Crook County, Oregon
Crook County, Oregon | |
|---|---|
 Crook County Courthouse in Prineville | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Oregon | |
 Oregon's location within the U.S. | |
| Founded | October 24, 1882 |
| Seat | Prineville |
| Largest city | Prineville |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,987 sq mi (7,736 km2) |
| • Land | 2,979 sq mi (7,716 km2) |
| • Water | 8.2 sq mi (21 km2), 0.3% |
| Population (est.) | |
| • (2016) | 22,570 |
| • Density | 7.0/sq mi (2.7/km2) |
| Congressional district | 2nd |
| Time zone | Pacific: UTC−8/−7 |
| Website | www.co.crook.or.us |
Crook County is a county in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2010 census, the population was 20,978.[1] The county seat is Prineville.[2] The county is named after George Crook, a U.S. Army officer who served in the American Civil War and various Indian Wars.
Crook County comprises the Prineville, OR Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is included in the Bend-Redmond-Prineville, OR Combined Statistical Area.[3]
Contents
1 History
2 Geography
2.1 Adjacent counties
2.2 National protected area
3 Demographics
3.1 2000 census
3.2 2010 census
4 Communities
4.1 City
4.2 Unincorporated communities
5 Politics
6 Economy
7 See also
8 References
9 Further reading
History

Logging in the Ochoco Mountains, circa 1900
Crook County was established on October 9, 1882, by an act of the Oregon State Legislature.[4] The county was named after General George Crook, a veteran of various battles against the indigenous peoples of Eastern Oregon in the middle of the 19th century.[4] The county was formed from territory formerly part of Wasco County, including the hilly region where the foothills of the Blue Mountains intersect the Cascade Mountain Range.[4]
Access into the region at first was difficult, which discouraged settlement. The first effort to develop routes into the area was in 1862 when a supply train with cattle crossed the Scott Trail. This was also the first group of non-natives to spend the winter in central Oregon. The discovery and development of the Santiam Pass in the 1860s improved access into the area.
Prineville, incorporated in 1880 and then the only incorporated town in the county, was established as the county seat.[4] This decision confirmed by the voters in the 1884 general election.
From the start cattle ranching has been one of the primary industries of the county, with huge herds grazing the countryside from the 1880s.[4] Farming was also developed in certain valley regions friendly to agriculture.[4]
Logging in the Ochoco Mountains and the timber mills that accompanied also greatly contributed to the economic and population growth of the county. The first recorded mention of a sawmill was made by George Barnes, speaking about the Swartz sawmill on Mill Creek, circa 1867.[5]
Geography
The county is located in the geographic center of Oregon. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 2,987 square miles (7,740 km2), of which 2,979 square miles (7,720 km2) is land and 8.2 square miles (21 km2) (0.3%) is water.[6] The largest body of water in Crook County is the Prineville Reservoir. The county has been reduced from its original size of 8,600 square miles (22,000 km2) by the creation of Jefferson County in 1914 and Deschutes County in 1916. The present boundaries were established in 1927.
The oldest geological formation in Oregon is in the southeastern corner of Crook County, near its boundary with Grant County. This formation is an outcropping of Devonian limestone created from a larger reef when most of Oregon was covered by water.
Adjacent counties
Deschutes County - southwest
Jefferson County - north
Wheeler County - north
Grant County - east
Harney County - southeast
National protected area
Ochoco National Forest (part)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1890 | 3,244 | — | |
| 1900 | 3,964 | 22.2% | |
| 1910 | 9,315 | 135.0% | |
| 1920 | 3,424 | −63.2% | |
| 1930 | 3,336 | −2.6% | |
| 1940 | 5,533 | 65.9% | |
| 1950 | 8,991 | 62.5% | |
| 1960 | 9,430 | 4.9% | |
| 1970 | 9,985 | 5.9% | |
| 1980 | 13,091 | 31.1% | |
| 1990 | 14,111 | 7.8% | |
| 2000 | 19,182 | 35.9% | |
| 2010 | 20,978 | 9.4% | |
| Est. 2016 | 22,570 | [7] | 7.6% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[8] 1790-1960[9] 1900-1990[10] 1990-2000[11] 2010-2016[1] | |||

From 2000 to 2007, Crook County's population grew by 34.9%, more than three times the state average. It was the second fastest growing county in the state, after neighboring Deschutes County.
2000 census
As of the census[12] of 2000, there were 19,182 people, 7,354 households, and 5,427 families residing in the county. The population density was 6 people per square mile (2/km²). There were 8,264 housing units at an average density of 3 per square mile (1/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 92.95% White, 0.04% Black or African American, 1.30% Native American, 0.43% Asian, 0.03% Pacific Islander, 3.81% from other races, and 1.43% from two or more races. 5.64% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 26.2% were of American, 14.8% German, 9.7% English and 8.9% Irish ancestry.
There were 7,354 households out of which 32.30% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 61.50% were married couples living together, 8.20% had a female householder with no husband present, and 26.20% were non-families. 21.30% of all households were made up of individuals and 9.50% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.57 and the average family size was 2.96.
In the county, the population was spread out with 26.60% under the age of 18, 7.50% from 18 to 24, 25.50% from 25 to 44, 25.70% from 45 to 64, and 14.70% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 39 years. For every 100 females there were 99.40 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 97.30 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $35,186, and the median income for a family was $40,746. Males had a median income of $32,166 versus $22,580 for females. The per capita income for the county was $16,899. About 8.10% of families and 11.30% of the population were below the poverty line, including 13.90% of those under age 18 and 8.10% of those age 65 or over.
2010 census
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 20,978 people, 8,558 households, and 6,025 families residing in the county.[13] The population density was 7.0 inhabitants per square mile (2.7/km2). There were 10,202 housing units at an average density of 3.4 per square mile (1.3/km2).[14] The racial makeup of the county was 92.7% white, 1.4% American Indian, 0.5% Asian, 0.2% black or African American, 0.1% Pacific islander, 3.2% from other races, and 2.0% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 7.0% of the population.[13] In terms of ancestry, 20.7% were German, 14.6% were English, 12.6% were Irish, and 6.2% were American.[15]
Of the 8,558 households, 27.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 57.1% were married couples living together, 9.0% had a female householder with no husband present, 29.6% were non-families, and 24.1% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.42 and the average family size was 2.84. The median age was 45.6 years.[13]
The median income for a household in the county was $46,059 and the median income for a family was $52,477. Males had a median income of $41,375 versus $29,545 for females. The per capita income for the county was $22,275. About 10.6% of families and 14.0% of the population were below the poverty line, including 26.1% of those under age 18 and 4.0% of those age 65 or over.[16]
Communities
City
Prineville (county seat)
Unincorporated communities
- Forest Crossing
- Lone Pine
- O'Neil
- Paulina
- Post
- Powell Butte
- Roberts
- Suplee
Politics
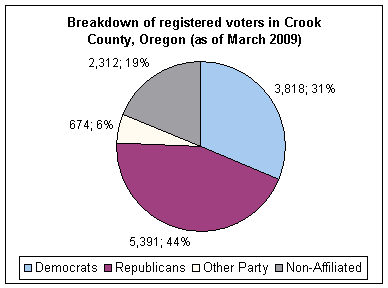
Though Crook County is the most central county in Oregon, politically it falls in line with the eastern side of the state. The majority of registered voters who are part of a political party in Crook County, as well as most counties in eastern Oregon, are members of the Republican Party.[17] In the 2008 presidential election, 61.54% of Crook County voters voted for Republican John McCain, while 35.09% voted for Democrat Barack Obama and 3.37% of voters either voted for a third-party candidate or wrote in a candidate.[18] These numbers show a small shift towards the Democratic candidate when compared to the 2004 presidential election, in which 68% of Crook Country voters voted for George W. Bush, while 30.1% voted for John Kerry, and 1.9% of voters either voted for a third-party candidate or wrote in a candidate.[19]
Crook county was formerly a Presidential bellwether county, voting with the winner since 1884, in 27 Presidential elections.[20] However, the county lost its bellwether status after voting for George H. W. Bush in 1992.[21] It further voted for the losing Presidential candidate in 1996, 2008, and 2012.
 [17]
[17]
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
2016 | 69.9% 8,511 | 21.7% 2,637 | 8.4% 1,024 |
2012 | 66.4% 6,790 | 30.3% 3,104 | 3.3% 336 |
2008 | 61.5% 6,371 | 35.1% 3,632 | 3.4% 349 |
2004 | 68.0% 6,830 | 30.1% 3,024 | 2.0% 197 |
2000 | 64.8% 5,363 | 29.9% 2,474 | 5.3% 440 |
1996 | 46.5% 3,250 | 37.3% 2,607 | 16.2% 1,132 |
1992 | 37.2% 2,703 | 34.5% 2,508 | 28.3% 2,060 |
1988 | 51.8% 3,049 | 46.2% 2,719 | 1.9% 114 |
1984 | 62.2% 3,773 | 37.4% 2,268 | 0.4% 23 |
1980 | 53.1% 3,113 | 36.9% 2,162 | 10.0% 587 |
1976 | 43.8% 2,093 | 53.1% 2,536 | 3.1% 148 |
1972 | 52.6% 2,167 | 42.3% 1,743 | 5.2% 213 |
1968 | 47.9% 1,727 | 44.7% 1,611 | 7.5% 269 |
1964 | 32.4% 1,161 | 67.5% 2,419 | 0.2% 6 |
1960 | 46.4% 1,732 | 53.7% 2,005 | |
1956 | 51.0% 1,879 | 49.0% 1,805 | |
1952 | 57.7% 2,124 | 40.5% 1,490 | 1.8% 67 |
1948 | 44.8% 960 | 53.7% 1,149 | 1.5% 32 |
1944 | 44.3% 932 | 54.4% 1,145 | 1.3% 28 |
1940 | 39.3% 942 | 60.0% 1,439 | 0.7% 17 |
1936 | 33.6% 589 | 62.0% 1,086 | 4.4% 77 |
1932 | 37.8% 626 | 59.8% 990 | 2.4% 40 |
1928 | 63.5% 877 | 35.2% 487 | 1.3% 18 |
1924 | 50.7% 725 | 30.4% 434 | 18.9% 270 |
1920 | 59.2% 872 | 35.9% 528 | 5.0% 73 |
1916 | 36.2% 1,675 | 58.3% 2,699 | 5.5% 252 |
1912 | 27.6% 770 | 38.0% 1,060 | 34.4% 960 |
1908 | 56.9% 915 | 34.1% 548 | 9.1% 146 |
1904 | 65.3% 763 | 22.8% 266 | 11.9% 139 |
Economy
Forest products, agriculture, livestock raising and recreation/tourism services constitute Crook County's total economy. Agriculture is supported by the development of irrigation districts, which permits the raising of hay, grain, mint, potatoes, and seed. Range and forest lands allow grazing for a sizable livestock industry. The Ochoco National Forest's stand of ponderosa pine is the main source of lumber. Tourism and recreation help round out the economy. Thousands of hunters, fishers, boaters, sightseers and rockhounds are annual visitors to its streams, reservoirs and the Ochoco Mountains. The Prineville Chamber of Commerce provides access to over 1,000 acres (4.0 km2) of mining claims to rockhounds, who can dig for free agates, limb casts, jasper and thundereggs.
See also
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Crook County, Oregon
- Cook County, Illinois
References
^ ab "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved November 14, 2013..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
^ "OMB Bulletin No. 13-01: Revised Delineations of Metropolitan Statistical Areas, Micropolitan Statistical Areas, and Combined Statistical Areas, and Guidance on Uses of the Delineations of These Areas" (PDF). United States Office of Management and Budget. February 28, 2013. Retrieved April 8, 2013.
^ abcdef Hubert Howe Bancroft, The Works of Hubert Howe Bancroft: Volume XXX: History of Oregon: Volume II, 1848-1888. San Francisco, CA: The History Company, 1888; pg. 710.
^ Shaver, F. A., Arthur P. Rose, R. F. Steele, and A. E. Adams, compilers. An Illustrated History of Central Oregon: Embracing Wasco, Sherman, Gilliam, Wheeler, Crook, Lake, & Klamath Counties. Spokane, WA: Western Historical Publishing Co., 1905.
^ "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved February 25, 2015.
^ "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved June 9, 2017.
^ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on May 12, 2015. Retrieved February 25, 2015.
^ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved February 25, 2015.
^ Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 27, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 25, 2015.
^ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Retrieved February 25, 2015.
^ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on September 11, 2013. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
^ abc "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2016-02-23.
^ "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2016-02-23.
^ "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2016-02-23.
^ "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2016-02-23.
^ ab Voter Registration by County Retrieved on 11/20/2018
^ Crook.or.us Archived 2009-05-23 at the Wayback Machine retrieved 4/20/09
^ City-data.com Retrieved on 4/21/09
^ Egan, Timothy (October 13, 1992). "THE 1992 CAMPAIGN: The Bellwether County; Bellwether County Gravitates To Clinton, if Only by Default". New York Times. Retrieved June 24, 2012.
^ Fredrickson, Keith (November 4, 1992). "No Bellwether Blues in Crook County". The Bend Bulletin. Retrieved June 24, 2012.
^ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 2018-04-11.
Further reading
Turnbull, George S. (1939). . . Binfords & Mort.
Coordinates: 44°08′N 120°22′W / 44.13°N 120.36°W / 44.13; -120.36

