodes