Intel 8288

Intel 8288
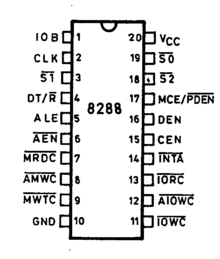
Pinout of 8288
The Intel 8288 is a bus controller designed for Intel 8086/8087/8088/8089. The chip is supplied in 20-pin DIP package. The 8086 (and 8088) operate in maximum mode, so they are configured primarily for multiprocessor operation or for working with coprocessors. Necessary control signals are generated by the 8288. It was used in the IBM PC, XT and its clones.[1]IBM PC AT used its successor Intel 82288.
Contents
1 Pin assignment and function for the control lines
2 Variants
3 References
4 External links
Pin assignment and function for the control lines
| Name | Pin | Input (I), Output (O) | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
VCC | 20 | Input power (+5 V) | |
| GND | 10 | Ground (0 V) | |
S0, S1, S2 | 19, 3, 18 | I | Status input |
| CLK | 2 | I | Clock |
AEN | 6 | I | Address Enable |
| CEN | 15 | I | Command Enable |
| IOB | 1 | I | Input/Output Bus Mode |
MRDC | 7 | O | Memory Read Command |
MWTC | 9 | O | Memory Write Command |
AMWC | 8 | O | Advanced Memory Write Command |
IORC | 13 | O | I/O Read Command |
IOWC | 11 | O | I/O Write Command |
AIOWC | 12 | O | Advanced I/O Write Command |
INTA | 14 | O | Interrupt Acknowledge |
| DT/R | 4 | O | Data Transmit/Receive |
| DEN | 16 | O | Data Enable |
| MCE/PDEN | 17 | O | MCE (if IOB is LOW), PDEN (if IOB is HIGH) |
| ALE | 5 | O | Address Latch Enable |
Variants
Both Intel 8288 and I8288 (industrial grade) version were available for US$14.30 and $33.75 in quantities of 100 respectively.[2][3]
References
^ "The structure of the original IBM PC's motherboard". tu-chemnitz.de. Retrieved November 27, 2013..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ The 8086 Family: Concepts and realities, Intel Preview Special Issue: 16-Bit Solutions, Intel Corporation, May/June 1980, page 19
^ 8086 Available for industrial environment, Intel Preview Special Issue: 16-Bit Solutions, Intel Corporation, May/June 1980, page 29
External links
- 8288 Bus-Controller data sheet