同步 (计算机科学)
计算机科学中, 同步(synchronization)是指两个不同但有联系的概念:进程同步与数据同步。进程同步指多个进程在特定点会合(join up)或者握手使得达成协议或者使得操作序列有序。数据同步指一个数据集的多份拷贝一致以维护完整性。常用进程同步原语实现数据同步。
目录
1 线程或进程同步
1.1 经典同步问题
2 参见
3 参考文献
4 外部链接
线程或进程同步

Figure 1: 3个进程同时访问共享资源(临界区)
多个线程(或进程)要执行同一个特定的不可重入的程序代码块(称为临界区),这就需要适当的并发控制同步技术[1]。否则,可能会发生竞态条件。
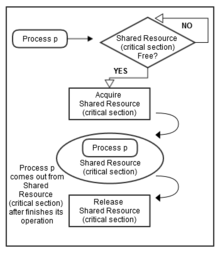
Figure 2: 一个进程访问共享资源基于某种同步技术。[2]
另一种同步要求产生于特定的操作顺序,如应该先买机票然后登机。[3]
同步还需处理:
- 死锁
- 资源饿死
- 优先级翻转
- 忙等待
经典同步问题
生产者消费者问题 (有限缓存区问题);
读写问题;
哲学家就餐问题.
参见
Futures and promises, 纯函数式编程中的同步机制
参考文献
^
Gramoli, V. More than you ever wanted to know about synchronization: Synchrobench, measuring the impact of the synchronization on concurrent algorithms (PDF). Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGPLAN Symposium on Principles and Practice of Parallel Programming. ACM: 1–10. 2015.
^ Janssen, Cory. Thread Synchronization. Techopedia. [23 November 2014].
^ Fatheisian, Halleh; Rosenberger, Eric. Synchronization. Department of Computer Science, George Mason University. [23 November 2014].
Schneider, Fred B. On concurrent programming. Springer-Verlag New York, Inc. 1997. ISBN 0-387-94942-9.
外部链接
Anatomy of Linux synchronization methods at IBM developerWorks
The Little Book of Semaphores, by Allen B. Downey
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||