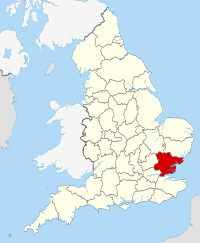
Essex
| Essex | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| County | |||||
| |||||
Motto: "Many Minds, One Heart" | |||||
 | |||||
| Coordinates: 51°45′N 0°35′E / 51.750°N 0.583°E / 51.750; 0.583Coordinates: 51°45′N 0°35′E / 51.750°N 0.583°E / 51.750; 0.583 | |||||
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom | ||||
| Constituent country | England | ||||
| Region | East | ||||
| Established | Ancient | ||||
| Ceremonial county | |||||
| Lord Lieutenant | John Petre | ||||
| High Sheriff | Bryan R H Burrough of Utting Wick [1] (2018-19) | ||||
| Area | 3,670 km2 (1,420 sq mi) | ||||
| • Ranked | 11th of 48 | ||||
| Population (mid-2017 est.) | 1,820,400 | ||||
| • Ranked | 7th of 48 | ||||
| Density | 496/km2 (1,280/sq mi) | ||||
| Ethnicity | 90.8% White British 3.6% White Other 2.5% Asian 1.3% Black 1.5% Mixed 0.3% Other | ||||
| Non-metropolitan county | |||||
| County council | Essex County Council | ||||
| Executive | Conservative | ||||
| Admin HQ | Chelmsford | ||||
| Area | 3,465 km2 (1,338 sq mi) | ||||
| • Ranked | 11th of 27 | ||||
| Population | 1,468,200 | ||||
| • Ranked | 2nd of 27 | ||||
| Density | 423/km2 (1,100/sq mi) | ||||
| ISO 3166-2 | GB-ESS | ||||
| ONS code | 22 | ||||
| GSS code | E10000012 | ||||
| NUTS | UKH33 | ||||
| Website | www.essex.gov.uk | ||||
| Unitary authorities | |||||
| Councils | Southend-on-Sea Borough Council Thurrock Council | ||||
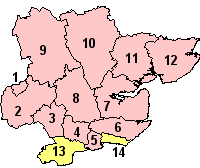 Districts of Essex Unitary County council area | |||||
| Districts |
| ||||
| Members of Parliament | List of MPs | ||||
| Police | Essex Police | ||||
| Time zone | Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | British Summer Time (UTC+1) | ||||
Essex (/ˈɛsɪks/) is a county in south-east England, north-east of London. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and London to the south-west. The county town is Chelmsford, the only city in the county.
Essex occupies the eastern part of the ancient Kingdom of Essex, which united with the other Anglian and Saxon kingdoms to make England a single nation state. As well as rural areas, the county also includes London Stansted Airport, the new towns of Basildon and Harlow, Lakeside Shopping Centre, the port of Tilbury and the borough of Southend-on-Sea.
Contents
1 History
1.1 County-wide administration
1.2 Parish-level administration – changes
1.3 Boundaries
1.4 Two unitary authorities
2 Geography
3 Economy
4 Politics
4.1 Westminster and the 2016 EU referendum
4.2 Essex County Council
4.2.1 Youth councils
4.3 Local government
5 Transport
6 Education
7 Culture
8 Sport
9 Landmarks
10 Places of interest
11 Notable people
12 Sister counties and regions
13 See also
14 Notes and references
15 External links
History
The name Essex originates in the Anglo-Saxon period of the Early Middle Ages and has its root in the Anglo-Saxon (Old English) name Ēastseaxe ("East Saxons"), the eastern kingdom of the Saxons who had come from the continent and settled in Britain (cf. Middlesex, Sussex and Wessex) during the Heptarchy. Originally recorded in AD 527, Essex occupied territory to the north of the River Thames, incorporating all of what later became Middlesex (which probably included Surrey) and most of what later became Hertfordshire. Its territory was later restricted to lands east of the River Lea.[2]
Colchester in the north-east of the county is Britain's oldest recorded town, dating from before the Roman conquest, when it was known as Camulodunum and was sufficiently well-developed to have its own mint. In AD 824, following the Battle of Ellandun, the kingdoms of the East Saxons, the South Saxons and the Jutes of Kent were absorbed into the kingdom of the West Saxons, uniting Saxland under King Alfred's grandfather Ecgberht. Before the Norman conquest the East Saxons were subsumed into the Kingdom of England. After the Norman conquest, Essex became a county.
During the medieval period, much of the area was designated a Royal forest, including the entire county in a period to 1204, when the area "north of the Stanestreet" was disafforested.[3] Gradually, the areas subject to forest law diminished, but at various times they included the forests of Becontree, Chelmsford, Epping, Hatfield, Ongar and Waltham.[4]
County-wide administration
Essex County Council was formed in 1889. However, County Boroughs of West Ham (1889–1965), Southend-on-Sea (1914–1974)[5] and East Ham (1915–1965) formed part of the county but were unitary authorities (not under county council control).[6] 12 boroughs and districts provide more localised services such as rubbish and recycling collections, leisure and planning, as shown in the map on the right.
Parish-level administration – changes
A few Essex parishes have been transferred to other counties. Before 1889, small areas were transferred to Hertfordshire near Bishops Stortford and Sawbridgeworth. At the time of the main changes around 1900, parts of Helions Bumpstead, Sturmer, Kedington and Ballingdon-with-Brundon were transferred to Suffolk; and Great Chishill, Little Chishill and Heydon were transferred to Cambridgeshire. Later, part of Hadstock, part of Ashton and part of Chrishall were transferred to Cambridgeshire and part of Great Horkesley went to Suffolk; and several other small parcels of land were transferred to all those counties.
Boundaries
The boundary with Greater London was established in 1965, when East Ham and West Ham county boroughs and the Barking, Chingford, Dagenham, Hornchurch, Ilford, Leyton, Romford, Walthamstow and Wanstead and Woodford districts[6] were transferred to form the London boroughs of Barking and Dagenham, Havering, Newham, Redbridge and Waltham Forest. Essex became part of the East of England Government Office Region in 1994 and was statistically counted as part of that region from 1999, having previously been part of the South East England region.
Two unitary authorities
In 1998, the boroughs of Southend-on-Sea and Thurrock were granted autonomy from the administrative county of Essex after successful requests to become unitary authorities (numbered 13 and 14 on the map to the right).[7][8]
Essex Police covers the administrative county and the two unitary authorities.[9] The county council chamber and main headquarters is at the County Hall in Chelmsford. Before 1938, the council regularly met in London near Moorgate, which with significant parts of the county close to that point and the dominance of railway travel had been more convenient than any place in the county. It currently has 75 elected councillors. Before 1965, the number of councillors reached over 100. The County Hall, made a listed building in 2007, dates largely from the mid-1930s and is decorated with fine artworks of that period, mostly the gift of the family who owned the textile firm Courtaulds.
Geography
The highest point of the county of Essex is Chrishall Common near the village of Langley, close to the Hertfordshire border, which reaches 482 feet (147 m). The ceremonial county of Essex is bounded to the south by the River Thames and its estuary (a boundary shared with Kent); to the southwest by Greater London; to the west by Hertfordshire with the boundary largely defined by the River Lea and the Stort; to the northwest by Cambridgeshire; to the north by Suffolk, a boundary mainly defined by the River Stour; and to the east by the North Sea.
The pattern of settlement in the county is diverse. The Metropolitan Green Belt has effectively prevented the further sprawl of London into the county, although it contains the new towns of Basildon and Harlow, originally developed to resettle Londoners after the destruction of London housing in the Second World War, since which they have been significantly developed and expanded. Epping Forest also prevents the further spread of the Greater London Urban Area. As it is not far from London with its economic magnetism, many of Essex's settlements, particularly those near or within short driving distance of railway stations, function as dormitory towns or villages where London workers raise their families.

The village of Finchingfield in north Essex
Part of the southeast of the county, already containing the major population centres of Basildon, Southend and Thurrock, is within the Thames Gateway and designated for further development. Parts of the southwest of the county, such as Buckhurst Hill and Chigwell, are contiguous with Greater London neighbourhoods and therefore form part of the Greater London Urban Area.
A small part of the southwest of the county (Sewardstone) is the only settlement outside Greater London to be covered by a postcode district of the London post town (E4). With the exception of major towns such as Colchester, Chelmsford and Southend-on-Sea, the county is rural, with many small towns, villages and hamlets largely built in the traditional materials of timber and brick, with clay tile or thatched roofs.
Economy
Industry is largely limited to the south of the county, with the majority of the land elsewhere being given over to agriculture. Harlow is a centre for electronics, science and pharmaceutical companies. Chelmsford has been an important location for electronics companies, such as the Marconi Company, since the industry was born; it is also the location for a number of insurance and financial services organisations, and until 2015 was the home of the soft drinks producer Britvic. Basildon is home to New Holland Agriculture's European headquarters, and Brentwood is home to the Ford Motor Company's British HQ. Debden, near Loughton, is home to a production facility for British and foreign banknotes.
Other businesses in the county are dominated by mechanical engineering, including but not limited to metalworking, glassmaking and plastics and the service sector. Colchester is a garrison town, and the local economy is helped by the Army's personnel living there. Basildon is the location of State Street Corporation's United Kingdom HQ International Financial Data Services, and remains heavily dependent on London for employment, due to its proximity and direct transport routes. Southend-on-Sea is home to the Adventure Island theme park and is one of the few still growing British seaside resorts, benefiting from direct, modern rail links from Fenchurch Street railway station and Liverpool Street station (so that housing is in high demand, especially for financial services commuters), which maintains the town's commercial and general economy.
Parts of eastern Essex suffer from high levels of deprivation; one of the most highly deprived wards is in the seaside town of Clacton.[10] In the Indices of deprivation 2007, Jaywick was identified as the most deprived Lower Super Output Area in Southern England.[11] Unemployment was estimated at 44% and many homes were found to lack very basic amenities. The Brooklands and Grasslands area of Jaywick was found to be the third-most deprived area in England; two areas in Liverpool and Manchester were rated more deprived. In contrast, west and south-west Essex is one of the most affluent parts of eastern England, forming part of the London commuter belt. There is a large middle class here, and the area is widely known for its private schools. In 2008, The Daily Telegraph found Ingatestone and Brentwood to be the 14th- and 19th-richest towns in the UK respectively.[12]
Politics
Westminster and the 2016 EU referendum
Essex is a strongly Conservative county, and 15 of its 18 constituency MPs had absolute majorities (over 50%) in the 2017 UK general election. Though all 18 MPs in Essex are currently Conservative, there have previously been some Labour MPs: most recently, Thurrock, Harlow and Basildon in Labour's 2005 election victory. The Liberal Democrats until 2015 had a sizeable following in Essex, gaining Colchester in the 1997 general election.

Results of the 2017 UK general Election in Essex
The 2015 general election saw a large vote in Essex for the UK Independence Party (UKIP), with its only MP, Douglas Carswell, retaining the seat of Clacton that he had won in a 2014 by-election, and other strong performances, notably in Thurrock and Castle Point. But in the 2017 general election, UKIP's vote share plummeted by 15.6% while both Conservative and Labour vote shares rose by 9%. This resulted in Labour regaining second place in Essex, increasing their vote share across the county and cutting some Conservative majorities in areas which had been unaffected by the 1997 general election, namely Rochford and Southend East and Southend West.
The most Conservative seat by vote share is Saffron Walden with almost 62% voting Conservative. In contrast, Thurrock is the most marginal seat. In 2015, Thurrock epitomised a three-party race with UKIP, Labour and the Conservatives gaining 30%, 31% and 32% respectively. In 2017, the Conservatives held Thurrock with an increased share of the vote, but a smaller margin of victory. It was the constituency in which UKIP performed best in 2017, with 20% of the vote while all other areas had been reduced to low single figure vote shares.
Several new MPs were elected in the 2017 election, with Alex Burghart, Vicky Ford, Giles Watling and Kemi Badenoch all replacing senior Conservative politicians such as Sir Eric Pickles, Sir Simon Burns, Douglas Carswell and Sir Alan Haselhurst, respectively.
In the EU referendum, Essex voted overwhelmingly to leave the EU, with all 14 District Council areas voting to leave, the smallest margin being in Uttlesford.[13]
| Party | Votes cast | % | Seats | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 2015 | 2017 | ± | 2010 | 2015 | 2017 | ± | 2010 | 2015 | 2017 | ± | ||
Conservative | 417,156 | 436,758 | 528,949 | 49.2 | 49.6 | 59.0 | 17 | 17 | 18 | ||||
Labour | 157,134 | 171,026 | 261,671 | 18.5 | 19.4 | 29.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
Liberal Democrat | 180,391 | 58,592 | 46,254 | 21.3 | 6.6 | 5.1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||
UKIP | 35,150 | 177,756 | 41,478 | 4.1 | 20.2 | 4.6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||
Green | 8,080 | 25,993 | 12,343 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Independents | 15,651 | 6,919 | 4,179 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
BNP | 29,030 | 108 | 640 | 3.4 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
Christian People's | 267 | 189 | 318 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
English Democrats | 4,130 | 453 | 289 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
YPP | N/A | 80 | 110 | N/A | 0 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Total | 847,090 | 879,918 | 896,231 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 18 | 18 | 18 | ||||
Essex County Council
This is the county council that governs the non-metropolitan county of Essex in England. It has 75 councillors, elected from 70 divisions, some of which elect more than one member, and is currently controlled by the Conservative Party.[2] The council meets at County Hall in the centre of Chelmsford.
At the time of the 2011 census it served a population of 1,393,600, which makes it one of the largest local authorities in England. As a non-metropolitan county council, responsibilities are shared between districts (including boroughs) and in many areas also between civil parish (including town) councils. Births, marriages/civil partnerships and death registration, roads, libraries and archives, refuse disposal, most of state education, of social services and of transport are provided at the county level.[3]
The county council was formed in 1889, governing the administrative county of Essex. The county council was reconstituted in 1974 as a non-metropolitan county council, regaining jurisdiction in Southend-on-Sea; however, the non-metropolitan county was reduced in size in 1998 and the council passed responsibilities to Southend-on-Sea Borough Council and Thurrock Council in those districts. For certain services the three authorities co-operate through joint arrangements, such as the Essex fire authority.
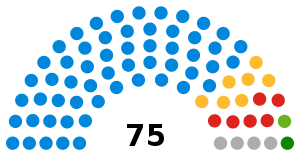
Composition of the Essex County Council in 2017 after the county election
At the 2013 County Council elections the Conservative Party retained overall control of the council, but its majority fell from twenty-two to four councillors. UKIP, Labour and the Liberal Democrats each won nine seats. Out of those three parties, UKIP gained the largest share of the county-wide vote, more than 10% ahead of Labour.[3] The Liberal Democrats remain as the official Opposition, despite winning fewer votes.[3] The Green Party gained two seats on the Council, despite its overall share of the vote falling. The Independent Loughton Residents Association and the Canvey Island Independent Party both returned one member and an Independent candidate was also elected.
The 2017 County Council elections saw a county-wide wipeout of UKIP. The Conservative Party profited most from this loss, regaining many of the seats it had lost at the previous election. Labour, despite a slight rise in its share of the vote, had fewer councillors elected. The Liberal Democrats also saw a notable revival, but were unable to translate this into seats. The Conservatives retained firm control of the council. The next election will be in 2021.
The county of Essex is divided into 12 district and borough councils with 2 unitary authorities (Southend on Sea and Thurrock). The 12 councils manage housing, local planning, refuse collection, street cleaning, elections and meet in their respective civic offices. The local representatives are elected in parts in local elections, held every year.[14]
With regard to the two unitary authorities, the county council is not used to conduct business, but works closely with the unitary authorities to deliver the “best value service” to all residents.
| Party | Votes cast | % | Seats | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 2013 | 2017 | ± | 2009 | 2013 | 2017 | ± | 2009 | 2013 | 2017 | ± | ||
Conservative | 169,975 | 112,229 | 184,901 | 43.3 | 34.4 | 49.3 | 60 | 42 | 56 | ||||
Labour | 42,334 | 57,290 | 63,470 | 10.8 | 16.4 | 16.9 | 1 | 9 | 6 | ||||
Liberal Democrat | 79,085 | 35,651 | 51,524 | 20.1 | 11.6 | 13.7 | 12 | 9 | 7 | ||||
UKIP | 18,186 | 90,812 | 29,796 | 4.6 | 27.6 | 7.9 | 0 | 9 | 0 | ||||
Green | 26,547 | 15,187 | 15,187 | 6.8 | 4.8 | 4.3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| Independents | 5,845 | 4,631 | 12,506 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 2.4 | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||||
Residents for Uttlesford | N/A | N/A | 5,231 | N/A | N/A | 1.4 | 0 | 0*(1) | 0 | ||||
Canvey Island Independents | 1,655 | 2,777 | 3,654 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
Loughton Residents | 2,764 | 3,286 | 2,824 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
Tendring First | 5,866 | 4,093 | 1,332 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
BNP | 35,037 | 909 | 847 | 8.9 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
English Democrats | 5,212 | 835 | 58 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
TUSC | N/A | 431 | N/A | N/A | 0.1 | N/A | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
National Front | N/A | 304 | N/A | N/A | 0.1 | N/A | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Total | 392,506 | 328,435 | 372,834 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 75 | 75 | 75 | ||||
Youth councils
The Essex County Council also has a Youth Assembly, 75 members aged between 11 and 19 who aim to represent all young people in their districts across Essex. They decide on the priorities for young people and campaign to make a difference.[15] With this, some district and unitary authorities may have their own youth councils, such as Epping Forest,[16]Uttlesford[17] and Harlow.[18]
All these councilors are elected by their schools. The elections to the Young Essex Assembly occur in the respective schools in which the candidates are standing, likewise for the youth councils at a district and unitary level. These young people will then go on to represent their school and their parish/ward or (in the case of the Young Essex Assembly) their entire district.
The initiative seeks to engage younger people in the county and rely on the youth councilors of all status to work closely with schools and youth centers to improve youth services in Essex and help promote the opinions of the Essex youth generation.[citation needed]
Local government
Town and parish councils vary in size from those with a population of around 200 to those with a population of over 30,000. Annual expenditure can vary greatly, depending on the circumstances of the individual council. Parish and town councils (local councils) have the same powers and duties, but a town council may elect a town mayor, rather than a chairman, each year in May.
There are just under 300 town and parish councils within Essex.[14]
Local councils play a vital role in representing the interests of their communities and improving the quality of life and the local environment. They can also influence other decision makers and can deliver services to meet local needs. Their powers and duties range from maintaining allotments and open spaces, to crime prevention and providing recreation facilities.
Local councils have the right to become statutory consultees at both district and county level and, although the decision remains with the planning authorities, local councils can influence the decision-making process by making informed comments and recommendations.[14]
Transport

London Stansted Airport, in the north west of the county
The main airport in Essex is London Stansted Airport, serving destinations in Europe, North Africa and Asia.[19] The Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition government formed in May 2010 agreed not to allow a further runway until a set time period,[when?] so curtailing the operator's ambitions for expansion. London Southend Airport, once one of Britain's busiest airports, opened a new runway extension, terminal building and railway station in March 2012.[20] It has a station on the Shenfield to Southend Line, with a direct link to London.
Southend Airport has scheduled flights to Ireland, the Channel Islands and multiple destinations in Europe. Essex has several smaller airfields, some of which owe their origins to military bases built during World War I or World War II, giving pleasure flights or flying lessons; these include Clacton Airfield, Earls Colne Airfield, and Stapleford Aerodrome.
The Port of Tilbury is one of Britain's three major ports, while the port of Harwich has passenger and freight services to the Hook of Holland and a freight service to Europoort. A service to Esbjerg, Denmark ceased in September 2014[21] and earlier a service to Cuxhaven in Germany was discontinued in December 2005.
The UK's largest container terminal London Gateway at Shell Haven in Thurrock partly opened in November 2013; final completion date is yet to be confirmed.[22] The port was opposed by the local authority and environmental and wildlife organisations.[23][24][25]

Queen Elizabeth II Bridge spanning the Thames from West Thurrock, Essex, to Dartford, Kent
East of the Dartford Road Crossing to Dartford, Kent, across the Thames Estuary, a pedestrian ferry to Gravesend, Kent operates from Tilbury during limited daily hours, and there are pedestrian ferries across some of Essex's rivers and estuaries in spring and summer. The M25 and M11 motorways both cross the county in the extreme south and west, enabling regular commuting between parts of the county and Kent, Hertfordshire and Cambridge. The A127 and A13 trunk roads are important radial routes connecting London and the M25 to the south of Essex. The A12 runs across the county from south west to north east and carries traffic not just within Essex but also between London and Suffolk, east Norfolk and the ports of Felixstowe and Harwich.
Rail goods have several ports and dedicated lines within Essex.[26]
Much of Essex lies within the London commuter belt. Greater Anglia is the main railway operator in the county, providing commuter services into London Liverpool Street and regional services throughout the East of England. The main railway routes in Essex include:
- Three lines from the City of London to Southend-on-Sea: two operated by c2c from Fenchurch Street (one route via Tilbury) and by Greater Anglia from Liverpool Street;
- The Great Eastern Main Line from Liverpool Street to Suffolk and Norfolk and to the international port at Harwich International;
- The West Anglia Main Line from Liverpool Street to Stansted Airport and onward to Cambridgeshire.
The southern part of Epping Forest district is served by the London Underground Central line. The routes operated by Greater Anglia were operated by National Express East Anglia from 2004 until 2012, and before that by First Great Eastern. Branch lines include:
- The Sunshine Coast Line linking Colchester to the seaside resorts of Clacton-on-Sea and Walton-on-the-Naze via the picturesque towns of Wivenhoe and Great Bentley.
- The Crouch Valley Line linking Wickford to Southminster via the riverside communities including South Woodham Ferrers and Burnham-on-Crouch.[27]
South Essex Rapid Transit is a proposed public transport scheme which would provide a fast, reliable public transport service in and between Thurrock, Basildon and Southend.[28]
Education
Education in Essex is substantially provided by three authorities: Essex County Council and the two unitary authorities, Southend-on-Sea and Thurrock. In all there are some 90 state secondary schools provided by these authorities, the majority of which are comprehensive, although one in Uttlesford, two in Chelmsford, two in Colchester and four in Southend-on-Sea are selective grammar schools. There are also various independent schools particularly, as mentioned above, in rural parts and the west of the county.[29][30]
The University of Essex, which was established in 1963, is located just outside Colchester, with two further campuses in Loughton and Southend-on-Sea.
University Campus Suffolk, with a main campus in Ipswich and five centres in the counties of Norfolk and Suffolk, is a joint venture between University of Essex and East Anglia polytechnic.
Culture

Depiction of the first king of the East Saxons, Æscwine, his shield showing the three seaxes emblem attributed to him (from John Speed's 1611 Saxon Heptarchy)
The county's coat of arms comprises three Saxon seax knives (although they look rather more like scimitars), mainly white and pointing to the right (from the point of view of the observer), arranged vertically one above another on a red background (Gules three Seaxes fessewise in pale Argent pomels and hilts Or points to the sinister and cutting edges upwards); the three-seax device is also used as the official logo of Essex County Council; this was granted in 1932.[31]
The emblem was attributed to Anglo-Saxon Essex in Early Modern historiography. The earliest reference to the arms of the East Saxon kings was by Richard Verstegan, the author of A Restitution of Decayed Intelligence (Antwerp, 1605), claiming that "Erkenwyne king of the East-Saxons did beare for his armes, three [seaxes] argent, in a field gules". There is no earlier evidence substantiating Verstegan's claim, which is an anachronism for the Anglo-Saxon period seeing that heraldry only evolved in the 12th century, well after the Norman Conquest.
John Speed in his Historie of Great Britaine (1611) follows Verstegan in his descriptions of the arms of Erkenwyne, but he qualifies the statement by adding "as some or our heralds have emblazed".[31]

The Hay Wain by John Constable shows the Essex landscape on the right bank.
Essex is also home to the Dunmow Flitch Trials, a traditional ceremony that takes place every four years and consists of a test of a married couple's devotion to one another. A common claim of the origin of the Dunmow Flitch dates back to 1104 and the Augustinian priory of Little Dunmow, founded by Lady Juga Baynard. Lord of the Manor Reginald Fitzwalter and his wife dressed themselves as humble folk and begged blessing of the Prior a year and a day after marriage. The prior, impressed by their devotion, bestowed upon them a flitch of bacon. Upon revealing his true identity, Fitzwalter gave his land to the priory on condition that a flitch should be awarded to any couple who could claim they were similarly devoted.
By the 14th century, the Dunmow Flitch Trials appear to have achieved a significant reputation outside the local area. The author William Langland, who lived on the Welsh borders, mentions it in his 1362 book The Vision of Piers Plowman in a manner that implies general knowledge of the custom among his readers.[32]
The Essex dialect, an accent related to the Suffolk dialect, was formerly prevalent in the county but has now been mostly replaced by Estuary English.
Sport
Essex is home to two English Football League teams: Southend United and Colchester United. Both teams have reached as high as the Championship (the second tier of English football) at some point in their history. As of 2018-19 Southend United are in League One, while Colchester United are in League Two. Braintree Town are the next highest-placed team, playing in the National League, followed by Chelmsford City, Concord Rangers and East Thurrock United, who play in the National League South. The highest domestic trophy for non-league teams, the FA Trophy, has been won on four occasions by Essex teams; most recently by Grays Athletic in 2006.
Essex County Cricket Club became a First-Class County in 1894. The county has won 7 County Championship league titles; 6 of these were won during the dominant period between 1979 and 1992, with a gap of 25 years before the county's next title in 2017.
The County is also home to the Chelmsford Chieftains ice hockey team and the Essex Leopards basketball team. It has previously been home to the Essex Eels rugby league team, as well as the Essex Pirates basketball team. Former speedway teams in the county (now no longer operating) include the Lakeside Hammers (formerly Arena Essex Hammers), the Rayleigh Rockets and the Romford Bombers.
During the 2012 London Olympics, Hadleigh Farm played host to the mountain bike races.
Essex has one horse racing venue, Chelmsford City Racecourse at Great Leighs, and horse racing also took place at Chelmsford Racecourse in Galleywood until 1935. The county has one current greyhound racing track, Harlow Stadium. Rayleigh Weir Stadium and Southend Stadium are former greyhound venues.
Team Essex Volleyball Club is Chelmsford's national league volleyball club. It has four teams which play in Volleyball England's national volleyball league. Its Men's 1st team currently competes in the top division in the country, the Super 8s while the Women's 1st team competes one tier below the men. The club has a strong junior program and trains in The Boswells School in Chelmsford.
Many famous sports stars have come from or trained in Essex. These have included swimmer Mark Foster; cricket stars Trevor Bailey, Nasser Hussain, Alastair Cook and Graham Gooch; footballers Peter Taylor, James Tomkins, Justin Edinburgh, Nigel Spink; tennis stars John Lloyd and David Lloyd; Olympic Gold-winning gymnast Max Whitlock; Olympic sailing champion Saskia Clark; World Champion snooker stars Stuart Bingham and Steve Davis; world champion boxers Terry Marsh, Nigel Benn and Frank Bruno; London Marathon winner Eamonn Martin; international rugby players Malcolm O'Kelly and Stuart Barnes; Formula 1 sports car drivers Johnny Herbert and Perry McCarthy.
Landmarks
Over 14,000 buildings have listed status in the county, and around 1000 of those are recognised as of Grade I or II* importance.[33] The buildings range from the 7th century Saxon church of St Peter-on-the-Wall, to the Royal Corinthian Yacht Club which was the United Kingdom's entry in the "International Exhibition of Modern Architecture" held at the Museum of Modern Art in New York City in 1932. Southend Pier is in the Guinness Book of Records as the longest pleasure pier in the world.

The church of St Peter-on-the-Wall, Bradwell-on-Sea

The Grade I listed Hedingham Castle, with the best preserved Norman keep in the UK
Thaxted Guildhall, dating from around 1450
The 17th century Audley End House, Saffron Walden

Royal Corinthian Yacht Club, Burnham-on-Crouch

Colchester Castle, Colchester

Hylands House, south of Writtle and south-west of Chelmsford

Southend Pier, Southend-on-Sea
Places of interest
Key | |
Abbey/Priory/Cathedral | |
| Accessible open space | |
Amusement/Theme Park | |
Castle | |
Country Park | |
English Heritage | |
Forestry Commission | |
Heritage railway | |
Historic House | |
Museum (free/not free) | |
National Trust | |
Theatre | |
Zoo | |

Skyline of Southend-on-Sea
- Abberton Reservoir
Ashdon (The site of the ancient Bartlow Hills and also a claimant as the location of the Battle of Ashingdon)
Ashingdon (The site of the Battle of Ashingdon in 1016), near Southend, with its isolated St Andrews Church and site of England's earliest aerodrome at South Fambridge
Audley End House and Gardens, Saffron Walden
Brentwood Cathedral
- Clacton-on-Sea
Chelmsford Cathedral
Colchester Castle
 [34]
[34]
Colchester Zoo
Colne Valley Railway
- Cressing Temple
East Anglian Railway Museum
- Epping Forest
Epping Ongar Railway
Finchingfield (home of the author Dodie Smith)- Frinton-on-Sea
Great Bentley, which has the largest village green in England[citation needed]
- Hadleigh Castle
- Harlow New Town
Hedingham Castle, between Stansted and Colchester, to the north of Braintree
Ingatestone Hall, Ingatestone, between Brentwood and Chelmsford- Kelvedon Hatch Secret Nuclear Bunker
- Lakeside Shopping Centre
Loughton, near Epping Forest
Maldon historic market town, close to Chelmsford and the North Sea, and site of the Battle of Maldon
Mangapps Railway Museum
 (Burnham-on-Crouch)
(Burnham-on-Crouch)
Marsh Farm Country Park (South Woodham Ferrers)
Mersea Island, birdwatching and rambling resort with one settlement, West Mersea
Mistley Towers, Manningtree, between Colchester and Ipswich, near Alton Water.
Mountfitchet Castle , Stansted
, Stansted- North Weald Airfield
Orsett Hall Hotel, Prince Charles Avenue, Orsett near Chadwell St Mary
St Peter-on-the-Wall
Saffron Walden

- Southend Pier
Thames Estuary
Tilbury Fort
Thaxted, south of Saffron Walden
- Thurrock Thameside Nature Park
University of Essex (Wivenhoe Park, Colchester and Loughton)
Waltham Abbey
Notable people
Sister counties and regions
 Jiangsu, China
Jiangsu, China
 Picardy, France
Picardy, France
 Thuringia, Germany
Thuringia, Germany
 Henrico County, Virginia, United States
Henrico County, Virginia, United States
 Accra, Ghana
Accra, Ghana
See also
- Essex girl
- The Earl of Essex
- List of Lord Lieutenants of Essex
- Healthcare in Essex
- List of High Sheriffs of Essex
Custos Rotulorum of Essex – Keepers of the Rolls- Historical list of MPs of Essex constituency
Q Camp: WWII camp in Essex- List of civil parishes in England
- The Only Way Is Essex
- List of Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Essex
- Essex Police
- Essex Police and Crime Commissioner
Notes and references
^ "No. 62229". The London Gazette. 15 March 2018. pp. 4814–4814..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Vision of Britain Archived 26 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine. – Essex ancient county boundaries map
^ The Free Dictionary Archived 16 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine. – definition
^ Raymond Grant (1991). The royal forests of England. Wolfeboro Falls, NH: Alan Sutton. ISBN 0-86299-781-X. 086299781X. Archived from the original on 1 March 2016. Retrieved 6 September 2015. see table, p224 for Essex Stanestreet and p221-229 for details of each forest
^ Vision of Britain Archived 14 August 2011 at the Wayback Machine. – Southend-on-Sea MB/CB
^ ab Vision of Britain Archived 26 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine. – Essex admin county (historic map Archived 30 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine.)
^ Essex County Council Archived 24 January 2008 at the Wayback Machine. – District or Borough Councils
^ OPSI Archived 4 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine. – The Essex (Boroughs of Colchester, Southend-on-Sea and Thurrock and District of Tendring) (Structural, Boundary and Electoral Changes) Order 1996
^ OPSI Archived 12 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine. – The Essex (Police Area and Authority) Order 1997
^ "Did you know deprivation in Chelmsford Diocese". Archived from the original on 8 March 2012. Retrieved 4 February 2016.
^ "Jackwich: Village 'third most deprived area in UK'". Archived from the original on 9 October 2011. Retrieved 4 February 2016.
^ "Britain's richest towns: 20 – 11". The Daily Telegraph. London. 18 April 2008. Archived from the original on 3 February 2014.
^ "Recap: EU referendum 2016 Essex reaction to historic Brexit vote". Essex Live. 23 June 2016. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
^ abc "Local government structure". www.essex.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 23 August 2016. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
^ "About us". www.young-essex-assembly.org.uk. Archived from the original on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
^ Warr, Mike. "Youth Council". www.eppingforestdc.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
^ R4U (14 December 2016). "Residents for Uttlesford [R4U] | R4U's Uttlesford Youth Council initiative gets green light". Residents for Uttlesford. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
^ "Youth Council | Harlow Council". www.harlow.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 11 February 2017. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
^ Cheap flights from London Stansted to Sharm El Sheikh Archived 27 June 2014 at the Wayback Machine.. easyJet.com (17 February 2013). Retrieved on 17 July 2013.
^ Topham, Gwyn (5 March 2012). "London Southend airport: flying under the radar (and to the left of the pier)". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 3 April 2015. Retrieved 5 March 2012.
^ "DFDS Harwich to Esbjerg ferry route's final journey - BBC News". Bbc.co.uk. Archived from the original on 30 November 2017. Retrieved 16 September 2017.
^ "London Gateway : Home". www.londongateway.com. Archived from the original on 13 June 2016. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ Portswatch: Current Port Proposals: London Gateway (Shell Haven) Archived 25 July 2008 at the Wayback Machine.. Retrieved 15 April 2009.
^ Thurrock Council. (26 February 2003). Shell Haven public inquiry opens Archived 15 September 2013 at the Wayback Machine.. Retrieved 15 April 2009.
^ Dredging News Online. (18 May 2008). Harbour Development, Shell Haven, UK Archived 3 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine.. Retrieved 15 April 2009.
^ "OS Maps - online and App mapping system | Ordnance Survey Shop". getamap.ordnancesurvey.co.uk. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ "National Rail Enquiries - Official source for UK train times and timetables". www.nationalrail.co.uk. Archived from the original on 25 February 2011. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ "FAQs". www.sert.org.uk. Archived from the original on 2 September 2009. Retrieved 18 June 2016.CS1 maint: Unfit url (link)
^ Essex County Council. (2006). Secondary School Information Archived 7 September 2008 at the Wayback Machine.. Retrieved 15 April 2009.
^ independent schools Directory. (2009). Independent Schools in Essex Archived 30 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine.. Retrieved 15 April 2009.
^ ab Robert Young. (2009). Civic Heraldry of England and Wales. Essex Archived 3 February 2007 at the Wayback Machine.. Retrieved 16 April 2009.
^ "Dunmow Flitch Trials - History - Background". www.dunmowflitchtrials.co.uk. Archived from the original on 9 June 2016. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ Bettley, James. (2008). Essex Explored: Essex Architecture. Essex County Council. Retrieved 15 April 2009.
^ "Colchester Castle Museum-Index". Colchestermuseums.org.uk. Archived from the original on 12 April 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Essex. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Essex (England). |
Essex at Curlie
- Essex County Council
- Seax – Essex Archives Online
Images of Essex at the English Heritage Archive









