Arab League
League of Arab States جامعة الدول العربية Jāmiʿat ad-Duwal al-ʿArabīyah | |
|---|---|
 Flag  Emblem | |
 | |
| Administrative center | Cairo, Egypt a |
| Official languages |
|
| Demonym(s) | Arabs |
| Type | Regional organization |
| Members | 22 states
|
| Leaders | |
• Arab League Secretariat | Ahmed Aboul Gheit |
• Arab Parliament | Ali Al-Daqbaashi |
• Council Presidency | |
| Legislature | Arab Parliament |
| Establishment | |
• Alexandria Protocol | 22 March 1945 |
| Area | |
• Total area | 13,132,327 km2 (5,070,420 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2015 estimate | 423,000,000[2] |
• Density | 27.17/km2 (70.4/sq mi) |
GDP (PPP) | 2016 estimate |
• Total | $6.484 trillion (4th) |
• Per capita | $9,347 |
GDP (nominal) | 2011 estimate |
• Total | $3.526 trillion |
• Per capita | $4,239 |
| Currency | 21
|
| Time zone | UTC+0 to +4 |
Website www.LasPortal.org | |
| |
| Part of a series on | |||||||||
| Arab League | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||
Issues
| |||||||||
Geography
| |||||||||
Governance
| |||||||||
Unity
| |||||||||
Foreign relations
| |||||||||
Military
| |||||||||
Economy
| |||||||||
Transportation
| |||||||||
Culture
| |||||||||
Demographics
| |||||||||
The Arab League (Arabic: الجامعة العربية al-Jāmiʻah al-ʻArabīyah), formally the League of Arab States (Arabic: جامعة الدول العربية Jāmiʿat ad-Duwal al-ʿArabīyah), is a regional organization of Arab states in and around North Africa, the Horn of Africa and Arabia. It was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945 with six members: Kingdom of Egypt, Kingdom of Iraq, Transjordan (renamed Jordan in 1949), Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Syria.[3]Yemen joined as a member on 5 May 1945. Currently, the League has 22 members, but Syria's participation has been suspended since November 2011, as a consequence of government repression during the Syrian Civil War.[4]
The League's main goal is to "draw closer the relations between member States and co-ordinate collaboration between them, to safeguard their independence and sovereignty, and to consider in a general way the affairs and interests of the Arab countries".[5]
Through institutions, such as the Arab League Educational, Cultural and Scientific Organization (ALECSO) and the Economic and Social Council of the Arab League's Council of Arab Economic Unity (CAEU), the Arab League facilitates political, economic, cultural, scientific, and social programmes designed to promote the interests of the Arab world.[6][7] It has served as a forum for the member states to coordinate their policy positions, to deliberate on matters of common concern, to settle some Arab disputes and to limit conflicts such as the 1958 Lebanon crisis. The League has served as a platform for the drafting and conclusion of many landmark documents promoting economic integration. One example is the Joint Arab Economic Action Charter, which outlines the principles for economic activities in the region.

Arab League of states establishment memorial stamp. Showing flags of the 8 establishing countries: Kingdom of Egypt, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the Mutawakkilite Kingdom (North Yemen), Syrian Republic, Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq, Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, Lebanese Republic
Each member state has one vote in the League Council, and decisions are binding only for those states that have voted for them. The aims of the league in 1945 were to strengthen and coordinate the political, cultural, economic and social programs of its members and to mediate disputes among them or between them and third parties. Furthermore, the signing of an agreement on Joint Defence and Economic Cooperation on 13 April 1950 committed the signatories to coordination of military defence measures. In March 2015, the Arab League General Secretary announced the establishment of a Joint Arab Force with the aim of counteracting extremism and other threats to the Arab States. The decision was reached while Operation Decisive Storm was intensifying in Yemen. Participation in the project is voluntary, and the army intervenes only at the request of one of the member states. The growing militarization of the region and the increase in violent civil wars as well as terrorist movements are the reason behind the creation of the JAF, financed by the rich Gulf countries.[8]
In the early 1970s, the Economic Council of the League of Arab States put forward a proposal to create the Joint Arab Chambers of Commerce across the European states. That led, under the decree of the League of Arab States no. K1175/D52/G, to the decision by the Arab governments to set up the Arab British Chamber of Commerce which was mandated to "promote, encourage and facilitate bilateral trade" between the Arab world and its major trading partner, the United Kingdom.
Contents
1 History
2 Geography
3 Membership
4 Politics and administration
5 Summits
6 Military
6.1 Emergency summits
7 Economic resources
7.1 Transport
8 Literacy in Arab league countries
9 Demographics
9.1 Religion
9.2 Linguistics
10 Culture
10.1 Sports
11 See also
12 References
13 External links
History
Following adoption of the Alexandria Protocol in 1944, the Arab League was founded on 22 March 1945. It aimed to be a regional organisation of Arab states with a focus to developing the economy, resolving disputes and coordinating political aims.[9] Other countries later joined the league.[10] Each country was given one vote in the council. The first major action was the joint intervention, allegedly on behalf of the majority Arab population being uprooted as the state of Israel emerged in 1948 (and in response to popular protest in the Arab world), but a major participant in this intervention, Transjordan, had agreed with the Israelis to divide up the Arab Palestinian state proposed by the United Nations General Assembly, and Egypt intervened primarily to prevent its rival in Amman from accomplishing its objective.[11]
It was followed by the creation of a mutual defence treaty two years later. A common market was established in 1965.[9][12]
Geography

Joining dates of member states; the Comoros (circled) joined in 1993.
1940s 1950s 1960s 1970s
The Arab League member states cover over 13,000,000 km2 (5,000,000 sq mi) and straddles two continents: Africa and Asia. The area largely consists of arid deserts, such as the Sahara. Nevertheless, it also contains several highly fertile lands like the Nile Valley, the Jubba Valley and Shebelle Valley in the Horn of Africa, the Atlas Mountains in the Maghreb, and the Fertile Crescent that stretches over Mesopotamia and the Levant. The area comprises deep forests in southern Arabia and parts of the world's longest river, the Nile.
Membership
The Charter of the Arab League, also known as the Pact of the League of Arab States, is the founding treaty of the Arab League. Adopted in 1945, it stipulates that "the League of Arab States shall be composed of the independent Arab States that have signed this Pact."[13]
Initially, in 1945, there were only six members. Today, the Arab League has 22 members, including three African countries among the largest by area (Sudan, Algeria and Libya) and the largest country in the Middle East, (Saudi Arabia).
Five countries have observer status that entitles them to express their opinion and give advice but denies them voting rights.[14]
There was a continual increase in membership during the second half of the 20th century. As of 2016[update], there are 22 member states:
 Algeria
Algeria
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Comoros
Comoros
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 Egypt
Egypt
 Iraq
Iraq
 Jordan
Jordan
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Lebanon
Lebanon
 Libya
Libya
 Mauritania
Mauritania
 Morocco
Morocco
 Oman
Oman
 Palestine
Palestine
 Qatar
Qatar
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Somalia
Somalia
 Sudan
Sudan
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Yemen
Yemen
and 5 observer states:
 Brazil
Brazil
 Eritrea
Eritrea
 India
India
 Venezuela[15]
Venezuela[15]
 Armenia
Armenia
Libya was suspended on 22 February 2011, following the start of the Libyan Civil War.[16] The National Transitional Council, the partially recognised interim government of Libya, sent a representative to be seated at the Arab League meeting on 17 August to participate in a discussion as to whether to readmit Libya to the organisation.[17]
Syria was suspended on 16 November 2011. On 6 March 2013, the Arab League gave the Syrian National Coalition Syria's seat in the Arab League.[18] On 9 March 2014, secretary general Nabil al-Arabi said that Syria's seat would remain vacant until the opposition completes the formation of its institutions.[19]
Politics and administration

Headquarters of the Arab League, Cairo.
Administrative divisions in the Arab League.
The Arab League is a political organization which tries to help integrate its members economically, and solve conflicts involving member states without asking for foreign assistance. It possesses elements of a state representative parliament while foreign affairs are often conducted under UN supervision.
The Charter of the Arab League[5] endorsed the principle of an Arab homeland while respecting the sovereignty of the individual member states. The internal regulations of the Council of the League[20] and the committees[21] were agreed in October 1951. Those of the Secretariat-General were agreed in May 1953.[22]
Since then, governance of the Arab League has been based on the duality of supra-national institutions and the sovereignty of the member states. Preservation of individual statehood derived its strengths from the natural preference of ruling elites to maintain their power and independence in decision making. Moreover, the fear of the richer that the poorer may share their wealth in the name of Arab nationalism, the feuds among Arab rulers, and the influence of external powers that might oppose Arab unity can be seen as obstacles towards a deeper integration of the league.
Mindful of their previous announcements in support of the Arabs of Palestine the framers of the Pact were determined to include them within the League from its inauguration.[23] This was done by means of an annex that declared:[5]
| “ | Even though Palestine was not able to control her own destiny, it was on the basis of the recognition of her independence that the Covenant of the League of Nations determined a system of government for her. Her existence and her independence among the nations can, therefore, no more be questioned de jure than the independence of any of the other Arab States. [...] Therefore, the States signatory to the Pact of the Arab League consider that in view of Palestine's special circumstances, the Council of the League should designate an Arab delegate from Palestine to participate in its work until this country enjoys actual independence | ” |
At the Cairo Summit of 1964, the Arab League initiated the creation of an organisation representing the Palestinian people. The first Palestinian National Council convened in East Jerusalem on 29 May 1964. The Palestinian Liberation Organization was founded during this meeting on 2 June 1964. Palestine was shortly admitted in to the Arab League, represented by the PLO. Today, State of Palestine is a full member of the Arab League.
At the Beirut Summit on 28 March 2002, the league adopted the Arab Peace Initiative,[24] a Saudi-inspired peace plan for the Arab–Israeli conflict. The initiative offered full normalisation of the relations with Israel. In exchange, Israel was required to withdraw from all occupied territories, including the Golan Heights, to recognise Palestinian independence in the West Bank and Gaza Strip, with East Jerusalem as its capital, as well as a "just solution" for the Palestinian refugees. The Peace Initiative was again endorsed at 2007 in the Riyadh Summit. In July 2007, the Arab League sent a mission, consisting of the Jordanian and Egyptian foreign ministers, to Israel to promote the initiative. Following Venezuela's move to expel Israeli diplomats amid the 2008–2009 Israel–Gaza conflict, Kuwaiti member of parliament Waleed Al-Tabtabaie proposed moving Arab League headquarters to Caracas, Venezuela.[25] On 13 June 2010, Amr Mohammed Moussa, Secretary-General of the Arab League, visited the Gaza Strip, the first visit by an official of the Arab League since Hamas' armed takeover in 2007.
In 2015, the Arab League voiced support for Saudi Arabian-led military intervention in Yemen against the Shia Houthis and forces loyal to former President Ali Abdullah Saleh, who was deposed in the 2011 uprising.[26]
On 15 April 2018, in response to the Turkish invasion of northern Syria aimed at ousting U.S.-backed Syrian Kurds from the enclave of Afrin, the Arab League passed a resolution calling on Turkish forces to withdraw from Afrin.[27]
Summits

2013 Arab League Summit Logo
| No. | Date | Host Country | Host City |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13–17 January 1964 | Cairo | |
| 2 | 5–11 September 1964 | Alexandria | |
| 3 | 13–17 September 1965 | Casablanca | |
| 4 | 29 August 1967 | Khartoum | |
| 5 | 21–23 December 1969 | Rabat | |
| 6 | 26–28 November 1973 | Algiers | |
| 7 | 29 October 1974 | Rabat | |
| 8 | 25–26 October 1976 | Cairo | |
| 9 | 2–5 November 1978 | Baghdad | |
| 10 | 20–22 November 1979 | Tunis | |
| 11 | 21–22 November 1980 | Amman | |
| 12 | 6–9 September 1982 | Fes | |
| 13 | 1985 | Casablanca | |
| 14 | 1987 | Amman | |
| 15 | June 1988 | Algiers | |
| 16 | 1989 | Casablanca | |
| 17 | 1990 | Baghdad | |
| 18 | 1996 | Cairo | |
| 19 | 27–28 March 2001 | Amman | |
| 20 | 27–28 March 2002 | Beirut | |
| 21 | 1 March 2003 | Sharm el-Sheikh | |
| 22 | 22–23 May 2004 | Tunis | |
| 23 | 22–23 March 2005 | Algiers | |
| 24 | 28–30 March 2006 | Khartoum | |
| 25 | 27–28 March 2007 | Riyadh | |
| 26 | 29–30 March 2008 | Damascus | |
| 27 | 28–30 March 2009 | Doha | |
| 28 | 27–28 March 2010 | Sirte | |
| 29 | 27–29 March 2012 | Baghdad | |
| 30 | 21–27 March 2013 | Doha[28] | |
| 31 | 25–26 March 2014 | Kuwait City[29] | |
| 32 | 28–29 March 2015 | Sharm El Sheikh[30] | |
| 33 | 20 July 2016 | Nouakchott | |
| 34 | 23–29 March 2017 | Amman[31] | |
| 35 | 15 April 2018 | Dhahran | |
| 36 | April 2019 | Tunis [32] |
Military
The Joint Defence Council of the Arab League is one of the Institutions of the Arab League.[33] It was established under the terms of the Joint Defence and Economic Co-operation Treaty of 1950 to coordinate the joint defence of the Arab League member states.[34]
The Arab League as an Organization has no military Force, like the UN or EU, but at the 2007 summit, the Leaders decided to reactivate their joint defense and establish a peacekeeping force to deploy in South Lebanon, Darfur, Iraq, and other hot spots.
At a 2015 summit in Egypt, member nations agreed in principle to form a joint military force.[35]
Emergency summits
| No. | Date | Host Country | Host City |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21–27 September 1970 | Cairo | |
| 2 | 17–28 October 1976 | Riyadh | |
| 3 | 7–9 September 1985 | Casablanca | |
| 4 | 8–12 November 1987 | Amman | |
| 5 | 7–9 June 1988 | Algiers | |
| 6 | 23–26 June 1989 | Casablanca | |
| 7 | 28–30 March 1990 | Baghdad | |
| 8 | 9–10 August 1990 | Cairo | |
| 9 | 22–23 June 1996 | Cairo | |
| 10 | 21–22 October 2000 | Cairo | |
| 11 | 7 January 2016 | Riyadh |
- Two summits are not added to the system of Arab League summits:
Anshas, Egypt: 28–29 May 1946.- Beirut, Lebanon: 13 – 15 November 1958.
- Summit 14 in Fes, Morocco, occurred in two stages:
- On 25 November 1981: the 5-hour meeting ended without an agreement on document.
- On 6–9 September 1982.
Economic resources
The Arab League is rich in resources, such as enormous oil and natural gas resources in certain member states. Another industry that is growing steadily in the Arab League is telecommunications. Within less than a decade, local companies such as Orascom and Etisalat have managed to compete internationally.[citation needed]
Economic achievements initiated by the League amongst member states have been less impressive than those achieved by smaller Arab organisations such as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).[36] Among them is the Arab Gas Pipeline, that will transport Egyptian and Iraqi gas to Jordan, Syria, Lebanon, and Turkey. As of 2013, a significant difference in economic conditions exist between the developed oil states of Algeria, Qatar, Kuwait and the UAE, and developing countries like Comoros, Djibouti, Mauritania, Somalia, Sudan and Yemen.
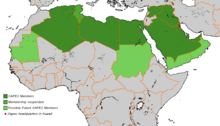
OAPEC Members
The Arab League also includes great fertile lands in the southern part of Sudan. It is referred to as the food basket of the Arab World, the region's instability including the independence of South Sudan has not affected its tourism industry, that is considered the fastest growing industry in the region, with Egypt, UAE, Lebanon, Tunisia, and Jordan leading the way. Another industry that is growing steadily in the Arab League is telecommunications.
Economical achievements within members have been low in the league's history, other smaller Arab Organizations have achieved more than the league has, such as the GCC, but lately several major economic projects that are promising are to be completed, the Arab Gas Pipeline is to end by the year 2010, Connecting Egyptian and Iraqi Gas to Jordan, Syria and Lebanon, and then to Turkey thus Europe, a free trade Agreement (GAFTA) is to be completed by 1 January 2008, making 95% of all Arab Products tax free of customs.
Transport
The Arab League is divided into five parts when it comes to transport, with the Arabian Peninsula and the Near East being entirely connected by air, sea, roads and railways. Another part of the League is the Nile Valley, made up of Egypt and Sudan. These two member states have started to improve the River Nile's navigation system to improve accessibility and thus foster trading. A new railway system is also set to connect the southern Egyptian city of Abu Simbel with the northern Sudanese city of Wadi Halfa and then to Khartoum and Port Sudan. The third division of the League is the Maghreb, where a 3,000 km stretch of railway runs from the southern cities of Morocco to Tripoli in Western Libya. The fourth division of the League is the Horn of Africa, whose member states include Djibouti and Somalia. These two Arab League states are separated by only ten nautical miles from the Arabian Peninsula by the Bab el Mandeb and this is quickly changing as Tarik bin Laden, the brother of Osama bin Laden, has initiated the construction of the ambitious Bridge of the Horns project, which ultimately aims to connect the Horn of Africa with the Arabian Peninsula via a massive bridge. The project is intended to facilitate and accelerate the already centuries-old trade and commerce between the two regions. The last division of the League is the isolated island of Comoros, which is not physically connected to any other Arab state, but still trades with other League members.
Literacy in Arab league countries

Literacy rate in Arab World.
In collecting literacy data, many countries estimate the number of literate people based on self-reported data. Some use educational attainment data as a proxy, but measures of school attendance or grade completion may differ. Because definitions and data collection methods vary across countries, literacy estimates should be used with caution. United Nations Development Programme, Human Development Report 2010. It is also important to note that the Persian Gulf region has had an oil boom, enabling more schools and universities to be set up.
| Rank | Country | Literacy rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 97.3[37] | |
| 2 | 96.5[37] | |
| 3 | 96.3[37] | |
| 4 | 95.7[37] | |
| 5 | 95.4[37] | |
| 6 | 94.4[37] | |
| 7 | 93.9[37] | |
| 8 | 93.8[37] | |
| 9 | 91.1[37] | |
| 10 | 91[37] | |
| 11 | 86.4[37] | |
| 12 | 85.7[37] | |
| 13 | 81.8[37] | |
| 14 | 81.8[37] | |
| 15 | 80.2[37] | |
| 16 | 75.9[37] | |
| 17 | 73.8[37] | |
| 18 | 70.1[37] | |
| 19 | 70.0[38] | |
| 20 | 68.5[37] | |
| 21 | 52.1[37] | |
| 22 | 44–72[39] |
Demographics
The Arab League is a culturally and ethnically one association of 22 member states, with the overwhelming majority of the League's population identified as Arab (on a cultural ethnoracial basis). As of July 1, 2013, about 359 million people live in the states of the Arab League. Its population grows faster than in most other global regions. The most populous member state is Egypt, with a population of about 91 million.[40] The least populated is the Comoros, with over 0.6 million inhabitants.
| Rank | Country | Population | Density (/km2) | Density (sq mi) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 97,075,300 | 101 | 262 | [41] | |
| 2 | 40,400,000 | 16 | 41 | [42] | |
| 3 | 37,202,572 | 80 | 207 | [43] | |
| 4 | 35,740,000 | 71 | 184 | [42] | |
| 5 | 39,578,828 | 16 | 41 | [44] | |
| 6 | 33,000,000 | 12 | 31 | [42] | |
| 7 | 27,584,213 | 45 | 117 | [42] | |
| 8 | 21,906,000 | 118 | 306 | [42] | |
| 9 | 11,304,482 | 65 | 168 | [45] | |
| 10 | 14,317,996 | 18 | 47 | [42] | |
| 11 | 10,159,967 | 71 | 184 | [42] | |
| 12 | 9,269,612 | 99 | 256 | [46] | |
| 13 | 6,293,253 | 3.8 | 9.8 | [42][47] | |
| 14 | 6,006,668 | 404 | 1,046 | [42] | |
| 15 | 4,550,368 | 756 | 1,958 | [48] | |
| 16 | 4,424,762 | 9.2 | 24 | [42] | |
| 17 | 4,301,018 | 3.2 | 8.3 | [42] | |
| 18 | 4,052,584 | 200 | 518 | [42] | |
| 19 | 2,641,669 | 154 | 399 | [42] | |
| 20 | 1,425,171 | 1,646 | 4,263 | [49] | |
| 21 | 942,333 | 37 | 96 | [42] | |
| 22 | 795,601 | 309 | 800 | [42] | |
| Total | 412,972,397 | 30.4 | 78.7 |
- Syrian demographics are before the Syrian civil war.
Religion
Almost all of the Arab League's citizens adhere to Islam, with Christianity being the second largest religion. At least 15 million Christians combined live in Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Sudan and Syria. In addition, there are smaller but significant numbers of Druze, Yazidis, Shabaks and Mandaeans. Numbers for nonreligious Arabs are generally not available, but research by the Pew Forum suggests around 1% of people in the MENA region are "unaffiliated".[50]
Linguistics
The official language of the Arab League is Literary Arabic, based on Classical Arabic. However, several Arab League member states have other co-official or national languages, such as Somali, Berber, Kurdish, Assyrian, and Nubian. Additionally, various different Arabic dialects are spoken, such as Egyptian Arabic, Levantine Arabic and Moroccan Arabic.
Culture
Sports
The Pan Arab Games are considered the biggest Arab sporting event, which brings together athletes from all the Arab countries to participate in a variety of different sports.
The Union of Arab Football Associations organises the Arab Nations Cup (for national teams) and the Arab Club Champions Cup (for clubs). Arab sport federations also exist for several games, include basketball, volleyball, handball, table tennis, tennis, squash and swimming.[citation needed]
See also
- Arab Charter on Human Rights
- Arab Cold War
Arab Fund for Economic and Social Development (AFESD)- Arab leaders
- Arab League and the Arab–Israeli conflict
- Arab League boycott of Israel
Arab Maghreb Union (UMA)- Arab Monetary Fund
- Arab Organization for Industrialization
- Arab Parliament
- Arab Union
- Bloudan Conference (1937)
Council of Arab Economic Unity (CAEU)- Flag of the Arab League
- General Arab Insurance Federation
- General Union of Chambers of Commerce, Industry and Agriculture for Arab Countries
Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
International Association of Arabic Dialectology (AIDA)- International Confederation of Arab Trade Unions
- List of conflicts in the Arab League
- List of country groupings
- List of largest cities in the Arab world
- List of multilateral free-trade agreements
- List of tallest buildings in the Arab League
- Lists of the Arab League
- Model Arab League
Orange card system – motor insurance scheme of the Arab League- Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC)
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)- Pan Arab Games
- Pan-Arabism
- Summit of South American-Arab Countries
- United Arab Command
- Arab Standardization and Metrology Organization
References
^ Syria suspended from Arab League, The Guardian
^ total population 450 million, CIA Factbook estimates an Arab population of 533 million, see article text.
^ "Arab League". The Columbia Encyclopedia. 2013. Retrieved 17 December 2013..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em} – via Questia (subscription required)
^ Sly, Liz (12 November 2011). "Syria suspended from Arab League". Washington Post.
^ abc "Pact of the League of Arab States, 22 March 1945". The Avalon Project. Yale Law School. 1998. Archived from the original on 25 July 2008. Retrieved 15 July 2012.
^ "The Arab League Educational, Cultural and Scientific Organization (ALESCO)".
^ Ashish K. Vaidya, Globalization (ABC-CLIO: 2006), p. 525.
^ Fanack. "The Joint Arab Force—Will It Ever Work?". Fanack.com. Archived from the original on 13 July 2015. Retrieved 13 July 2015.
^ ab Arab League formed — History.com This Day in History — 3/22/1945. History.com. Retrieved on 2014-04-28.
^ HowStuffWorks "Arab League". History.howstuffworks.com (2008-02-27). Retrieved on 2014-04-28.
^ Avi Shlaim, Collusion Across the Jordan: King Abdullah, the Zionist Movement and the Partition of Palestine. Oxford, U.K., Clarendon Press, 1988; Uri Bar-Joseph, Uri, The Best of Enemies: Israel and Transjordan in the War of 1948. London, Frank Cass, 1987; Joseph Nevo, King Abdullah and Palestine: A Territorial Ambition (London: Macmillan Press; New York: St. Martin's Press, 1996.
^ Robert W. MacDonald, The League of Arab States: A Study in Regional Organization. Princeton, New Jersey, United States, Princeton University Press, 1965.
^ "Pact of the League of Arab States, March 22, 1945". Yale Law School. Retrieved 9 July 2016 – via law.yale.edu.
^ "India invited as observer for Arab League summit". Press Trust of India. 27 March 2007. Retrieved 13 June 2007.
[permanent dead link]
^ "Arab League Fast Facts". CNN.com. 30 July 2013.
^ "Libya suspended from Arab League sessions". Ynetnews.com. 1995-06-20. Retrieved 2014-04-28.
^ "Arab League Recognizes Libyan Rebel Council". RTT News. 25 August 2011. Archived from the original on 8 December 2011. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
^ Black, Ian. "Syrian opposition takes Arab League seat". The Guardian. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
^ "Syria opposition 'not yet ready for Arab League seat'". The Daily Star Newspaper. Lebanon. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
^ "Internal Regulations of the Council of the League of Arab States". Model League of Arab States. Ed Haynes, Winthrop University. 6 April 1998. Archived from the original on 6 April 2008. Retrieved 9 July 2008.
^ "Internal Regulations of the Committees of the League of Arab States". Model League of Arab States. Ed Haynes, Winthrop University. 6 April 1998. Archived from the original on 6 April 2008. Retrieved 9 July 2008.
^ "Internal Regulations of the Secretariat-General of the League". Model League of Arab States. Ed Haynes, Winthrop University. 6 April 1998. Archived from the original on 6 April 2008. Retrieved 9 July 2008.
^ Geddes, 1991, p. 208.
^ Council of Arab States (1 October 2005). "The Arab Peace Initiative, 2002". al bab. Archived from the original on 4 June 2009. Retrieved 9 July 2008.
^ "Kuwaiti MP calls to move Arab league to Venezuela". AFP, via CaribbeanNetNews. 15 January 2009. Archived from the original on 4 March 2009. Retrieved 16 January 2009.
^ Boyle, Christina; al-Alayaa, Zaid (29 March 2015). "Arab League's joint military force is a 'defining moment' for region". Los Angeles Times.
^ "Turkey slams Arab League resolution on Afrin operation". Yeni Safak. 18 April 2018.
^ Arab League Summit 2013. Qatarconferences.org (2013-03-27). Retrieved on 2014-04-28.
^ Arab League summit hit by new rifts - Features. Al Jazeera English. Retrieved on 2014-04-28.
^ Opposition fail to get Syria Arab League seat - Middle East. Al Jazeera English. Retrieved on 2014-04-28.
^ "الأردن يستضيف القمة العربية في مارس". www.alarabiya.net.
^ https://www.egypttoday.com/Article/1/47928/Tunisia-to-host-next-Arab-summit
^ "Arab-Israeli Wars: 60 Years of Conflict". ABC-CLIO. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
^ Osmańczyk, Edmund Jan (2003). "League of Arab States". In Mango, Anthony. Encyclopedia of the United Nations and international agreements. 2 (3 ed.). New York: Routledge. p. 1290.
^ "Arab summit agrees on unified military force for crises". Reuters. 29 Mar 2015.
^ "Reuters.com". Reuters. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
^ abcdefghijklmnopqrst The World Factbook. Cia.gov. Retrieved on 2014-04-28.
^ DK Publishing (2012). Compact Atlas of the World. Penguin. p. 138. ISBN 0756698596.
^ "Family Ties: Remittances and Livelihoods Support in Puntland and Somaliland" (PDF). FSNAU. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
^ "Central Agency for Public Mobilization And Statistics". Archived from the original on 26 April 2011.
^ Official Egyptian Population clock Archived 30 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine
^ abcdefghijklmno "World Population Prospects, Table A.1" (PDF). 2008 revision. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. 2009: 17. Retrieved 22 September 2010.
^ "Site institutionnel du Haut-Commissariat au Plan du Royaume du Maroc". Site institutionnel du Haut-Commissariat au Plan du Royaume du Maroc.
^ "الجهاز المركزي للإحصاء". www.cbs.gov.sd.
^ "National Statistics Institute of Tunisia". Archived from the original on 4 September 2015. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
^ "المركز الوطني للإحصاء: المواطنون 947.9 ألفاً - جريدة الاتحاد". Alittihad.ae. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 16 August 2011.
^ "The World Factbook". cia.gov.
^ "Estimated Population in the Palestinian Territory Mid-Year by Governorate,1997-2016". Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics. State of Palestine. Archived from the original on 8 June 2014. Retrieved 8 June 2014.
^ Bahraini Census 2010 - تعداد السكــان العام للبحريــن 2010 Archived 20 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Census2010.gov.bh. Retrieved on 2014-04-28.
^ "Religious Diversity Around The World – Pew Research Center". Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. 4 April 2014.
External links
Wikisource has original text related to this article: Arab League Pact |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to League of Arab States. |
(in Arabic) The League of Arab States (official site).
(in English) League of Arab States Office in Washington D.C. – USA
The League of Arab States at Al-Bab.com
The Arab League at Council on Foreign Relations
Profile: Arab League, BBC News, updated 9 August 2011
Arab League at Jewish Virtual Library
Arab League at WorldStatesmen.org
Arab League Summit 2013 in Qatar (in English)
Arab Turk Conference and Expo at Bursa
Arab League collected news and commentary at The Jerusalem Post
"Arab League collected news and commentary". The New York Times.
