Acetate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name Acetate | |
Systematic IUPAC name Ethanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C 2H 3O− 2 |
Molar mass | 59.04 g·mol−1 |
Conjugate acid | Acetic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Infobox references | |
An acetate /ˈæsɪteɪt/ is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with an alkaline, earthy, metallic or nonmetallic and other base. "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called an anion) typically found in aqueous solution and written with the chemical formula C
2H
3O−
2. The neutral molecules formed by the combination of the acetate ion and a positive ion (called a cation) are also commonly called "acetates" (hence, acetate of lead, acetate of aluminum, etc.). The simplest of these is hydrogen acetate (called acetic acid) with corresponding salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion CH
3CO−
2, or CH
3COO−
.
Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In nature, acetate is the most common building block for biosynthesis. For example, the fatty acids are produced by connecting the two carbon atoms from acetate to a growing fatty acid.[1]
Contents
1 Nomenclature and common formula
2 Salts
3 Esters
4 Acetate in biology
5 Fermentation acetyl CoA to acetate
6 Fermentation of acetate
7 Structures
8 See also
9 References
10 External links
Nomenclature and common formula
When part of a salt, the formula of the acetate ion is written as CH
3CO−
2, C
2H
3O−
2, or CH
3COO−
. Chemists often represent acetate as OAc− or, less commonly, AcO−. Thus, HOAc is the symbol for acetic acid, NaOAc for sodium acetate, and EtOAc for ethyl acetate.[2] The pseudoelement symbol "Ac" is also sometimes encountered in chemical formulas as indicating the entire acetate ion (CH3CO2−), or the acetyl group (CH3CO). It is not to be confused with the symbol of actinium, the first element of the actinide series; context guides disambiguation. For example, the formula for sodium acetate might be abbreviated as "NaAc", rather than "NaC2H3O2". Care should also be taken to avoid confusion with peracetic acid when using the OAc abbreviation; for clarity and to avoid errors when translated, HOAc should be avoided in literature mentioning both compounds.
Although its systematic name is ethanoate (/ɪˈθænoʊ.eɪt/), the common acetate remains the preferred IUPAC name.[3]
Salts

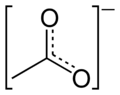
acetate anion
The acetate anion, [CH3COO]−,(or [C2H3O2]−) is one of the carboxylate family. It is the conjugate base of acetic acid. Above a pH of 5.5, acetic acid converts to acetate:[2]
- CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COO− + H+
Many acetate salts are ionic, indicated by their tendency to dissolve well in water. A commonly encountered acetate in the home is sodium acetate, a white solid that can be prepared by combining vinegar and sodium bicarbonate ("bicarbonate of soda"):
- CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COO−Na+ + H2O + CO2
Transition metals can be complexed by acetate. Examples of acetate complexes include chromium(II) acetate and basic zinc acetate.
Commercially important acetate salts are aluminium acetate, used in dyeing, ammonium acetate, a precursor to acetamide, and potassium acetate, used as a diuretic. All three salts are colourless and highly soluble in water.[4]
Esters
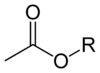
acetate ester
Acetate esters have the general formula CH3CO2R, where R is an organyl group. The esters are the dominant forms of acetate in the marketplace. Unlike the acetate salts, acetate esters are often liquids, lipophilic, and sometimes volatile. They are popular because they have inoffensive, often sweet odors, they are inexpensive, and they are usually of low toxicity.
Almost half of acetic acid production is consumed in the production of vinyl acetate, precursor to polyvinyl alcohol, which is a component of many paints. The second largest use of acetic acid is consumed in the production of cellulose acetate. In fact, "acetate" is jargon for cellulose acetate, which is used in the production of fibres or diverse products, e.g. the acetate discs used in audio record production. Cellulose acetate can be found in many household products. Many industrial solvents are acetates, including methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, isopropyl acetate, ethylhexyl acetate. Butyl acetate is a fragrance used in food products.[4]
Acetate in biology
Acetate is a common anion in biology. It is mainly utilized by organisms in the form of acetyl coenzyme A.[5]
Intraperitoneal injection of sodium acetate (20 or 60 mg per kg body mass) was found to induce headache in sensitized rats, and it has been proposed that acetate resulting from oxidation of ethanol is a major factor in causing hangovers. Increased serum acetate levels lead to accumulation of adenosine in many tissues including the brain, and administration of the adenosine receptor antagonist caffeine to rats after ethanol was found to decrease nociceptive behavior.[6][7]
Fermentation acetyl CoA to acetate
Pyruvate is converted into acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. This acetyl-CoA is then converted into acetate in E. coli, whilst producing ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. Acetate formation requires two enzymes: phosphate acetyltransferase and acetate kinase.[8]

The Mixed Acid Fermentation pathway is characteristic of the Enterobacteriaceae family that includes E. coli
acetyl-CoA + phosphate → acetyl-phosphate + CoA
acetyl-phosphate + ADP → acetate + ATP
Fermentation of acetate
Acetic acid can also undergo a dismutation reaction to produce methane and carbon dioxide:[9][10]
- CH3COO− + H+ → CH4 + CO2 ΔG° = −36 kJ/mol
This disproportionation reaction is catalysed by methanogen archaea in their fermentative metabolism. One electron is transferred from the carbonyl function (e− donor) of the carboxylic group to the methyl group (e− acceptor) of acetic acid to respectively produce CO2 and methane gas.
Structures

Space-filling model of the acetate anion
resonance hybrid of the acetate anion

canonical forms of the acetate anion
See also
- Acetylation
- Cellulose acetate
- Copper(II) acetate
- Fermentation (biochemistry)
- Sodium acetate
- Mixed acid fermentation
- Acetic acid
- Acetyl chloride
- Zinc acetate
References
^ March, J. “Advanced Organic Chemistry” 4th Ed. J. Wiley and Sons, 1992: New York. .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
ISBN 0-471-60180-2.
^ ab Zumdahl, S. S. “Chemistry” Heath, 1986: Lexington, MA.
ISBN 0-669-04529-2.
^ R-9.1 Trivial and semisystematic names retained for naming organic compounds, A Guide to IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds, IUPAC Commission on Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry
^ ab Hosea Cheung, Robin S. Tanke, G. Paul Torrence "Acetic acid" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH, 2005. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_045
^ Nelson, D. L.; Cox, M. M. "Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry" 3rd Ed. Worth Publishing: New York, 2000.
ISBN 1-57259-153-6.
^ Maxwell, Christina; et al. (2010). "Acetate Causes Alcohol Hangover Headache in Rats". PLoS ONE. 5 (12): e15963. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...515963M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015963. PMC 3013144. PMID 21209842.
^ 'Is coffee the real cure for a hangover?' by Bob Holmes, New Scientist, Jan. 15 2011, p. 17.
^ Keseler, Ingrid M.; et al. (2011). "EcoCyc: a comprehensive database of Escherichia coli biology". Nucleic Acids Research. 39: D583–D590. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1143. PMC 3013716. PMID 21097882.
^ Ferry, J.G. (1992). "Methane from acetate". Journal of Bacteriology. 174 (17): 5489–5495. Retrieved 2011-11-05.
^ Vogels, G. D.; Keltjens, J. T.; Van Der Drift, C. (1988). "Biochemistry of methane production". In Zehnder A.J.B. Biology of anaerobic microorganisms. New York: Wiley. pp. 707–770.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Acetates. |
Acetyl halides and salts of the acetate ion | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
AcOH | He | ||||||||||||||||||
LiOAc | Be(OAc)2 BeAcOH | B(OAc)3 | AcOAc ROAc | NH4OAc | AcOOH | FAc | Ne | ||||||||||||
NaOAc | Mg(OAc)2 | Al(OAc)3 ALSOL Al(OAc)2OH Al2SO4(OAc)4 | Si | P | S | ClAc | Ar | ||||||||||||
KOAc | Ca(OAc)2 | Sc(OAc)3 | Ti(OAc)4 | VO(OAc)3 | Cr(OAc)2 Cr(OAc)3 | Mn(OAc)2 Mn(OAc)3 | Fe(OAc)2 Fe(OAc)3 | Co(OAc)2, Co(OAc)3 | Ni(OAc)2 | Cu(OAc)2 | Zn(OAc)2 | Ga(OAc)3 | Ge | As(OAc)3 | Se | BrAc | Kr | ||
RbOAc | Sr(OAc)2 | Y(OAc)3 | Zr(OAc)4 | Nb | Mo(OAc)2 | Tc | Ru(OAc)2 Ru(OAc)3 Ru(OAc)4 | Rh2(OAc)4 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgOAc | Cd(OAc)2 | In | Sn(OAc)2 Sn(OAc)4 | Sb(OAc)3 | Te | IAc | Xe | ||
CsOAc | Ba(OAc)2 | | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt(OAc)2 | Au | Hg2(OAc)2, Hg(OAc)2 | TlOAc Tl(OAc)3 | Pb(OAc)2 Pb(OAc)4 | Bi(OAc)3 | Po | At | Rn | ||
| Fr | Ra | | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | ||
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||||
La(OAc)3 | Ce(OAc)x | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm(OAc)3 | Eu(OAc)3 | Gd(OAc)3 | Tb | Dy(OAc)3 | Ho(OAc)3 | Er | Tm | Yb(OAc)3 | Lu(OAc)3 | |||||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UO2(OAc)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||||

