Visayas
Native name:
| |
|---|---|
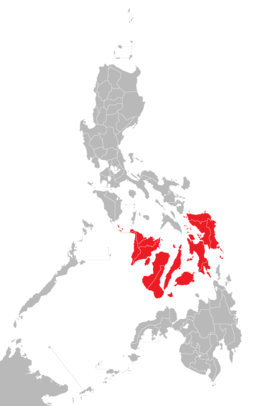 Location of the Visayas within the Philippines | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Southeast Asia |
| Archipelago | Philippines |
| Major islands |
|
| Area | 71,503 km2 (27,607 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 2,435 m (7,989 ft) |
| Highest point | Kanlaon Volcano |
| Administration | |
Philippines | |
| Regions |
|
| Largest settlement | Cebu City (pop. 922,611) |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym |
|
| Population | 19,373,431 (2015)[1] |
| Pop. density | 292 /km2 (756 /sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups |
|
The Visayas (/vɪˈsaɪəz/ vi-SY-əz), or the Visayan Islands[2] (Visayan: Kabisay-an, locally [kabiˈsajʔan]; Tagalog: Kabisayaan [kabiˈsɐjaʔan]), is one of the three principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the archipelago, it consists of several islands, primarily surrounding the Visayan Sea, although the Visayas are also considered the northeast extremity of the entire Sulu Sea.[3] Its inhabitants are predominantly the Visayan peoples.
The major islands of the Visayas are Panay, Negros, Cebu, Bohol, Leyte and Samar.[6] The region may also include the provinces of Masbate, Romblon and Palawan, whose populations identify as Visayan and whose languages are more closely related to other Visayan languages than to the major languages of Luzon.
There are three administrative regions in the Visayas: Western Visayas (pop. 7.1 million), Central Visayas (6.8 million) and Eastern Visayas (4.1 million).[7] The Negros Island Region existed from 2015 to 2017, separating Negros Occidental and its capital Bacolod from Western Visayas and Negros Oriental from Central Visayas. The region has been dissolved since.
Contents
1 Etymology
2 History
2.1 Mythical allusions and hypotheses
3 Administrative divisions
3.1 Western Visayas (Region VI)
3.2 Central Visayas (Region VII)
3.3 Eastern Visayas (Region VIII)
4 Major cities and municipalities
4.1 Table notes
5 Language
6 See also
7 Notes
8 References
9 External links
Etymology
The term Visayas was derived from the name of the 7th-century thalassocratic empire of Srivijaya (Sanskrit: श्रीविजय) in Sumatra.[8] In Sanskrit, sri (श्री) means "fortunate," "prosperous," or "happy" and vijaya (विजय) means "victorious" or "excellent". The archipelagoes of Visayas and Sulu were once Hindu-Buddhist and were either subject states or tributaries of the empire.[9]
History
The early inhabitants of the Visayas were the Austronesian peoples and Ati peoples, who migrated to the archipelago about 6,000 to 30,000 years ago.[10] These early settlers were animist tribes. In the 12th century, settlers from the collapsing Buddhist Srivijaya Empire led by Datu Putih and his retinue, settled in the island of Panay and its surrounding islands.[11] It was also during the 12th century that Visayans are said to have made a series of raids along the southern coasts of China. They were said to have a fearsome reputation, and the mention of their names would cause many to flee in horror and terror.[12] These tribes practiced a mixture of Hinduism, Buddhism and Animist-Polytheist beliefs although there are those in the population which exclusively practiced Hinduism, Buddhism or Animism. Besides the neighbouring Southeast Asians, there is evidence of trade among other Asian peoples. The Visayans were thought to have kept close diplomatic relations with Malaysian and Indonesian kingdoms, since the people of Cebu were able to converse with Enrique of Malacca using the Malay language when the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan arrived in 1521. The Visayas is subsequently home to several Precolonial kingdoms, like the Kedatuan of Madja-as (now Western Visayas) which was a rump-state of Srivijaya and had conducted resistance movements against the Hindu Chola dynasty and the Majapahit empire, the Rajahnate of Cebu which had allied herself with fellow Hindus in Butuan at Mindanao and Kutai in southern Borneo, and the Kedatuan of Dapitan which was at war with the Papuan Sultanate of Ternate.[13] Among the archaeological proofs of the existence of this Hiligaynon nation are the artifacts found in pre-European tombs from many parts of the island, which are now in display at Iloilo Museum. There are also recent discoveries of burial artifacts of eight-foot inhabitants of Isla de Gigantes, including extra-large Lungon (wooden coffins) and pre-Hispanic potteries.[14]
After the Magellan expedition, King Philip II of Spain sent Miguel López de Legazpi in 1543 and 1565 and claimed the islands for Spain. The Visayas region and many kingdoms began converting to Christianity and adopting western culture. By the 18th and 19th centuries, the effects of colonization on various ethnic groups soon turned sour and revolutions such as those of Francisco Dagohoy began to emerge.
Various personalities who fought against the Imperial Spanish Colonial Government arose within the archipelago. Among the notable ones are Graciano Lopez Jaena[15] and Martin Delgado from Iloilo, Aniceto Lacson, León Kilat and Diego de la Viña from Negros, Venancio Jakosalem Fernandez from Cebu,[16] and two personalities from Bohol by the name of Tamblot, who led the Tamblot Uprising in 1621 to 1622 and Francisco Dagohoy, the leader of the Bohol Rebellion that lasted from 1744 to 1829.[17] Negros briefly stood as an independent nation in the Visayas in the form of the Cantonal Republic of Negros, before it was absorbed back to the Philippines because of the American takeover of the archipelago.[18]
On May 23, 2005, Palawan (including its highly-urbanized capital city of Puerto Princesa) were transferred from MIMAROPA (Region IV-B) to Western Visayas (Region VI) under Executive Order No. 429, signed by Gloria Macapagal Arroyo, who was the president at that year.[19] However, Palaweños criticized the move, citing a lack of consultation, with most residents in Puerto Princesa and all Palawan municipalities but one preferring to stay in MIMAROPA (Region IV-B). Consequently, Administrative Order No. 129 was issued on 19 August 2005 that the implementation of E.O. 429 be held in abeyance, pending approval by the president of its Implementation Plan.[20] The Philippine Commission on Elections reported the 2010 Philippine general election results for Palawan as a part of the Region IV-B results.[21] As of 30 June 2011[update], the abeyance was still in effect, with Palawan and its capital city remaining under MIMAROPA (Region IV-B).
On May 29, 2015, the twin provinces of Negros Occidental (including its highly-urbanized capital city of Bacolod) and Negros Oriental were joined together to form the Negros Island Region under Executive Order No. 183, signed by President Benigno Aquino III. It separated both, the former province and its capital city from Western Visayas and the latter province from Central Visayas.
On August 9, 2017, President Rodrigo Duterte signed Executive Order No. 38, revoking the Executive Order No. 183 signed by (former) President Benigno Aquino III on May 29, 2015, due to the reason of the lack of funds to fully establish the NIR according to Benjamin Diokno, the Secretary of Budget and Management.
Mythical allusions and hypotheses
Historical documents written in 1907 by Visayan historian Pedro Alcántara Monteclaro in his book Maragtas tell the story of the ten leaders (Datus) who escaped from the tyranny of Rajah Makatunaw from Borneo and came to the islands of Panay. The chiefs and followers were said to be the ancestors (from the collapsing empires of Srivijaya and Majapahit) of the Visayan people. The documents were accepted by Filipino historians and found their way into the history of the Philippines. As a result, the arrival of Bornean tribal groups in the Visayas is celebrated in the festivals of the Ati-Atihan in Kalibo, Aklan and Binirayan in San Jose de Buenavista, Antique. Foreign historians such as William Henry Scott maintains that the book contains a Visayan folk tradition.[22]
A contemporary theory based on a study of genetic markers in present-day populations is that Austronesian peoples from Taiwan populated the larger island of Luzon and headed south to the Visayas and Mindanao, and then to Indonesia and Malaysia, then to Pacific Islands and finally to the island of Madagascar, at the west of the Indian Ocean.[23] The study, though, may not explain inter-island migrations, which are also possible, such as Filipinos migrating to any other Philippine provinces.
According to Visayan folk traditions, the Visayas were populated by Malays from the collapsing empires of Srivijaya and Majapahit migrating from Borneo to Mindanao and to the Visayas, while other Malay groups crossed to Palawan through Sabah.[citation needed] Other Malays were suggested to have crossed from the island of Samar to the Bicol Region in Luzon. The theory suggests that those ancient tribal groups who passed through Palawan may have migrated to what is now the island of Luzon.[citation needed]
A supplementary theory was that at that period, the Malay people were moving north from Mindanao to the Visayas and to Luzon.
Administrative divisions

A map of the Visayas colour-coded according to the constituent regions.
Central Visayas
Eastern Visayas
Western Visayas

A map of the Visayas color-coded according to its constituent regions during inclusion of the then Negros Island Region (2015-2017).
Western Visayas
Negros Island Region
Central Visayas
Eastern Visayas
Administratively, the Visayas is divided into 3 regions, namely Western Visayas, Central Visayas and Eastern Visayas. Each region is headed by a Regional Director who is elected from a pool of governors from the different provinces in each region.
The Visayas is composed of 16 provinces, each headed by a Governor. A governor is elected by popular vote and can serve a maximum of three terms consisting of three years each.
Western Visayas (Region VI)
Western Visayas consists of the islands of Panay and Guimaras and the western half of Negros. The regional center is Iloilo City. Its provinces are:
- Aklan
- Antique
- Capiz
- Guimaras
- Iloilo
- Negros Occidental
Central Visayas (Region VII)
Central Visayas includes the islands of Cebu, Siquijor and Bohol and the eastern half of Negros. The regional center is Cebu City. Its provinces are:
- Bohol
- Cebu
- Negros Oriental
- Siquijor
Eastern Visayas (Region VIII)
Eastern Visayas consists of the islands of Leyte,
Samar and Biliran. The regional center is Tacloban City. Its provinces are:
- Biliran
- Leyte
- Southern Leyte
- Eastern Samar
- Northern Samar
- Samar
Scholars have argued that the region of Mimaropa and the province of Masbate are all part of the Visayas in line with the non-centric view. This is contested by a few politicians in line with the Manila-centric view.[24][25]
Major cities and municipalities
Below is a list of cities and major towns in the Visayas by population.
| City or municipality | Population (2010)[i] | Area[ii] | Density | Province[iii] | Region | Legal class[iv] | Income class[iv] | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cebu City | 866,171 | 315.00 | 121.62 | 2,700 | 7,000 | Cebu | VII | HUC | 1st | Capital of Cebu; regional center of Region 7 | |
Bacolod | 511,820 | 162.67 | 62.81 | 3,100 | 8,000 | Negros Occidental | VI | HUC | 1st | Capital of Negros Occidental | |
Iloilo City | 424,619 | 78.34 | 30.25 | 6,200 | 16,000 | Iloilo | VI | HUC | 1st | Capital of Iloilo; regional center of Region 6 | |
Lapu-Lapu | 350,467 | 58.10 | 22.43 | 6,000 | 16,000 | Cebu | VII | HUC | 1st | ||
Mandaue | 331,320 | 25.18 | 9.72 | 13,000 | 34,000 | Cebu | VII | HUC | 1st | ||
Tacloban | 221,174 | 201.72 | 77.88 | 1,100 | 2,800 | Leyte | VIII | HUC | 1st | Capital of Leyte; regional center of Region 8 | |
Talisay | 200,772 | 39.87 | 15.39 | 5,000 | 13,000 | Cebu | VII | CC | 1st | ||
Ormoc | 191,200 | 613.60 | 236.91 | 310 | 800 | Leyte | VIII | ICC | 1st | ||
Kabankalan | 167,666 | 697.35 | 269.25 | 240 | 620 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | 1st | ||
Bago | 163,045 | 401.20 | 154.90 | 410 | 1,100 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | 1st | ||
Toledo | 157,078 | 216.28 | 83.51 | 730 | 1,900 | Cebu | VII | CC | 1st | ||
Roxas | 156,197 | 95.07 | 36.71 | 1,600 | 4,100 | Capiz | VI | CC | 1st | Capital of Capiz | |
Cadiz | 151,500 | 542.57 | 209.49 | 280 | 730 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | 1st | ||
Sagay | 140,740 | 330.34 | 127.54 | 430 | 1,100 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | 1st | ||
San Carlos | 129,981 | 451.50 | 174.33 | 290 | 750 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | 1st | ||
Silay | 120,999 | 214.80 | 82.93 | 560 | 1,500 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | 1st | ||
Dumaguete | 120,883 | 33.62 | 12.98 | 3,600 | 9,300 | Negros Oriental | VII | CC | 1st | Capital of Negros Oriental | |
Danao | 119,252 | 107.30 | 41.43 | 1,100 | 2,800 | Cebu | VII | CC | 1st | ||
Bayawan | 114,074 | 699.08 | 269.92 | 160 | 410 | Negros Oriental | VII | CC | 1st | ||
Carcar | 107,323 | 116.78 | 45.09 | 920 | 2,400 | Cebu | VII | CC | 1st | ||
Himamaylan | 103,006 | 367.04 | 141.71 | 280 | 730 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | 1st | ||
Baybay | 102,841 | 459.30 | 177.34 | 220 | 570 | Leyte | VIII | CC | |||
Naga | 101,571 | 101.97 | 39.37 | 1,000 | 2,600 | Cebu | VII | CC | |||
Talisay | 97,571 | 223.73 | 86.38 | 440 | 1,100 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | 1st | ||
Tagbilaran | 96,792 | 331.80 | 128.11 | 290 | 750 | Bohol | VII | CC | 1st | Capital of Bohol | |
Catbalogan | 94,317 | 274.22 | 105.88 | 340 | 880 | Samar | VIII | CC | |||
Guihulngan | 93,675 | 388.56 | 150.02 | 240 | 620 | Negros Oriental | VII | CC | |||
Escalante | 93,005 | 192.76 | 74.43 | 480 | 1,200 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | |||
Victorias | 88,299 | 133.92 | 51.71 | 660 | 1,700 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | 1st | ||
Catarman | 84,833 | 464.43 | 179.32 | 180 | 470 | Northern Samar | VIII | Municipality | 1st | Capital of Northern Samar | |
Maasin | 81,250 | 211.71 | 81.74 | 380 | 980 | Southern Leyte | VIII | CC | 1st | Capital of Southern Leyte | |
Passi | 79,633 | 251.39 | 97.06 | 320 | 830 | Iloilo | VI | CC | 1st | ||
Tanjay | 79,098 | 267.05 | 103.11 | 300 | 780 | Negros Oriental | VII | CC | 1st | ||
Kalibo | 74,619 | 45.75 | 17.66 | 1,600 | 4,100 | Aklan | VI | Municipality | 1st | Capital of Aklan | |
Bais | 74,722 | 319.64 | 123.41 | 230 | 600 | Negros Oriental | VII | CC | 1st | ||
Bogo | 69,911 | 103.52 | 39.97 | 680 | 1,800 | Cebu | VII | CC | 1st | ||
Sipalay | 67,403 | 379.78 | 146.63 | 180 | 470 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | 1st | ||
Borongan | 64,457 | 475.00 | 183.40 | 140 | 360 | Eastern Samar | VIII | CC | Capital of Eastern Samar | ||
La Carlota | 63,852 | 137.29 | 53.01 | 470 | 1,200 | Negros Occidental | VI | CC | 1st | ||
Canlaon | 50,627 | 170.93 | 66.00 | 300 | 780 | Negros Oriental | VII | CC | 1st | ||
San Jose de Buenavista | 62,534 | 48.56 | 18.75 | 1,300 | 3,400 | Antique | VI | Municipality | 1st | Capital of Antique | |
Sibalom | 60,306 | 201.30 | 77.72 | 300 | 780 | Antique | VI | Municipality | 2nd | Municipality in Antique | |
Mabinay | 74,187 | 319.44 | 123.34 | 230 | 600 | Negros Oriental | VII | Municipality | 1st | ||
Naval | 48,799 | 108.24 | 41.79 | 450 | 1,200 | Biliran | VIII | Municipality | 1st | Capital of Biliran | |
Jordan | 34,791 | 126.11 | 48.69 | 280 | 730 | Guimaras | VI | Municipality | 1st | Capital of Guimaras | |
Siquijor | 25,231 | 82.06 | 31.68 | 310 | 800 | Siquijor | VII | Municipality | 1st | Capital of Siquijor | |
| |||||||||||
Language
Languages spoken at home are primarily Visayan languages despite the usual misconception that these are dialects of a single macrolanguage. Major languages include Hiligaynon or Ilonggo in much of Western Visayas, Cebuano in Central Visayas, and Waray in Eastern Visayas. Other dominant languages are Aklanon, Kinaray-a, and Capiznon. Filipino, the 'national language' based on Tagalog, is widely understood but seldom used. English, another official language, is more widely known and is preferred as the second language most especially among urbanized Visayans. For instance, English rather than Tagalog is frequently used in schools, public signs and mass media.
See also
- Visayans
- Regions of the Philippines
- Provinces of the Philippines
Notes
^
Census of Population (2015). Highlights of the Philippine Population 2015 Census of Population. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Visayan Islands" Merriam-Webster Dictionary. http://www.merriam-webster.com/concise/visayan%20islands
^ C.Michael Hogan. 2011. Sulu Sea. Encyclopedia of Earth. Eds. P.Saundry & C.J.Cleveland. Washington DC
^ "Executive Order No. 429". President of the Philippines. Archived from the original on 2007-07-07. Retrieved 2009-05-18.
^ "Administrative Order No. 129". President of the Philippines. Archived from the original on 2009-07-13. Retrieved 2009-05-18.
^ On May 23, 2005, Palawan and Puerto Princesa City were moved to Western Visayas by Executive Order No. 429.[4] However, on August 19, 2005, President Arroyo issued Administrative Order No. 129 to hold the earlier E.O. 429 in abeyance pending a review.[5] As of 2010[update], Palawan and the highly urbanized city of Puerto Princesa still remain a part of the MIMAROPA region.
^ "PSA Makati ActiveStats - PSGC Interactive - List of Regions". Philippine Statistics Authority. June 30, 2015. Archived from the original on October 27, 2008. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
^ Jovito S. Abellana, "Bisaya Patronymesis Sri Visjaya" (Ms., Cebuano Studies Center, ca. 1960)
^ Rasul, Jainal D. (2003). Agonies and Dreams: The Filipino Muslims and Other Minorities. Quezon City: CARE Minorities. pp. 77.
^ Gray, RD; Drummond, AJ; Greenhill, SJ (2009). "Language Phylogenies Reveal Expansion Pulses and Pauses in Pacific Settlement". Science. 323 (5913): 479–483. doi:10.1126/science.1166858. PMID 19164742.
^ G. Nye Steiger, H. Otley Beyer, Conrado Benitez, A History of the Orient, Oxford: 1929, Ginn and Company, p. 120.
^ Scott, William Henry (1984). Prehispanic Source Materials. p. 74.
^ In Panay, the existence of highly developed and independent principalities of Ogtong (Oton) and Araut (Dumangas) was well known to early Spanish settlers in the Philippines. The Augustinian historian Gaspar de San Agustin, for example, wrote about the existence of an ancient and illustrious nobility in Araut, in his book Conquistas de las Islas Filipinas (1565–1615). He said: "También fundó convento el Padre Fray Martin de Rada en Araut- que ahora se llama el convento de Dumangas- con la advocación de nuestro Padre San Agustín...Está fundado este pueblo casi a los fines del río de Halaur, que naciendo en unos altos montes en el centro de esta isla (Panay)...Es el pueblo muy hermoso, ameno y muy lleno de palmares de cocos. Antiguamente era el emporio y corte de la más lucida nobleza de toda aquella isla." Gaspar de San Agustin, O.S.A., Conquistas de las Islas Filipinas (1565-1615), Manuel Merino, O.S.A., ed., Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas: Madrid 1975, pp. 374-375.
^ https://www.facebook.com/photo.php?fbid=491869557572311&set=a.216088591817077.50089.112008012225136&type=1&theater
^ Dr. Robert L. Yoder, FAPC."Graciano López Jaena". Universitat Wien. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
^ "Venancio's Leon Kilat". Inquirer.net. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
^ "The Dagohoy Rebellion". Watawat.net. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
^ WorldStatesmen. "Philippines - Republic of Negros". Retrieved 10 August 2010.
^ President of the Philippines (May 23, 2005). "Executive Order No. 429 s. 2005". Official Gazette. Philippine Government.
^ President of the Philippines (August 19, 2005). "Administrative Order No. 129 s. 2005". Official Gazette. Philippine Government.
^ Philippine 2010 Election Results: Region IV-B, Philippine Commission on Elections.
^ Scott 1984, pp. 81–103.
^ Cristian Capelli; et al. (2001). "A Predominantly Indigenous Paternal Heritage for the Austronesian-Speaking Peoples of Insular Southeast Asia and Oceania" (PDF). American Journal of Human Genetics. 68 (2): 432–443. doi:10.1086/318205. PMC 1235276. PMID 11170891. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-05-11.
^ http://news.abs-cbn.com/halalan2016/nation/05/10/16/nene-pimentel-gives-details-on-proposal-for-federalist-government
^ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7yRvtREhJdI
References
Scott, William Henry (1984). Prehispanic Source Materials for the study of Philippine History. New Day Publishers. ISBN 971-10-0226-4.
External links
 Media related to Visayas at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Visayas at Wikimedia Commons
 Visayas travel guide from Wikivoyage
Visayas travel guide from Wikivoyage
 The dictionary definition of visayas at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of visayas at Wiktionary
Coordinates: 11°00′N 123°30′E / 11.000°N 123.500°E / 11.000; 123.500

