Mechanism of action
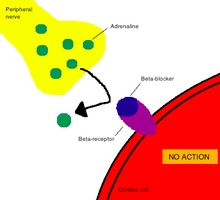
Mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect.[1] A mechanism of action usually includes mention of the specific molecular targets to which the drug binds, such as an enzyme or receptor.[2] Receptor sites have specific affinities for drugs based on the chemical structure of the drug, as well as the specific action that occurs there. Drugs that do not bind to receptors produce their corresponding therapeutic effect by simply interacting with chemical or physical properties in the body. Common examples of drugs that work in this way are antacids and laxatives.[1]
In comparison, a mode of action (MoA) describes functional or anatomical changes, at the cellular level, resulting from the exposure of a living organism to a substance.
Contents
1 Why mechanism of action is important
2 How mechanism of action is determined
2.1 Microscopy-based methods
2.2 Direct biochemical methods
2.3 Computation inference methods
3 Drugs with known mechanisms of action
3.1 Aspirin
4 Drugs with unknown mechanisms of action
5 Versus mode of action
6 See also
7 References
Why mechanism of action is important
Elucidating the mechanism of action of novel drugs and medications is important for several reasons:
- In the case of anti-infective drug development, the information permits anticipation of problems relating to clinical safety. Drugs disrupting the cytoplasmic membrane or electron transport chain, for example, are more likely to cause toxicity problems than those targeting components of the cell wall (peptidoglycan or β-glucans) or 70S ribosome, structures which are absent in human cells.[3][4]
- By knowing the interaction between a certain site of a drug and a receptor, other drugs can be formulated in a way that replicates this interaction, thus producing the same therapeutic effects. Indeed, this method is used to create new drugs.
- It can help identify which patients are most likely to respond to treatment. Because the breast cancer medication trastuzumab is known to target protein HER2, for example, tumors can be screened for the presence of this molecule to determine whether or not the patient will benefit from trastuzumab therapy.[5][6]
- It can enable better dosing because the drug's effects on the target pathway can be monitored in the patient. Statin dosage, for example, is usually determined by measuring the patient’s blood cholesterol levels.[5]
- It allows drugs to be combined in such a way that the likelihood of drug resistance emerging is reduced. By knowing what cellular structure an anti-infective or anticancer drug acts upon, it is possible to administer a cocktail that inhibits multiple targets simultaneously, thereby reducing the risk that a single mutation in microbial or tumor DNA will lead to drug resistance and treatment failure.[3][7][8][9]
- It may allow other indications for the drug to be identified. Discovery that sildenafil inhibits phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) proteins, for example, enabled this drug to be repurposed for pulmonary arterial hypertension treatment, since PDE-5 is expressed in pulmonary hypertensive lungs.[10][11]
How mechanism of action is determined
Microscopy-based methods
Bioactive compounds induce phenotypic changes in target cells, changes that are observable by microscopy, and which can give insight into the mechanism of action of the compound.[12] With antibacterial agents, for example, the conversion of target cells to spheroplasts can be an indication that peptidoglycan synthesis is being targeted, and filamentation of target cells can be an indication that FtsZ or DNA is being targeted.[3] In the case of anticancer agents, bleb formation can be an indication that the compound is disrupting the plasma membrane.[13] A current limitation of this approach is the time required to manually generate and interpret data, but advances in automated microscopy and image analysis software may help resolve this.[3][12]
Direct biochemical methods
Direct biochemical methods include methods in which a protein or a small molecule, such as a drug candidate, is labeled and is traced throughout the body.[14] This proves to be the most direct approach to find target protein that will bind to small targets of interest, such as a basic representation of a drug outline, in order to identify the pharmacophore of the drug. Due to the physical interactions between the labeled molecule and a protein, biochemical methods can be used to determine the toxicity, efficacy, and the mechanism of action of the drug.
Computation inference methods
Typically, computation inference methods are primarily used to predict protein targets for small molecule drugs based on computer based pattern recognition.[14] However, this method could also be used for finding new targets for existing or newly developed drugs. By identifying the pharmacophore of the drug molecule, the profiling method of pattern recognition can be carried out where a new target is identified.[14] This provides an insight at a possible mechanism of action, as it is known what certain functional components of the drug are responsible for interacting with a certain area on a protein, thus, leading to a therapeutic effect.
Drugs with known mechanisms of action
There are many drugs in which the mechanism of action is known. One example is aspirin.
Aspirin
The mechanism of action of aspirin involves irreversible inhibition of the enzyme cyclooxygenase;[15] therefore suppressing the production of prostaglandins and thromboxanes, thus reducing pain and inflammation. This mechanism of action is specific to aspirin, and is not constant for all nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Rather, aspirin is the only NSAID that irreversibly inhibits COX-1.[16]
Drugs with unknown mechanisms of action
Some drug mechanisms of action are still unknown. However, even though the mechanism of action of a certain drug is unknown, the drug still functions; it is just unknown or unclear how the drug interacts with receptors and produces its therapeutic effect.
- Acamprosate
- Antidepressants
- Armodafinil
- Cyclobenzaprine
- Demeclocycline
- Fabomotizole
- Lithium
- Meprobamate
- Methocarbamol
- Paracetamol
- Phenytoin
- PRL-8-53
- Metformin
- Thalidomide
Versus mode of action
In some literature articles, the term mechanism of action and mode of action (MoA) are used interchangeably; typically referring to the way in which the drug interacts and produces a medical effect. However, in actuality, a mode of action describes functional or anatomical changes, at the cellular level, resulting from the exposure of a living organism to a substance.[17] This differs from a mechanism of action, as it is a more specific term that focuses on the interaction between the drug itself and an enzyme or receptor and its particular form of interaction, whether through inhibition, activation, agonism, or antagonism. Furthermore, the term mechanism of action is the main term that is primarily used in pharmacology, whereas mode of action will more often appear in the field of microbiology or certain aspects of biology.
See also
- Mode of action (MoA)
- Pharmacodynamics
References
^ ab Spratto, G.R.; Woods, A.L. (2010). Delmar Nurse's Drug Handbook. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1-4390-5616-5.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link) .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Grant, R.L.; Combs, A.B.; Acosta, D. (2010) "Experimental Models for the Investigation of Toxicological Mechanisms". In McQueen, C.A. Comprehensive Toxicology (2nd ed.). Oxford: Elsevier. p. 204.
ISBN 978-0-08-046884-6.
^ abcd Cushnie, T.P.; O’Driscoll, N.H.; Lamb, A.J. (2016). "Morphological and ultrastructural changes in bacterial cells as an indicator of antibacterial mechanism of action". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 73 (23): 4471–4492. doi:10.1007/s00018-016-2302-2. PMID 27392605.
^ Chang, C.C.; Slavin, M.A.; Chen, S.C. (2017). "New developments and directions in the clinical application of the echinocandins". Archives of Toxicology. 91: 1613–1621. doi:10.1007/s00204-016-1916-3. PMID 28180946.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ ab No authors listed (2010). "Mechanism matters". Nature Medicine. 16 (4): 347. doi:10.1038/nm0410-347. PMID 20376007.
^ Joensuu, H. (2017). "Escalating and de-escalating treatment in HER2-positive early breast cancer". Cancer Treatment Reviews. 52: 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.11.002. PMID 27866067.
^ Cihlar, T.; Fordyce, M. (2016). "Current status and prospects of HIV treatment". Current Opinion in Virology. 18: 50–56. doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2016.03.004. PMID 27023283.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Antony, H.A.; Parija, S.C. (2016). "Antimalarial drug resistance: An overview". Tropical Parasitology. 6 (1): 30–41. doi:10.4103/2229-5070.175081. PMC 4778180. PMID 26998432.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Bozic, I.; Reiter, J.G.; Allen, B.; Antal, T.; Chatterjee, K.; Shah, P.; Moon, Y.S.; Yaqubie, A.; Kelly, N.; Le, D.T.; Lipson, E.J.; Chapman, P.B.; Diaz, L.A.; Vogelstein, B., Nowak, M.A. (2013). "Evolutionary dynamics of cancer in response to targeted combination therapy". eLIFE. 2: Article ID e00747. doi:10.7554/eLife.00747. PMC 3691570. PMID 23805382.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Tari, L.; Vo, N.; Liang, S.; Patel, J.; Baral, C.; Cai, J. (2012). "Identifying novel drug indications through automated reasoning". PLOS ONE. 7 (7): Article e40946. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040946. PMC 3402456. PMID 22911721.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Hayardeny, L. (2014). Why is it important to know the mode of action of drugs? (Conference presentation). New Frontiers in Neuroscience and Methods of Transdisciplinary Education Workshop, Tel Aviv University, Israel: Tel Aviv University. Retrieved 18 March 2017.
^ ab Fetz, V.; Prochnow, H.; Brönstrup, M.; Sasse, F. (2016). "Target identification by image analysis". Natural Product Reports. 33 (5): 655–667. doi:10.1039/c5np00113g. PMID 26777141.
^ Dubovskii, P.V.; Vassilevski, A.A.; Kozlov, S.A.; Feofanov, A.V.; Grishin, E.V.; Efremov, R.G. (2015). "Latarcins: versatile spider venom peptides". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 72 (23): 4501–4522. doi:10.1007/s00018-015-2016-x. PMID 26286896.
^ abc Schenone, M.; Dančík, V.; Wagner, B.K.; Clemons, P.A. (2013). "Target identification and mechanism of action in chemical biology and drug discovery". Nature Chemical Biology. 9 (4): 232–240. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1199. ISSN 1552-4450.
^ Tóth, L.; Muszbek, L.;Komaromi, I. (2013). "Mechanism of the irreversible inhibition of human cyclooxygenase-1 by aspirin as predicted by QM/MM calculations". Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling. 40: 99–109. doi:10.1016/j.jmgm.2012.12.013. PMID 23384979.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Sharma, S.; Sharma, S. C. (1997). "An update on eicosanoids and inhibitors of cyclooxygenase enzyme systems". Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 35 (10): 1025–1031. ISSN 0019-5189. PMID 9475035.
^ "Mechanisms and mode of dioxin action" (PDF). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved 11 June 2012.