Isocyanide
![{displaystyle left[{ce {R}}-{overset {oplus }{ce {N}}}{ce {#}}{overset {ominus }{ce {C}}}{ce {:,<->R-{ddot {N}}=C{:}}}right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/31596ad44ed69b7ad7230333e4059f48ef0d3b65)
An isocyanide (also called isonitrile or carbylamine) is an organic compound with the functional group -N≡C. It is the isomer of the related cyanide (-C≡N), hence the prefix iso.[1] The organic fragment is connected to the isocyanide group via the nitrogen atom, not via the carbon. They are used as building blocks for the synthesis of other compounds.
Contents
1 Properties
1.1 Structure and bonding
1.2 Spectroscopy
1.3 Odour
1.4 Toxicity
2 Synthesis
2.1 Silver cyanide route
2.2 From formamides
2.3 From dichlorocarbene
2.4 Other methods
3 Reactions
3.1 Ligands in coordination chemistry
4 Naturally occurring isocyanides
5 Nomenclature
6 References
Properties
Structure and bonding
The C-N distance in isocyanides is very short, 1.158 Å in methyl isocyanide. The C-N-C angles are near 180°.[2]
Akin to carbon monoxide, isocyanides are described by two resonance structures, one with a triple bond between the nitrogen and the carbon and one with a double bond between. The π lone pair of the nitrogen, responsible for the zwitterionic structure, stabilizes the structure and is responsible of the linearity of isocyanides, although the reactivity of isocyanides reflects some carbene character, at least in a formal sense. Thus, both resonance structures are useful representations.[3] They are susceptible to polymerization.[3]
Spectroscopy
Isocyanides exhibit a strong absorption in their IR spectra in the range: 2165–2110 cm−1[4]
The electronic symmetry about the isocyanide 14N nucleus results in a slow quadrupolar relaxation so that 13C-14N nuclear spin coupling can be observed, with coupling constants of ca. 5 Hz for the isocyanide 13C nucleus and 5–14 Hz for the 13C nucleus which the isocyanide group is attached to.[4]
Odour
Their disagreeable odour is legendary. To quote from Lieke, "Es besitzt einen penetranten, höchst unangenehmen Geruch; das Oeffnen eines Gefässes mit Cyanallyl reicht hin, die Luft eines Zimmers mehrere Tage lang zu verpesten, ..." (It has a penetrating, extremely unpleasant odour; the opening of a flask of allyl [iso]cyanide is enough to foul up the air in a room for several days). Note that in Lieke's day, the difference between isocyanide and nitrile was not fully appreciated.
Ivar Karl Ugi states that "The development of the chemistry of isocyanides has probably suffered only little delay through the characteristic odor of volatile isonitriles, which has been described by Hofmann and Gautier as 'highly specific, almost overpowering', 'horrible', and 'extremely distressing'. It is true that many potential workers in this field have been turned away by the odour, but this is heavily outweighed by the fact that isonitriles can be detected even in traces, and that most of the routes leading to the formation of isonitriles were discovered through the odor of these compounds."[5] Isocyanides have been investigated as potential non-lethal weapons.[6]
Some isocyanides convey less offensive odours such as malt, natural rubber, creosote, mild cherry or old wood.[7] Non-volatile derivatives such as tosylmethyl isocyanide do not have objectionable odors.[8]
Toxicity
While some isocyanides (e.g., cyclohexyl isocyanide) are toxic, others "exhibit no appreciable toxicity for mammals". Referring to ethyl isocyanide, toxicological studies in the 1960s at Bayer showed that "oral and subcutaneous doses of 500-5000 mg/kg can be tolerated by mice".[5]
Synthesis
Silver cyanide route
The first isocyanide, allyl isocyanide, was reported in 1859 by the chemist Lieke from the reaction of allyl iodide and silver cyanide.[9] Normally the alkylation of an alkali metal cyanide gives a nitrile, but the silver ion protects the carbon end of the cyanide.
- RX + AgCN → RNC + AgX
From formamides
Commonly, isocyanides are synthesized by dehydration of formamides. The formamide can be dehydrated with toluenesulfonyl chloride, phosphorus oxychloride, phosgene, diphosgene, or the Burgess reagent in the presence of a base such as pyridine or triethylamine.[10][11][12]
- RNHC(O)H + ArSO2Cl + 2C5H5N → RNC + [C5H5NH]+[ArSO3]– + [C5H5NH]+Cl–
From dichlorocarbene
In the carbylamine reaction (also known as the Hofmann isocyanide synthesis) alkali base reacts with chloroform to produce dichlorocarbene. The carbene then converts primary amines to isocyanides. As it is only effective for primary amines this reaction can be used as a chemical test for their presence. Illustrative is the synthesis of tert-Butyl isocyanide from tert-butylamine in the presence of catalytic amount of the phase transfer catalyst benzyltriethylammonium chloride.[13]
- Me3CNH2 + CHCl3 + 3 NaOH → Me3CNC + 3 NaCl + 3 H2O
Other methods
Another route to isocyanides entails deprotonation of oxazoles and benzoxazoles in the 2-position.[7] The resulting organolithium compound exists in chemical equilibrium with the 2-isocyanophenolate, which can be captured by an electrophile such as an acid chloride.
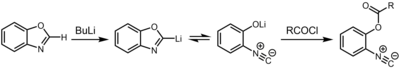
Reactions
Isocyanides are stable to strong base (they are often made under strongly basic conditions), but they are sensitive to acid. In the presence of aqueous acid, isocyanides hydrolyse to the corresponding formamides:
- RNC + H2O → RN(H)C(O)H
This reaction is used to destroy odorous isocyanide mixtures. Some isocyanides can polymerize in the presence of Lewis and Bronsted acids.[14]
Isocyanides participate in many multicomponent reactions of interest in organic synthesis, two of which are: the Ugi reaction and the Passerini reaction.
Isocyanides also participate in cycloaddition reactions, such as the [4+1] cycloaddition with tetrazines.[15] Depending on the degree of substitution of the isocyanide, this reaction converts isocyanides into carbonyls or gives stable cycloadducts.[16] They also undergo insertion into the C–Cl bonds of acyl chlorides in the Nef isocyanide reaction, a process that is believed to be concerted and illustrates their carbene character.
Isocyanides have also been shown to be a useful reagent in palladium catalysed reactions with a wide variety of compounds being formed using this method.[17]
The α position of isocyanides have substantial acidity. For example, benzyl isocyanide has a pKa of 27.4. In comparison, benzyl cyanide has a pKa of 21.9.[18] In the gas phase, CH3NC is 1.8 kcal/mol less acidic than CH3CN.[19]
Ligands in coordination chemistry

Technetium sestamibi is a commercial isocyanide complex that is used in medicine for imaging.
Isocyanides form coordination complexes with most transition metals.[20] They behave as electron-rich analogues of carbon monoxide. For example tert-Butyl isocyanide forms Fe2(tBuNC)9, which is analogous to Fe2(CO)9.[21] Although structurally similar, the analogous carbonyls differ in several ways, mainly because t-BuNC is a better donor ligand than CO. Thus, Fe(tBuNC)5 is easily protonated, whereas its counterpart Fe(CO)5 is not.[22]
Naturally occurring isocyanides
Only few naturally occurring compounds exhibit the isocyanide functionality. The first was discovered in 1957 in an extract of the mold Penicillium notatum Westling. The compound xanthocillin later was used as an antibiotic. Since then numerous other isocyanides have been isolated. Most of the marine isocyanides are terpenoid, while some of the terrestrial isocyanides originate from α-aminoacids.[23]

Xanthocillin is a rare natural product that contains an isocyanide group (two in fact).
Nomenclature
Whereas in IUPAC nomenclature in most cases the suffix "nitrile" or "carbonitrile" is used for organic cyanides (R-C≡N),[24]
names for isocyanides have the prefix "isocyano". IUPAC names become isocyanomethane, isocyanoethane, isocyanopropane, etc.
The suffix "isonitrile" can be ambiguous, since the carbon counting is different from "nitrile". For example, ethanenitrile ( CH3CN) and ethaneisonitrile (C2H5NC) are not isomers, as the prefix "iso" in the suffix might suggest. In contrast, "isocyanide" does not have this ambiguity: ethyl cyanide (C2H5CN) and ethyl isocyanide (C2H5NC) are indeed isomers.
The sometimes used term "carbylamine" conflicts with systematic nomenclature. An amine always has three single bonds,[25] whereas an isocyanide has only one single and one multiple bond.
The isocyanamide functional group consists of a amino group attached to an isocyano moiety.
References
^ IUPAC Goldbook isocyanides
^ Kessler, M.; Ring, H.; Trambarulo, R.; Gordy, W. (1950). "Microwave Spectra and Molecular Structures of Methyl Cyanide and Methyl Isocyanide". Physical Review. 79 (1): 54–56. Bibcode:1950PhRv...79...54K. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.79.54..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab Ramozzi, R.; Chéron, N.; Braïda, B.; Hiberty, P. C.; Fleurat-Lessard, P. (2012). "A Valence Bond View of Isocyanides' Electronic Structure". New Journal of Chemistry. 36 (5): 1137–1340. doi:10.1039/C2NJ40050B.
^ ab Stephany, R. W.; de Bie, M. J. A.; Drenth, W. (1974). "A 13C-NMR and IR study of isocyanides and some of their complexes". Organic Magnetic Resonance. 6 (1): 45–47. doi:10.1002/mrc.1270060112.
^ ab Ugi, I.; Fetzer, U.; Eholzer, U.; Knupfer, H.; Offermann, K. (1965). "Isonitrile Syntheses". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 4 (6): 472–484. doi:10.1002/anie.196504721.
^ Pirrung, M. C.; Ghorai, S.; Ibarra-Rivera, T. R. (2009). "Multicomponent Reactions of Convertible Isonitriles". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 74 (11): 4110–4117. doi:10.1021/jo900414n. PMID 19408909.
^ ab Pirrung, M. C.; Ghorai, S. (2006). "Versatile, Fragrant, Convertible Isonitriles". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 128 (36): 11772–11773. doi:10.1021/ja0644374. PMID 16953613.
^ B. E. Hoogenboom, O. H. Oldenziel, and A. M. van Leusen "Toluenesulfonylmethyl isocyanide" Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 6, p.987 (1988).
^ Lieke, W. (1859). "Über das Cyanallyl". Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie. 112 (3): 316–321. doi:10.1002/jlac.18591120307.
^ Schuster, R. E.; Scott, J. E. (1966). "Methyl isocyanide". Organic Syntheses. 46: 75. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.046.0075.
^ Ugi, I.; Meyr, R. (1958). "Neue Darstellungsmethode für Isonitrile". Angewandte Chemie. 70 (22–23): 702–703. doi:10.1002/ange.19580702213.
^ Creedon, Siobhan; Crowley, H. Kevin; McCarthy, Daniel G. (1998). "Dehydration of formamides using the Burgess Reagent: a new route to isocyanides". J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 (6): 1015–1018. doi:10.1039/a708081f.
^ Gokel, G.W.; Widera, R.P.; Weber, W.P. (1988). "Phase-transfer Hofmann Carbylamine Reaction: tert-Butyl Isocyanide". Organic Syntheses. 55: 232. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.055.0096.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Deming, T. J.; Novak, B. M. "Mechanistic Studies on the Nickel Catalyzed Polymerization of Isocyanides" J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 9101.
^ Imming, P.; Mohr, R.; Müller, E.; Overheu, W.; Seitz, G. (1982). "[4 + 1]Cycloaddition of Isocyanides to 1,2,4,5-Tetrazines: A Novel Synthesis of Pyrazole". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 21 (4): 284. doi:10.1002/anie.198202841.
^ Stöckmann, H.; Neves, A.; Stairs, S.; Brindle, K.; Leeper, F. (2011). "Exploring Isonitrile-Based Click Chemistry for Ligation with Biomolecules". Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. 9 (21): 7303–7305. doi:10.1039/C1OB06424J. PMID 21915395.
^ Lang, S. (2013). "Unravelling the labyrinth of palladium catalysed reactions involving isocyanides". Chemical Society Reviews. 42 (12): 4867–4880. doi:10.1039/C3CS60022J. PMID 23443313.
^ "Bordwell pKa Table (Acidity in DMSO)". www.chem.wisc.edu. Retrieved 2018-12-20.
^ Filley, Jonathan; DePuy, Charles H.; Bierbaum, Veronica M. (1987-09-01). "Gas-phase negative-ion chemistry of methyl isocyanide". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 109 (20): 5992–5995. doi:10.1021/ja00254a017. ISSN 0002-7863.
^ Eric Singleton, Hester E. Oosthuizen "Metal Isocyanide Complexes"Advances in Organometallic Chemistry 1983, Volume 22, Pages 209–310. doi:10.1016/S0065-3055(08)60404-9
^ Bassett, J.M.; Barker, G.K.; Green, M.; Howard, J.A.; Stone, G.A.; Wolsey, W.C. "Chemistry of low-valent metal isocyanide complexes" J.C.S. Dalton, 1981, 219-227.
^ Bassett, J.-M.; Farrugia, L. J.; Stone, F. G. A. "Protonation of pentakis(t-butyl isocyanide)iron" J.C.S. Dalton, 1980, 1789-1790. doi:10.1039/DT9800001789
^ Scheuer, P. J. (1992). "Isocyanides and Cyanides as Natural Products". Accounts of Chemical Research. 25 (10): 433–439. doi:10.1021/ar00022a001.
^ IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds (Recommendations 1993)
^ IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds (Recommendations 1993)
