Siege of Charleston
The Siege of Charleston was a major engagement and major British victory, fought between March 29 to May 12, 1780 during the American Revolutionary War. The British, following the collapse of their northern strategy in late 1777 and their withdrawal from Philadelphia in 1778, shifted their focus to the American Southern Colonies.
After approximately six weeks of siege, Major General Benjamin Lincoln, commanding the Charleston garrison, surrendered his forces to the British, resulting in one of the worst American defeats of the war.
Contents
1 Background
2 Siege
3 Aftermath
4 Order of Battle
4.1 British forces
4.2 Franco-American forces
5 Preservation
6 See also
7 References
8 External links
Background
By late 1779, two major British strategic efforts had failed. An army invading from Quebec under John Burgoyne had surrendered to the Americans under Horatio Gates at the Battles of Saratoga, compelling the Kingdom of France and Spain to declare war on Great Britain in support of the Americans. Meanwhile, a strategic effort led by Sir William Howe to capture the Revolutionary capital of Philadelphia had met with limited success. Having replaced his superior as Commander-in-Chief of the American Station, Sir Henry Clinton withdrew all his forces back to New York City to reinforce the city against a possible Franco-American attack.[3]
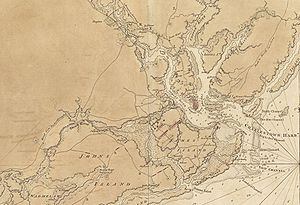
Detail of a 1780 map drawn by a British engineer showing the Charleston defenses
Stymied by the Fabian strategy adopted by George Washington, and, under increasing political pressure to deliver victory, the British turned to launching their "Southern Strategy" for forcing a capitulation of the Americans. The British were persuaded that there was a strong Loyalist sentiment in the south. It was expected that these Loyalists would rise against the American Patriots in large numbers. The opening British move was the Capture of Savannah, Georgia in December 1778. After repulsing an assault on Savannah by a combined Franco-American force in October 1779, the British planned to capture Charleston, South Carolina, intending to use the city as a base for further operations in the southern colonies.[3]
Sir Henry Clinton evacuated Newport, Rhode Island in Oct. 1779, and left the substantial garrison of New York City under the command of Wilhelm von Knyphausen. In December, the day after Christmas 1779, Clinton and his second in command Charles Cornwallis, sailed southward with 8,500 troops and 5,000 sailors on 90 troopships and 14 warships. After a very stormy voyage, the fleet anchored in Savannah River on 1 Feb. 1780. By 12 Feb., Clinton had landed his army 30 miles south of Charleston on Simmons Island. By 24 Feb., the British had crossed the Stono River onto James Island, and by 10 March, Lord Cornwallis had made it to the mainland. By 22 March, they had advanced to Middleton Place and Drayton Hall, and on 29 March 1780, crossed the Ashley River.[3]:39–40,42,44
Siege
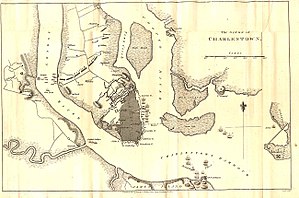
Charleston map showing the distribution of British forces during the siege
Cutting the city off from relief, Clinton began a siege of the city on April 1, 800 yards from the American fortifications located at today's Marion Square. Whipple, deciding the bar was undefendable, ended up scuttling his fleet at the mouth of the Cooper River. Then Arbuthnot, on 8 April, brought his 14 vessels safely into the harbor, past the roaring guns of Fort Moultrie, the same day Woodford arrived with 750 Virginia Continentals.[3]:46,52–53,55–57
In order to consolidate British control of the immediate area, Clinton dispatched Banastre Tarleton and Patrick Ferguson to capture Monck's Corner on 14 April. On 18 April, Lt. Col. Lord Rawdon arrived with 2,500 men, including the 42nd Highlanders, the Hessian von Ditfurth Regiment, the Queen's Rangers, Prince of Wales American Volunteers, and the Volunteers of Ireland. Charleston was then completely surrounded.[3]:60–64
Governor John Rutledge escaped on 13 April, before Cornwallis crossed the Cooper River, and joined Webster in blocking escape from the left bank. On 21 April, Lincoln requested a surrender with "honours of war", which was rejected by Clinton. On 25 April, civilians led by Christopher Gadsden prevented any action on Lincoln's part in withdrawing the Continental regiments. On 6 May, Tarleton won another engagement in the Battle of Lenud's Ferry, while the British siege works had advanced far enough towards the Charleston fortifications to drain the canal in front.[3]:66–67[6][7][8][9]
On 7 May, Fort Moultrie surrendered without a fight. On May 8, Clinton called for Lincoln's unconditional surrender, but Lincoln again attempted to negotiate for the honours of war. On May 11, Gadsden and other citizens asked Lincoln to surrender. While on the same day, the British fired heated shot into the city, burning several homes, compelling Lincoln to call for a parlay to negotiate terms for surrender. On May 12, Lincoln formally surrendered 3,371 men to the British.[3][3]:69–70
When word reached the back-country, the American troops holding Ninety-Six and Camden also surrendered to the British.[2]
Aftermath
The British captured some 5,266 prisoners, 311 artillery pieces, 9,178 artillery rounds, 5,916 muskets, 33,000 rounds of ammunition, 15 Regimental colours, 49 ships and 120 boats, plus 376 barrels of flour, and large magazines of rum, rice and indigo.[2] Following the surrender, the captured ordnance was brought to a powder magazine. A Hessian officer warned that some of the guns might still be loaded, but he was ignored. One prematurely fired, detonating 180 barrels of powder, further discharging 5,000 muskets in the magazine. The accident killed approximately 200 people and destroyed six houses.[2] The prisoners of the siege were diverted to multiple locations, including prison shops, the old barracks where the College of Charleston is today, and the Old Exchange and Provost "Dungeon". Prison hulks awaited the majority of the 2,571 Continental prisoners, while parole was granted to the militia and civilians who promised not to take up arms. However, this also meant there no longer existed an American army in the South.[3]:70
The defeat was a serious blow to the American cause.[10] It was the largest surrender of an American force under arms, until the 1862 surrender of Union troops at Harper's Ferry during the Antietam Campaign. The surrender left no substantial army in the South, and the colonies were wide open for a British advance. The British troops consolidated their hold, and had driven the remaining Continental Army troops from South Carolina consequent to the May 29 Battle of Waxhaws.
During their surrender the American forces were denied honours of war, leading General George Washington to deny the same to the British during their surrender at the Siege of Yorktown, with Washington saying "The same Honors will be granted to the Surrendering Army as were granted to the Garrison of Charles Town."[9]
On June 5, Clinton sailed back to New York City, believing his presence necessary to defend against a potential Franco-American attack, leaving command of the southern theatre to Lord Cornwallis, with orders to reduce opposition in North Carolina. Though the effects of the surrender at Charleston were substantial, the British error in strategy soon became apparent. There was no popular uprising of Loyalists, making control of the countryside difficult. Instead, resistance in South Carolina degenerated into a period of chaotic guerrilla warfare in the outlying areas.
Order of Battle
British forces
The joint British naval-army forces were led overall by Sir Henry Clinton, with his subordinate, Lord Cornwallis as his second-in-command. The British regular troops were led by Brigadier General Alexander Leslie.
The ground and naval forces were composed thus:
British Order of Battle[2][11] |
|---|
The British naval forces that accompanied the invasion were commanded by Vice Admiral Mariot Arbuthnot, and were composed thus:
|
Franco-American forces
The Franco-American garrison of Charleston was overall led by Benjamin Lincoln. The Continental Army troops were nominally led by Brigadier General William Moultrie
The ground and naval forces were composed thus:
Franco-American Order of Battle[2] |
|---|
The Franco-American naval forces that accompanied the defence of the city were commanded by Commodore Abraham Whipple, and were composed thus:
|
Preservation
The American Battlefield Trust and its partners have acquired and preserved 88 acres (0.36 km2) of historic land in Charleston related to the siege.[13]
See also
- List of American Revolutionary War battles
References
- Footnotes
^ (3,371 regulars & officers captured)[3]:70
- Citations
^ "Battle of Charleston ***". Landofthebrave.info. Retrieved 29 May 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abcdefg "The American Revolution in South Carolina - The Siege of Charlestown". Carolana.com. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
^ abcdefghijk Buchanan, John (1997). The Road to Guilford Courthouse. New York: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 26–29. ISBN 9780471327165.
^ Greene, Franics Vinton (1911). The Revoulutionary War and the Military Policy of the United States. New York Public Library. p. 210.
^ Morrill, Dan L (1993). Southern Campaigns of the American Revolution. Nautical & Aviation Publishing Company. p. 73. ISBN 9781877853210.
^ David B. Mattern (1998). Benjamin Lincoln and the American Revolution. Univ of South Carolina Press. p. 101. ISBN 978-1-57003-260-8.
^ Carl P. Borick (2003). A Gallant Defense. Univ of South Carolina Press. p. 169. ISBN 978-1-57003-487-9.
^ J. E. Kaufmann (2004). Fortress America. Tomasz Idzikowski (illus.). Da Capo Press. pp. 124–125. ISBN 978-0-306-81294-1.
^ ab "George Washington on General Cornwallis' Surrender at Yorktown". The American Revolution, 1763-1783. Library of Congress. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
^ Johnston, Henry Phelps (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 844.
Johnston, Henry Phelps (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 844.
^ Robert Beeton, Naval and Military Memoreess of Great Britain, from 1727 to 1783, London: shortman
, Hurst, Rees and Orme, 1804, vol. 6, pp. 203-206
^ *Rene Chartrand (1992) The French Army in the American War of Independence Osprey Publishing
ISBN 9781855321670 Chartrand, p. 3
^ "Saved Land". Battlefields.org. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
 Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 9 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 944.
Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 9 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 944.
External links
- Original papers relating to the siege of Charleston, 1780 By Benjamin Lincoln 1898
