Susquehanna River
| Susquehanna River | |
|---|---|
 Susquehanna River in Bradford County, Pennsylvania | |
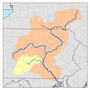
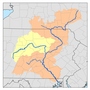
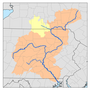
 The Susquehanna watershed | |
| Native name | Siskëwahane |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Maryland, Pennsylvania, New York |
| Cities | Harrisburg, Pa. (state capital), Wilkes-Barre, Pa., Binghamton, N.Y., Havre de Grace, Md., Williamsport, Pa., Owego, N. Y., Bloomsburg, Pa., Port Deposit, Md., Sunbury, Pa., Northumberland, Pa., Pittston, Pa. |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Otsego Lake |
| - location | Cooperstown[1], Otsego County, New York, USA |
| - coordinates | 42°42′02″N 74°55′10″W / 42.70056°N 74.91944°W / 42.70056; -74.91944 |
| - elevation | 1,180 ft (360 m) |
| Mouth | Chesapeake Bay |
Cecil County / Harford County, at Havre de Grace, Maryland, USA | |
- coordinates | 39°32′35″N 76°04′32″W / 39.54306°N 76.07556°W / 39.54306; -76.07556Coordinates: 39°32′35″N 76°04′32″W / 39.54306°N 76.07556°W / 39.54306; -76.07556 |
- elevation | 0 ft (0 m) |
| Length | 464 mi (747 km) |
| Basin size | 27,500 sq mi (71,000 km2) |
| Discharge | |
| - location | Conowingo Dam, MD |
| - average | 40,080 cu ft/s (1,135 m3/s) |
| - minimum | 2,990 cu ft/s (85 m3/s) |
| - maximum | 1,130,000 cu ft/s (32,000 m3/s)June 24, 1972[2] |
| Discharge | |
| - location | Danville, PA |
| - average | 29,000 cu ft/s (820 m3/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| - left | Lackawanna River, Mahanoy Creek, Swatara Creek, Conestoga River |
| - right | Oaks Creek, Unadilla River, Chenango River, Chemung River, West Branch, Juniata River |
The Susquehanna River (/ˌsʌskwəˈhænə/; Lenape: Siskëwahane[3]) is a major river located in the northeastern and mid-Atlantic United States. At 464 miles (747 km) long,[4] it is the longest river on the East Coast of the United States that drains into the Atlantic Ocean. With its watershed, it is the 16th-largest river in the United States,[5][6] and the longest river in the early 21st-century continental United States without commercial boat traffic.
The Susquehanna River forms from two main branches: the "North Branch", which rises in Cooperstown, New York, and is regarded by federal mapmakers as the main branch or headwaters,[7] and the West Branch, which rises in western Pennsylvania and joins the main branch near Northumberland in central Pennsylvania.
The river drains 27,500 square miles (71,000 km2), including nearly half of the land area of Pennsylvania. The drainage basin (watershed) includes portions of the Allegheny Plateau region of the Appalachian Mountains, cutting through a succession of water gaps in a broad zigzag course to flow across the rural heartland of southeastern Pennsylvania and northeastern Maryland in the lateral near-parallel array of mountain ridges. The river empties into the northern end of the Chesapeake Bay at Perryville and Havre de Grace, Maryland, providing half of the Bay's freshwater inflow. The Chesapeake Bay is the ria of the Susquehanna.
Contents
1 Geology
2 Course
2.1 North Branch Susquehanna
2.2 West Branch Susquehanna
2.3 Main Susquehanna flow
3 Etymology
4 History
5 Bridges, ferries, canals and dams
6 Environmental threats
7 Recreation
8 See also
9 References
10 Further reading
11 External links
Geology
The Susquehanna River is one of the oldest existing rivers in the world, being dated as 320-340 Mya,[8] older than the mountain ridges through which it flows. These ridges resulted from the Alleghenian orogeny uplift events, when Africa (as part of Gondwana) slammed into the Northern part of EurAmerica). The Susquehanna basin reaches its ultimate outflow in the Chesapeake Bay. It was well established in the flat tidelands of eastern North America during the Mesozoic era[9] about 252 to 66 million years ago. This is the same period when the Hudson, Delaware and Potomac rivers were established.[9]
Course

Looking upstream in Danville, Pennsylvania
Both branches and the lower Susquehanna were part of important regional transportation corridors. The river was extensively used for muscle-powered ferries, boats, and canal boat shipping of bulk goods in the brief decades before the Pennsylvania Canal System was eclipsed by the coming of age of steam-powered railways. While the railroad industry has been less prevalent since the closures and mergers of the 1950s–1960s, a wide-ranging rail transportation infrastructure still operates along the river's shores.
North Branch Susquehanna

Susquehanna River at source, looking at Otsego Lake.
Also called the Main Branch Susquehanna, the longer branch of the river rises at the outlet of Otsego Lake in Cooperstown, New York. From there, the north branch of the river runs west-southwest through rural farmland and dairy country, receiving the Unadilla River at Sidney. It dips south into Pennsylvania briefly to turn sharply north at Great Bend hooking back into New York. It receives the Chenango in downtown Binghamton. After meandering westwards, it turns south crossing the line again through the twin-towns of Waverly, NY–Sayre and their large right bank railyard, once briefly holding the largest building in the world.[10]
A couple miles south, just across the New York state line, in Athens Township (just south of Waverly, New York) in northern Pennsylvania it receives the Chemung from the northwest. It makes a right-angle curve between Sayre and Towanda to cut through the Endless Mountains in the Allegheny Plateau of Pennsylvania. It receives the Lackawanna River southwest of Scranton and turns sharply to the southwest, flowing through the former anthracite industrial heartland in the mountain ridges of northeastern Pennsylvania, past Pittston City (Greater Pittston), Wilkes-Barre, Nanticoke, Shickshinny, Berwick, Bloomsburg, and Danville.

Looking downriver at Sunbury, Pennsylvania
West Branch Susquehanna
The origin of the official West Branch is near northern Cambria County, Pennsylvania near the contemporary junction of Mitchel Road and US Route 219[11] (locally Plank Road). It travels northeasterly through Curwensville (where the river is dammed to form a lake), into and through Clearfield, Pennsylvania, where it's joined by the Clearfield Creek right bank tributary.
The Clearfield Creek tributary rises in a Loretto woodlands source spring[12] outflow, initially running northerly while draining the north-face and eastern slopes of the drainage divide crossing athwart the greater pass — the irregular rolling terrain of the several local gaps of the Allegheny—several of which end in the hilly pass around Gallitzin Borough, and Gallitzin Township, Tunnelhill, Cresson area — all above and within the greater Altoona, Pennsylvania area.
Clearfield Creek passes through Cresson Lake and bends to flow generally northeast or north-northeast, passing through other tarns and gradually receiving tributary waters along its descending meanders. Outside the pass flats, it is mostly paralleled by PA Route 53, which was built in the river valley, passing through small towns such as Ashville, Glen Hope and others that developed along its banks. It makes its way north and east to the confluence in Clearfield—this valley is also exploited as a railroad corridor from Clearfield, climbing to end in a wye within Cresson in the same broad saddle pass as did the upper works of the Allegheny Portage Railroad. The railroad joins the railroad mainline, climbing a nearby incline through the famous Horseshoe Curve (created by another Susquehanna River (main branch) tributary, in this case one feeding the waters of the Juniata River). The West Branch turns to the southeast and passes through Lock Haven and Williamsport before turning south. The West Branch joins the North Branch flowing from the northwest at Northumberland, just above Sunbury.

Harrisburg, with the Pennsylvania State Capitol dome, seen from Wormleysburg
Main Susquehanna flow
Downstream from the confluence of its branches in Northumberland, the river flows south past Selinsgrove, where it is joined by its Penns Creek tributary, and cuts through a water gap at the western end of Mahantongo Mountain. It receives the Juniata River from the northwest at Duncannon, then passes through its last water gap, the Susquehanna Gap through the Blue Mountain Ridge, just northwest of Harrisburg.
Downtown Harrisburg developed on the east side of the river, which is nearly a mile wide here. Harrisburg is the largest city located on the lower river, which flows southeast across South Central Pennsylvania, forming the border between York and Lancaster counties, and receiving Swatara Creek from the northeast. It crosses into northern Maryland approximately 30 miles (48 km) northeast of Baltimore and is joined by Octoraro Creek from the northeast and Deer Creek from the northwest. The river enters the northern end of the Chesapeake Bay at Havre de Grace. Concord Point Light was built here in 1827 to accommodate the increasing navigational traffic.[13]
Etymology

Looking north of Columbia, Pennsylvania
"Susquehanna" comes from the Len'api (or Delaware Indian) term Sisa'we'hak'hanna, which means "Oyster River."[14] Oyster beds were widespread in the bay near the mouth of the river, which the Lenape farmed, leaving oyster shell middens.[15]
The Len'api were a Native American people at Con'esto'ga ("Roof-place" or "town," modern Washington Boro, Lancaster County), also called Ka'ot'sch'ie'ra ("Place-crawfish," modern Chickisalunga, Lancaster County), or Gasch'guch'sa ("Great-fall-in-river," modern Conewago Falls, Lancaster County) as either Minquas ("quite different"), or Sisa'we'hak'hanna'lenno'wak ("Oyster-river-people").[16][citation needed] The Len'api also called the area Sisa'we'hak'hanna'unk ("Oyster-river-place").[17]
Peoples of the mid-Atlantic Coast included coastal peoples who spoke Algonquian languages, such as the Len'api (whose bands spoke three dialects of Lenape), and Iroquoian languages-speaking peoples of the interior, such as the Eroni and the Five Nations of the Iroquois.[18] The English of Pennsylvania referred to the Eroni people of Conestoga as "Susquehannocks" or "Susquehannock Indians," a name derived from the Lenape term.[18] In addition, John Smith of Jamestown, Virginia, labeled their settlement as "Sasquesahanough" on his 1612 map when he explored the upper Chesapeake Bay area.[19] In Virginia and other southern colonies, Siouan-speaking tribes constituted a third major language family, with their peoples occupying much of the middle areas of the interior. Iroquoian speakers, such as the Cherokee and Tuscarora, generally occupied areas to the interior near the Piedmont and foothills.[20]
History
In the 1670s the Conestoga, or Susquehannock people, succumbed to Iroquois conquest by the powerful Five Nations based in present-day New York, and assimilated with them. In the aftermath, the Iroquois resettled some of the semi-tributary Lenape in this area, as it was near the western boundary of the Lenape's former territory, known as Lenapehoking.
The river has played an important role throughout the history of the United States. In the 18th century, William Penn, the founder of the Pennsylvania Colony, negotiated with the Lenape to allow white settlement in the area between the Delaware River and the Susquehanna, which was part of Lenape territory. In late colonial times, the river became an increasingly important transportation corridor, used to ship anthracite coal discovered by Necho Allen in its upper reaches in the mountains.
In 1779 during the American Revolutionary War, General James Clinton led an expedition down the Susquehanna from its headwaters. His party had made the upper portion navigable by damming the river's source at Otsego Lake, allowing the lake's level to rise, and then destroying the dam and flooding the river in order for his flotilla to travel for miles downstream. James Fenimore Cooper described this event in the introduction to his historical novel, The Pioneers (1823).

Monument at the site of Gen. Clinton's dam at the river's source at Otsego Lake in Cooperstown, New York
At Athens, Pennsylvania, then known as Tioga or "Tioga Point", Clinton met with General John Sullivan and his forces, who had marched from Easton, Pennsylvania. Together on August 29, they defeated the Tories and warriors of allied Iroquois bands at the Battle of Newtown (near present-day Elmira, New York). This was part of what was known as the "Sullivan-Clinton Campaign" or the "Sullivan Expedition". They swept through western New York, destroying more than 40 Seneca and other Iroquois villages, as well as the stores of crops the people set aside for winter. Many of the Iroquois left New York and went to Canada as refugees; casualties from exposure and starvation were high that winter.
Following the United States gaining independence in the Revolutionary War, in 1790 Colonel Timothy Matlack, Samuel Maclay and John Adlum were commissioned by the Supreme Executive Council of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania to survey the headwaters of the Susquehanna river. They were to explore a route for a passage to connect the West Branch with the waters of the Allegheny River, which flowed to Pittsburgh and the Ohio River.[21] In 1792, the Union Canal was proposed in order to link the Susquehanna and the Delaware rivers in Pennsylvania along Swatara and Tulpehocken creeks. In the 19th century, many industrial centers developed along the Susquehanna, using its water power to drive mills and coal machinery, to cool machines, and as a waterway for the transport of raw and manufactured goods.
Pennsylvania and Connecticut both claimed land from the colonial era in the Wyoming Valley along the Susquehanna. Connecticut founded Westmoreland County here and defended its claim in the Pennamite Wars. Under federal arbitration, eventually the state ceded this territory to Pennsylvania.
In the 1790s English Lake Poets Robert Southey, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, and Robert Lovell formulated the "Pantisocracy Plan" to marry three sisters and move to the banks of the Susquehanna River to start a socialist experiment. They made the marriages but Southey moved to Lisbon, Portugal to visit an uncle, and they abandoned the plan to move to the United States.
In 1833 John B. Jervis began a canal system to extend the Chenango River and connect the waters of the Susquehanna from Chenango Point to the Erie Canal, which ran through the Mohawk Valley of New York, ultimately connecting with Lake Erie through the Wood Canal. In October 1836, water from the Susquehanna was connected to the Erie Canal at Utica, New York. Water travel was popular during that era, and the Erie Canal dramatically expanded trade between communities around the Great Lakes and markets in New York and Pennsylvania. With the expansion of construction of railroad lines, canal-transport became unprofitable, as it could not compete in speed or flexibility.[22] Boats had to climb a net height of 1,009 feet between basins, requiring the use of more than 100 water locks, which were too expensive to be maintained under the new competition.[22]
The Susquehanna River figures in the history of the Latter Day Saint movement. It holds that Joseph Smith and Oliver Cowdery received the priesthood from heavenly beings at a site along the Susquehanna in Western New York and performed their first baptisms of Latter Day Saints in the North Branch of the river. Smith and Cowdery said that they were visited on May 15, 1829, by the resurrected John the Baptist and given the Aaronic priesthood. Following his visit, Smith and Cowdery baptized each other in the river. Later that year, they said they were visited near the river by the apostles Peter, James and John. Both events took place in unspecified locations near the river's shore in Susquehanna County, Pennsylvania.
During the Civil War's 1863 Gettysburg Campaign, the commander of the Department of the Susquehanna, Union Major General Darius N. Couch, resolved that Robert E. Lee's Confederate Army of Northern Virginia would not cross the Susquehanna. He positioned militia units under Maj. Granville Haller to protect key bridges in Harrisburg and Wrightsville, as well as nearby fords. Confederate forces reached the river at several locations in Cumberland and York counties but were recalled on June 29 when Lee chose to concentrate his army to the west.[23]
In 1972 the remnants of Hurricane Agnes stalled over the New York-Pennsylvania border, dropping as much as 20 inches (510 mm) of rain on the hilly lands. Much of that precipitation was received into the Susquehanna from its western tributaries, and the valley suffered disastrous flooding. Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, was among the hardest-hit communities and the capital Harrisburg was flooded. The Chesapeake Bay received so much fresh water that it altered the ecosystem, killing much of the marine life that depended on saltwater.
The Mid-Atlantic Flood of June 2006, caused by a stalled jet stream-driven storm system, affected portions of the river system. The worst affected area was Binghamton, New York, where record-setting flood levels forced the evacuation of thousands of residents.

In March 2011, Crary Park in Shickshinny, Pennsylvania, was inundated with a flood when the river rose above 27 feet at Wilkes-Barre.[24] Six months later, the town was devastated by a 42-foot record flood.[25]
In September 2011 the Susquehanna River and its communities were hit by Tropical Storm Lee, which caused the worst flooding since Agnes in 1972.
Bridges, ferries, canals and dams
The Susquehanna River has played an important role in the transportation history of the United States. Prior to the 1818 opening of the Port Deposit Bridge, the river formed a barrier between the northern and southern states, as it could be crossed only by ferry. The earliest dams were constructed to support ferry operations in low water. The presence of many rapids in the river meant that while commercial traffic could navigate down the river in the high waters of the spring thaws, nothing could move up.
The Susquehanna was improved by navigations throughout the 1820s and 1830s as the Pennsylvania Canal. Together with facilities of the Allegheny Portage Railroad, loaded barges were transferred from the canal and hoisted across the mountain ridge into the Pittsburgh area with access to the Monongahela, Allegheny Rivers and their confluence into the Ohio River flowing southwestwards towards the Mississippi River. The 82-mile Union Canal was completed in 1828 to connect the Schuylkill River (flowing southeast towards the Delaware River at Philadelphia) at Reading westwards to the Susquehanna River above the state capital of Harrisburg.[26] Competition from faster transport via the railroad industry by the 1850s resulted in reducing the reliance on the river for transport.[27]
Two different canal systems were constructed on the lower Susquehanna to bypass the rapids. The first was the Susquehanna Canal, also called the Conowingo Canal or the Port Deposit Canal, completed in 1802 by a Maryland company known as the Proprietors of the Susquehanna Canal. The second was the much longer and more successful Susquehanna and Tidewater Canal. The canals required additional dams to provide sufficient canal water and navigation pools.
As the industrial age progressed, bridges replaced ferries, and railroads replaced canals. The railroads were often constructed on top of the canal right-of-way along the river. Many canal remnants can be seen in Havre de Grace, Maryland, along US Route 15 in Pennsylvania, and in upstate New York at various locations. These latter remnants are parts of the upstream divisions of the Pennsylvania Canal, of privately funded canals, and of canals in the New York system.
Today 200 bridges cross the Susquehanna. The Rockville Bridge, which crosses the river from Harrisburg to Marysville, Pennsylvania, was the longest stone masonry arch bridge in the world when it was constructed, a distinction that it continues to hold. It was built by the Pennsylvania Railroad in 1902, replacing an earlier iron bridge. Two seasonal ferries continue to operate across the Susquehanna. The Millersburg Ferry at Millersburg, Pennsylvania is a practical ferry for up to four vehicles and 50 passengers, while the Pride of the Susquehanna, based at Harrisburg, provides a passenger-only pleasure cruise.
Most of the canals have been filled in or are partially preserved as a part of historical parks. Dams generally are used to generate power or to provide lakes for recreation.
Environmental threats

Satellite photo of the river (upper left) where it empties into the Chesapeake Bay (center)
The environmental group American Rivers named the Susquehanna "America's Most Endangered River for 2005" because of the excessive pollution it receives. Most of the pollution in the river is caused by excess animal manure from farming, agricultural runoff, urban and suburban stormwater runoff, and raw or inadequately treated sewage. In 2003 the river contributed 44% of the nitrogen, 21% of the phosphorus, and 21% of the sediment flowing into the Chesapeake Bay.[28]
It was designated as one of the American Heritage Rivers in 1997.[29] The designation provides for technical assistance from federal agencies to state and local governments working in the Susquehanna watershed.
Another environmental concern is radioactivity released during the 1979 Three Mile Island accident.[30] However, extensive radionuclide studies over a 25 year period from 1979 through 2003, confirm that the Three Mile Island accident has not resulted in any harmful radiation effects.[31] The areas in and along a 262-km length of the Susquehanna River in Pennsylvania were monitored for the presence of radioactive materials. This study began two months after the 1979 Three Mile Island (TMI) partial reactor meltdown; it spanned the next 25 years. Monitoring points included stations at the PPL Susquehanna and TMI nuclear power plants. Monthly gamma measurements documented concentrations of radionuclides from natural and anthropogenic sources. During this study, various series of gamma-emitting radionuclide concentration measurements were made in many general categories of animals, plants, and other inorganic matter, both within and near the river. Sampling began in 1979 before the first start-up of the PPL Susquehanna power plant. Although all species were not continuously monitored for the entire period, an extensive database was compiled. In 1986, the ongoing measurements detected fallout from the Chernobyl nuclear accident. These data may be used in support of dose or environmental transport calculations.
In 2015, a smallmouth bass with a rare, cancerous tumor was caught from the river, raising renewed concerns about toxic materials and water pollution.[32][33] The Environmental Protection Agency reported, "we do not have sufficient data at this time to scientifically support listing the main stem of the Susquehanna as impaired."[32]
Recreation
The Susquehanna River has attracted boaters who watch or fish for its migratory species. Many tourists and local residents use the Susquehanna in the summer for recreation purposes such as kayaking, canoeing, and motor-boating. Canoe races are held annually on various sections of the river, such as the amateur race held in Oneonta, New York.
Susquehanna rowing and paddling have a long history. Starting in 1874, rowers from Shamokin Dam, Pennsylvania, raced men from Sunbury. The General Clinton Canoe Regatta, a 70-mile flat-water race, takes place each year in Bainbridge, New York, on Memorial Day weekend. Binghamton University Crew and Hiawatha Island Boat Club are also located on the river, in the Southern Tier of New York.
See also
- List of crossings of the Susquehanna River
- City Island (Pennsylvania)
- Garrett Island (Maryland)
- Geography of Pennsylvania
- List of Maryland rivers
- List of New York rivers
- List of Pennsylvania rivers
- McCormick Island
- Spades Wharf Island
- Three Mile Island accident
- List of parks in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area
References
^ "Susquehanna River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved September 25, 2017..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "USGS 01578310 Susquehanna River at Conowingo, MD". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved August 3, 2010.
^ "Lenape Talking Dictionary". Archived from the original on November 13, 2013. Retrieved May 27, 2012.
^ U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map Archived April 5, 2012, at WebCite, accessed August 8, 2011
^ Susquehanna River Trail Pennsylvania Fish and Boat Commission, accessed March 25, 2010.
^ Susquehanna River Archived April 17, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Green Works Radio, accessed March 25, 2010.
^ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Susquehanna River
^ "Clearwaters, Spring 2009, Historical Look at the Susquehanna River Watershed" (PDF). nywea.org.
[circular reference]
^ ab "Description of the Geology of York County Peninsula". Penn State University Libraries. Archived from the original on October 29, 2007. Retrieved October 26, 2007.
^ Lehigh Valley Railroad's Engine refurbishment and construction work at Sayre yard.
^ 297 Mitchel Rd, Carrolltown, Cambria County, PA 15722 Lat,Lng: 40.584789, -78.718370 per BING Maps
^ lesser right bank tributary source, (40.480772, -78.647088), 1) Birdseye view: In woodland 2)on Map view: Coords: near jct. Vale Rd with Dream Rd, 101-227 Dream Rd, Loretta, PA 15940.
^ Simms, William Q. "Two Lights on the Hill". Lighthouse Digest. Retrieved December 28, 2006.
^ Brinton, Daniel G., C.F. Denke, and Albert Anthony. A Lenâpé – English Dictionary. Biblio Bazaar, 2009.
ISBN 978-1-103-14922-3, p. 132.
^ History on the Half-Shell: The Story of New York City and Its Oysters. (n.d.). Retrieved May 20, 2017, from https://www.nypl.org/blog/2011/06/01/history-half-shell-intertwined-story-new-york-city-and-its-oysters
^ Brinton, Daniel G., C.F. Denke, and Albert Anthony. A Lenâpé – English Dictionary. Biblio Bazaar, 2009.
ISBN 978-1-103-14922-3, pp. 81, 85,132.
^ Zeisberger, David. Indian Dictionary: English, German, Iroquois—The Onondaga and Algonquin—The Delaware. Harvard University Press, 1887.
ISBN 1-104-25351-8, pp. 48, 161, and 222.
^ ab Zeisberger, David. Indian Dictionary: English, German, Iroquois—The Onondaga and Algonquin—The Delaware. Harvard University Press, 1887.
ISBN 1-104-25351-8, p. 141.
^ "John Smith, A Map of Virginia, 1612". www.marinersmuseum.org.
^ Heinemann, Ronald L.; Kolp, John G.; Parent, Jr., Anthony S.; Shade, William G. (2007). Old Dominion, New Commonwealth. Charlottesville: University of Virginia Press. ISBN 978-0-8139-2609-4.
^ Storey, Henry Wilson. History of Cambria County, Pennsylvania. New York: The Lewis Publishing Company, 1907.
^ ab Chenango, Whitford. http://www.mikalac.com/tech/tra/chenango.html
^ "Civil War Timeline", National Park Service
^ Skrapits, Elizabeth (March 12, 2011). "Winter flood slams Shickshinny". The Citizens' Voice. Retrieved March 18, 2011.
^ Hughes, Matt (November 5, 2011). "Shickshinny offered help from group of Buddhists". Wilkes-Barre Times Leader. Retrieved November 18, 2011.
[dead link]
^ Bartholomew, Ann M.; Metz, Lance E.; Kneis, Michael (1989). Delaware and Lehigh Canals (First ed.). Oak Printing Company, Bethlehem, Pennsylvania: Center for Canal History and Technology, Hugh Moore Historical Park and Museum, Inc., Easton, Pennsylvania. pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-0930973094. LCCN 89-25150.
^ Paddle the Susquehanna Archived April 7, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, accessed September 10, 2011.
^ Chesapeake Bay Foundation. Annapolis, MD. "Susquehanna River Named America's Most Endangered River for 2005." April 13, 2005.
^ U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Washington, D.C. "American Heritage Rivers: Upper Susquehanna and Lackawanna Rivers." October 19, 2006.
^ Sturgis, Sue (April 2, 2009). "Investigation: Revelations about Three Mile Island Disaster Raise Doubts over Nuclear Plant Safety". Facing South. Institute for Southern Studies. Archived from the original on October 22, 2014. Retrieved October 18, 2014.
^ Harris, Charles; Kreeger, Danielle; Patrick, Ruth; Palms, John (May 2015). "Twenty-five Years of Environmental Radionuclide Concentrations near a Nuclear Power Plant". Health Physics. 108 (5): 503–513. doi:10.1097/hp.0000000000000266. ISSN 0017-9078. PMID 25811148.
^ ab Ohlheiser, Abby (May 5, 2015). "Why a smallmouth bass with a rare, cancerous tumor has Pa. officials worried". Washington Post. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
^ Begley, Sarah (May 8, 2015). "Rare Cancer Discovered in Pennsylvania Smallmouth Bass". TIME.com. Retrieved May 8, 2015.
Further reading
Miller, Peter (March 1985). "Susquehanna: America's Small-Town River". National Geographic. Vol. 167 no. 3. pp. 352–383. ISSN 0027-9358. OCLC 643483454.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Susquehanna River. |
Wikisource has the text of The New Student's Reference Work article "Susquehanna River". |
- U.S. Geological Survey: PA stream gaging stations
- Susquehanna River Basin Commission
- American Rivers article: Susquehanna River "Most Endangered"
- History of the Susquehanna River Ark
- Hiawatha Island Boat Club – Owego, NY
- Binghamton University Crew – Binghamton, NY