Normans

Victorian interpretation of the Normans' national dress, 1000–1100
| Part of a series on the |
| Norse people |
|---|
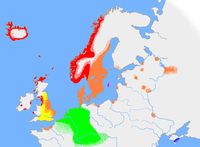 Extension of Norse language in 900 A.D.: Western Norse in red and Eastern Norse in orange. |
|
History
|
Mythology
|
Cosmology
|
Rituals and worship
|
Society
|
Events
|
Sources
|
WikiProject Norse history and culture |
The Normans (Norman: Normaunds; French: Normands) are an ethnic group that arose in Normandy, a northern region of France, from contact between indigenous Franks and Gallo-Romans, and Norse Viking settlers.[1] The settlements followed a series of raids on the French coast from Denmark, Norway, and Iceland, and they gained political legitimacy when the Viking leader Rollo agreed to swear fealty to King Charles III of West Francia.[2] The distinct cultural and ethnic identity of the Normans emerged initially in the first half of the 10th century, and it continued to evolve over the succeeding centuries.[3]
The Norman dynasty had a major political, cultural and military impact on medieval Europe and the Near East.[4][5] The Normans were famed for their martial spirit and eventually for their Catholic piety, becoming exponents of the Catholic orthodoxy of the Romance community into which they assimilated.[2] They adopted the Gallo-Romance language of the Frankish land they settled, their dialect becoming known as Norman, Normaund or Norman French, an important literary language which is still spoken today in parts of Normandy and the nearby Channel Islands. The Duchy of Normandy, which they formed by treaty with the French crown, was a great fief of medieval France, and under Richard I of Normandy was forged into a cohesive and formidable principality in feudal tenure.[6][7]
The Normans are noted both for their culture, such as their unique Romanesque architecture and musical traditions, and for their significant military accomplishments and innovations. Norman adventurers played a role in founding the Kingdom of Sicily under Roger II after briefly conquering southern Italy and Malta from the Saracens and Byzantines, during an expedition on behalf of their duke, William the Conqueror, which also led to the Norman conquest of England at the historic Battle of Hastings in 1066.[8] In the ninth century, the Normans captured Seville in Southern Spain,[9] and Norman and Anglo-Norman forces contributed to the Iberian Reconquista from the early eleventh to the mid-thirteenth centuries.[10]
Norman cultural and military influence spread from these new European centres to the Crusader states of the Near East, where their prince Bohemond I founded the Principality of Antioch in the Levant, to Scotland and Wales in Great Britain, to Ireland, and to the coasts of north Africa and the Canary Islands. The legacy of the Normans persists today through the regional languages and dialects of France, England, Spain, and Sicily, as well as the various cultural, judicial, and political arrangements they introduced in their conquered territories.[5][11]
Contents
1 Etymology
2 Settling of Normandy
3 Conquests and military offensives
3.1 Italy
3.2 Byzantium
3.3 England
3.4 Ireland
3.5 Scotland
3.6 Wales
3.7 On crusade
3.8 Anglo-Norman conquest of Cyprus
3.9 Canary Islands
4 Culture
4.1 Norman law
4.2 Architecture
4.3 Visual arts
4.4 Music
5 Rulers
6 See also
7 References
8 Sources
8.1 Primary
8.2 Secondary
9 Further reading
10 External links
Etymology
The English name "Normans" comes from the French words Normans/Normanz, plural of Normant,[12] modern French normand, which is itself borrowed from Old Low Franconian Nortmann "Northman"[13] or directly from Old Norse Norðmaðr, Latinized variously as Nortmannus, Normannus, or Nordmannus (recorded in Medieval Latin, 9th century) to mean "Norseman, Viking".[14]
The 11th century Benedictine monk and historian, Goffredo Malaterra, characterised the Normans thus:
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
Specially marked by cunning, despising their own inheritance in the hope of winning a greater, eager after both gain and dominion, given to imitation of all kinds, holding a certain mean between lavishness and greediness, that is, perhaps uniting, as they certainly did, these two seemingly opposite qualities. Their chief men were specially lavish through their desire of good report. They were, moreover, a race skillful in flattery, given to the study of eloquence, so that the very boys were orators, a race altogether unbridled unless held firmly down by the yoke of justice. They were enduring of toil, hunger, and cold whenever fortune laid it on them, given to hunting and hawking, delighting in the pleasure of horses, and of all the weapons and garb of war.[15]
Settling of Normandy

Duchy of Normandy between 911 and 1050. In blue the areas of intense Norse settlement
In the course of the 10th century, the initially destructive incursions of Norse war bands going upstream into the rivers of France penetrated further into interior Europe, and evolved into more permanent encampments that included local French women and personal property.[16] The Duchy of Normandy, which began in 911 as a fiefdom, was established by the treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte between King Charles III (Charles the Simple) (879–929, ruled 893–929) of West Francia and the famed Viking ruler Rollo also known as Gaange Rolf (c. 846-c. 929), from Scandinavia, and was situated in the former Frankish kingdom of Neustria.[17] The treaty offered Rollo and his men the French coastal lands along the English Channel between the river Epte and the Atlantic Ocean coast in exchange for their protection against further Viking incursions.[17] As well as granting to protect the area of Rouen from Viking invasion, Rollo had to swear not to invade further Frankish lands himself, accept baptism and conversion to the Roman Catholic faith of Christianity becoming Christian and swear fealty to King Charles III. He became the first Duke of Normandy and Count of Rouen. [18]The area corresponded to the northern part of present-day Upper Normandy down to the river Seine, but the Duchy would eventually extend west beyond the Seine.[2] The territory was roughly equivalent to the old province of Rouen, and reproduced the old Roman Empire's administrative structure of Gallia Lugdunensis II (part of the former Gallia Lugdunensis in Gaul).

10th–11th century History of the Normans, by Dudo of Saint-Quentin
Before Rollo's arrival, Normandy's populations did not differ from Picardy or the Île-de-France, which were considered "Frankish". Earlier Viking settlers had begun arriving in the 880s, but were divided between colonies in the east (Roumois and Pays de Caux) around the low Seine valley and in the west in the Cotentin Peninsula, and were separated by traditional pagii, where the population remained about the same with almost no foreign settlers. Rollo's contingents from Scandinavia who raided and ultimately settled Normandy and parts of the European Atlantic coast included Danes, Norwegians, Norse–Gaels, Orkney Vikings, possibly Swedes, and Anglo-Danes from the English Danelaw territory which earlier came under Norse control in the early 11th century.
The descendants of Rollo's Vikings and their Frankish wives would replace the Norse religion and Old Norse language with Roman Catholicism (Christianity) and the Gallo-Romance language of the local people, descending from the Latin of the Romans, blending their maternal Frankish heritage with Old Norse traditions and customs to synthesize a unique "Norman" culture in the north of France.[6] The Norman language was forged by the adoption of the indigenous langue d'oïl branch of Romance by a Norse-speaking ruling class, and it developed into the French regional languages that survives today.[2]
The Normans thereafter adopted the growing feudal doctrines of the rest of France, and worked them into a functional hierarchical system in both Normandy and in Norman dominated England.[6] The new Norman rulers were culturally and ethnically distinct from the old French aristocracy, most of whom traced their lineage to the Franks of the Carolingian dynasty from the days of Charlemagne in the 9th century. Most Norman knights remained poor and land-hungry, and by the time of the expedition and invasion of England in 1066, Normandy had been exporting fighting horsemen for more than a generation. Many Normans of Italy, France and England eventually served as avid Crusaders soldiers under the Italo-Norman prince Bohemund I of Antioch and the Anglo-Norman king Richard the Lion-Heart, one of the more famous and illustrious Kings of England.
Conquests and military offensives
Italy

The early Norman castle at Adrano
Opportunistic bands of Normans successfully established a foothold in southern Italy. Probably as the result of returning pilgrims' stories, the Normans entered southern Italy as warriors in 1017 at the latest. In 999, according to Amatus of Montecassino, Norman pilgrims returning from Jerusalem called in at the port of Salerno when a Saracen attack occurred. The Normans fought so valiantly that Prince Guaimar III begged them to stay, but they refused and instead offered to tell others back home of the Prince's request. William of Apulia tells that, in 1016, Norman pilgrims to the shrine of the Archangel Michael at Monte Gargano were met by Melus of Bari, a Lombard nobleman and rebel, who persuaded them to return with more warriors to help throw off the Byzantine rule, which they did.
The two most prominent Norman families to arrive in the Mediterranean were descendants of Tancred of Hauteville and the Drengot family.
A group of Normans with at least five brothers from the Drengot family fought the Byzantines in Apulia under the command of Melo di Bari. Between 1016 and 1024, in a fragmented political context, the County of Ariano was founded by another group of Norman knights headed by Gilbert Buatère and hired by Melo di Bari. Defeated at Canne, Melo di Bari escaped to Bamberg, Germany, where he died in 1022. The County, which replaced the pre-existing chamberlainship, was considered to be the first political body established by the Normans in the South of Italy[19].
Then Rainulf Drengot, from the same family, received the county of Aversa from Duke Sergius IV of Naples in 1030.
The Hauteville family achieved princely rank by proclaiming Prince Guaimar IV of Salerno "Duke of Apulia and Calabria". He promptly awarded their elected leader, William Iron Arm, with the title of count in his capital of Melfi. The Drengot family thereafter attained the principality of Capua, and Emperor Henry III legally ennobled the Hauteville leader, Drogo, as "dux et magister Italiae comesque Normannorum totius Apuliae et Calabriae" ("Duke and Master of Italy and Count of the Normans of all Apulia and Calabria") in 1047.[citation needed]
From these bases, the Normans eventually captured Sicily and Malta from the Saracens, under the leadership of the famous Robert Guiscard, a Hauteville, and his younger brother Roger the Great Count. Roger's son, Roger II of Sicily, was crowned king in 1130 (exactly one century after Rainulf was "crowned" count) by Antipope Anacletus II. The Kingdom of Sicily lasted until 1194, when it was transferred to the House of Hohenstaufen through marriage.[20] The Normans left their legacy in many castles, such as William Iron Arm's citadel at Squillace, and cathedrals, such as Roger II's Cappella Palatina at Palermo, which dot the landscape and give a distinct architectural flavor to accompany its unique history.
Institutionally, the Normans combined the administrative machinery of the Byzantines, Arabs, and Lombards with their own conceptions of feudal law and order to forge a unique government. Under this state, there was great religious freedom, and alongside the Norman nobles existed a meritocratic bureaucracy of Jews, Muslims and Christians, both Catholic and Eastern Orthodox. The Kingdom of Sicily thus became characterized by Norman, Byzantine, Greek, Arab, Lombard and "native" Sicilian populations living in harmony, and its Norman rulers fostered plans of establishing an empire that would have encompassed Fatimid Egypt as well as the crusader states in the Levant.[21][22][23] One of the great geographical treatises of the Middle Ages, the "Tabula Rogeriana", was written by the Andalusian al-Idrisi for King Roger II of Sicily, and entitled "Kitab Rudjdjar" ("The Book of Roger").[24]
Byzantium
This section provides insufficient context for those unfamiliar with the subject. (December 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Soon after the Normans began to enter Italy, they entered the Byzantine Empire and then Armenia, fighting against the Pechenegs, the Bulgars, and especially the Seljuk Turks. Norman mercenaries were first encouraged to come to the south by the Lombards to act against the Byzantines, but they soon fought in Byzantine service in Sicily. They were prominent alongside Varangian and Lombard contingents in the Sicilian campaign of George Maniaces in 1038–40. There is debate whether the Normans in Greek service actually were from Norman Italy, and it now seems likely only a few came from there. It is also unknown how many of the "Franks", as the Byzantines called them, were Normans and not other Frenchmen.

Norman expansion by 1130
One of the first Norman mercenaries to serve as a Byzantine general was Hervé in the 1050s. By then, however, there were already Norman mercenaries serving as far away as Trebizond and Georgia. They were based at Malatya and Edessa, under the Byzantine duke of Antioch, Isaac Komnenos. In the 1060s, Robert Crispin led the Normans of Edessa against the Turks. Roussel de Bailleul even tried to carve out an independent state in Asia Minor with support from the local population, but he was stopped by the Byzantine general Alexius Komnenos.
Some Normans joined Turkish forces to aid in the destruction of the Armenian vassal-states of Sassoun and Taron in far eastern Anatolia. Later, many took up service with the Armenian state further south in Cilicia and the Taurus Mountains. A Norman named Oursel led a force of "Franks" into the upper Euphrates valley in northern Syria. From 1073 to 1074, 8,000 of the 20,000 troops of the Armenian general Philaretus Brachamius were Normans—formerly of Oursel—led by Raimbaud. They even lent their ethnicity to the name of their castle: Afranji, meaning "Franks". The known trade between Amalfi and Antioch and between Bari and Tarsus may be related to the presence of Italo-Normans in those cities while Amalfi and Bari were under Norman rule in Italy.
Several families of Byzantine Greece were of Norman mercenary origin during the period of the Comnenian Restoration, when Byzantine emperors were seeking out western European warriors. The Raoulii were descended from an Italo-Norman named Raoul, the Petraliphae were descended from a Pierre d'Aulps, and that group of Albanian clans known as the Maniakates were descended from Normans who served under George Maniaces in the Sicilian expedition of 1038.
Robert Guiscard, another Norman adventurer previously elevated to the dignity of count of Apulia as the result of his military successes, ultimately drove the Byzantines out of southern Italy. Having obtained the consent of Pope Gregory VII and acting as his vassal, Robert continued his campaign conquering the Balkan peninsula as a foothold for western feudal lords and the Catholic Church. After allying himself with Croatia and the Catholic cities of Dalmatia, in 1081 he led an army of 30,000 men in 300 ships landing on the southern shores of Albania, capturing Valona, Kanina, Jericho (Orikumi), and reaching Butrint after numerous pillages. They joined the fleet that had previously conquered Corfu and attacked Dyrrachium from land and sea, devastating everything along the way. Under these harsh circumstances, the locals accepted the call of Emperor Alexius I Comnenus to join forces with the Byzantines against the Normans. The Albanian forces could not take part in the ensuing battle because it had started before their arrival. Immediately before the battle, the Venetian fleet had secured a victory in the coast surrounding the city. Forced to retreat, Alexius ceded the city of Dyrrachium to the Count of the Tent (or Byzantine provincial administrators) mobilizing from Arbanon (i.e., ἐξ Ἀρβάνων ὁρμωμένω Κομισκόρτη; the term Κομισκόρτη is short for κόμης της κόρτης meaning "Count of the Tent").[25] The city's garrison resisted until February 1082, when Dyrrachium was betrayed to the Normans by the Venetian and Amalfitan merchants who had settled there. The Normans were now free to penetrate into the hinterland; they took Ioannina and some minor cities in southwestern Macedonia and Thessaly before appearing at the gates of Thessalonica. Dissension among the high ranks coerced the Normans to retreat to Italy. They lost Dyrrachium, Valona, and Butrint in 1085, after the death of Robert.
A few years after the First Crusade, in 1107, the Normans under the command of Bohemond, Robert's son, landed in Valona and besieged Dyrrachium using the most sophisticated military equipment of the time, but to no avail. Meanwhile, they occupied Petrela, the citadel of Mili at the banks of the river Deabolis, Gllavenica (Ballsh), Kanina and Jericho. This time, the Albanians sided with the Normans, dissatisfied by the heavy taxes the Byzantines had imposed upon them. With their help, the Normans secured the Arbanon passes and opened their way to Dibra. The lack of supplies, disease and Byzantine resistance forced Bohemond to retreat from his campaign and sign a peace treaty with the Byzantines in the city of Deabolis.
The further decline of Byzantine state-of-affairs paved the road to a third attack in 1185, when a large Norman army invaded Dyrrachium, owing to the betrayal of high Byzantine officials. Some time later, Dyrrachium—one of the most important naval bases of the Adriatic—fell again to Byzantine hands.
England
| House of Normandy |
|---|
 William the Conqueror invades England |
William I
|
William II |
Henry I
|
Stephen
|
Monarchy of the United Kingdom |
The Normans were in contact with England from an early date. Not only were their original Viking brethren still ravaging the English coasts, they occupied most of the important ports opposite England across the English Channel. This relationship eventually produced closer ties of blood through the marriage of Emma, sister of Duke Richard II of Normandy, and King Ethelred II of England. Because of this, Ethelred fled to Normandy in 1013, when he was forced from his kingdom by Sweyn Forkbeard. His stay in Normandy (until 1016) influenced him and his sons by Emma, who stayed in Normandy after Cnut the Great's conquest of the isle.
When Edward the Confessor finally returned from his father's refuge in 1041, at the invitation of his half-brother Harthacnut, he brought with him a Norman-educated mind. He also brought many Norman counsellors and fighters, some of whom established an English cavalry force. This concept never really took root, but it is a typical example of Edward's attitude. He appointed Robert of Jumièges archbishop of Canterbury and made Ralph the Timid earl of Hereford. He invited his brother-in-law Eustace II, Count of Boulogne to his court in 1051, an event that resulted in the greatest of early conflicts between Saxon and Norman and ultimately resulted in the exile of Earl Godwin of Wessex.

Siege of a motte-and-bailey castle from the Bayeux Tapestry
On 14 October 1066, William the Conqueror gained a decisive victory at the Battle of Hastings, which led to the conquest of England three years later;[26] this can be seen on the Bayeux tapestry (a linen, embroidered cloth). The invading Normans and their descendants replaced the Anglo-Saxons as the ruling class of England. The nobility of England were part of a single Norman culture and many had lands on both sides of the channel. Early Norman kings of England, as Dukes of Normandy, owed homage to the King of France for their land on the continent. They considered England to be their most important holding (it brought with it the title of King—an important status symbol).
Eventually, the Normans merged with the natives, combining languages and traditions, so much so that Marjorie Chibnall says "writers still referred to Normans and English; but the terms no longer meant the same as in the immediate aftermath of 1066."[27] In the course of the Hundred Years' War, the Norman aristocracy often identified themselves as English. The Anglo-Norman language became distinct from the Latin language, something that was the subject of some humour by Geoffrey Chaucer. The Anglo-Norman language was eventually absorbed into the Anglo-Saxon language of their subjects (see Old English) and influenced it, helping (along with the Norse language of the earlier Anglo-Norse settlers and the Latin used by the church) in the development of Middle English. It in turn evolved into Modern English.
Ireland

Norman keep in Trim, County Meath
The Normans had a profound effect on Irish culture and history after their invasion at Bannow Bay in 1169. Initially, the Normans maintained a distinct culture and ethnicity. Yet, with time, they came to be subsumed into Irish culture to the point that it has been said that they became "more Irish than the Irish themselves". The Normans settled mostly in an area in the east of Ireland, later known as the Pale, and also built many fine castles and settlements, including Trim Castle and Dublin Castle. Both cultures intermixed, borrowing from each other's language, culture and outlook. Norman descendants today can be recognised by their surnames. Names such as French, (De) Roche, Devereux, D'Arcy, Treacy and Lacy are particularly common in the southeast of Ireland, especially in the southern part of County Wexford, where the first Norman settlements were established. Other Norman names, such as Furlong, predominate there. Another common Norman-Irish name was Morell (Murrell), derived from the French Norman name Morel. Names beginning with Fitz (from the Norman for son) indicate Norman ancestry. These included Fitzgerald, FitzGibbons (Gibbons) dynasty, Fitzmaurice. Families bearing such surnames as Barry (de Barra) and De Búrca (Burke) are also of Norman extraction.
Scotland
One of the claimants of the English throne opposing William the Conqueror, Edgar Atheling, eventually fled to Scotland. King Malcolm III of Scotland married Edgar's sister Margaret, and came into opposition to William who had already disputed Scotland's southern borders. William invaded Scotland in 1072, riding as far as Abernethy where he met up with his fleet of ships. Malcolm submitted, paid homage to William and surrendered his son Duncan as a hostage, beginning a series of arguments as to whether the Scottish Crown owed allegiance to the King of England.
Normans went into Scotland, building castles and founding noble families that would provide some future kings, such as Robert the Bruce, as well as founding a considerable number of the Scottish clans. King David I of Scotland, whose elder brother Alexander I had married Sybilla of Normandy, was instrumental in introducing Normans and Norman culture to Scotland, part of the process some scholars call the "Davidian Revolution". Having spent time at the court of Henry I of England (married to David's sister Maud of Scotland), and needing them to wrestle the kingdom from his half-brother Máel Coluim mac Alaxandair, David had to reward many with lands. The process was continued under David's successors, most intensely of all under William the Lion. The Norman-derived feudal system was applied in varying degrees to most of Scotland. Scottish families of the names Bruce, Gray, Ramsay, Fraser, Rose, Ogilvie, Montgomery, Sinclair, Pollock, Burnard, Douglas and Gordon to name but a few, and including the later royal House of Stewart, can all be traced back to Norman ancestry.
Wales

Chepstow Castle in Wales, built by William fitzOsbern in 1067
Even before the Norman Conquest of England, the Normans had come into contact with Wales. Edward the Confessor had set up the aforementioned Ralph as earl of Hereford and charged him with defending the Marches and warring with the Welsh. In these original ventures, the Normans failed to make any headway into Wales.
Subsequent to the Conquest, however, the Marches came completely under the dominance of William's most trusted Norman barons, including Bernard de Neufmarché, Roger of Montgomery in Shropshire and Hugh Lupus in Cheshire. These Normans began a long period of slow conquest during which almost all of Wales was at some point subject to Norman interference. Norman words, such as baron (barwn), first entered Welsh at that time.
On crusade
The legendary religious zeal of the Normans was exercised in religious wars long before the First Crusade carved out a Norman principality in Antioch. They were major foreign participants in the Reconquista in Iberia. In 1018, Roger de Tosny travelled to the Iberian Peninsula to carve out a state for himself from Moorish lands, but failed. In 1064, during the War of Barbastro, William of Montreuil led the papal army and took a huge booty.
In 1096, Crusaders passing by the siege of Amalfi were joined by Bohemond of Taranto and his nephew Tancred with an army of Italo-Normans. Bohemond was the de facto leader of the Crusade during its passage through Asia Minor. After the successful Siege of Antioch in 1097, Bohemond began carving out an independent principality around that city. Tancred was instrumental in the conquest of Jerusalem and he worked for the expansion of the Crusader kingdom in Transjordan and the region of Galilee.[citation needed]
Anglo-Norman conquest of Cyprus

Illuminated manuscript showing king Richard the Lion-hearted authorizing Guy de Lusignan to take Cyprus
The conquest of Cyprus by the Anglo-Norman forces of the Third Crusade opened a new chapter in the history of the island, which would be under Western European domination for the following 380 years. Although not part of a planned operation, the conquest had much more permanent results than initially expected.
In April 1191, Richard the Lion-hearted left Messina with a large fleet in order to reach Acre.[28] But a storm dispersed the fleet. After some searching, it was discovered that the boat carrying his sister and his fiancée Berengaria was anchored on the south coast of Cyprus, together with the wrecks of several other ships, including the treasure ship. Survivors of the wrecks had been taken prisoner by the island's despot Isaac Komnenos.[29] On 1 May 1191, Richard's fleet arrived in the port of Limassol on Cyprus.[29] He ordered Isaac to release the prisoners and the treasure.[29] Isaac refused, so Richard landed his troops and took Limassol.[30]

Castle of Limassol, near which Richard's wedding with Berengaria of Navarre is said to have taken place
Various princes of the Holy Land arrived in Limassol at the same time, in particular Guy de Lusignan. All declared their support for Richard provided that he support Guy against his rival Conrad of Montferrat.[31] The local barons abandoned Isaac, who considered making peace with Richard, joining him on the crusade, and offering his daughter in marriage to the person named by Richard.[32] But Isaac changed his mind and tried to escape. Richard then proceeded to conquer the whole island, his troops being led by Guy de Lusignan. Isaac surrendered and was confined with silver chains, because Richard had promised that he would not place him in irons. By 1 June, Richard had conquered the whole island. His exploit was well publicized and contributed to his reputation; he also derived significant financial gains from the conquest of the island.[33] Richard left for Acre on 5 June, with his allies.[33] Before his departure, he named two of his Norman generals, Richard de Camville and Robert de Thornham, as governors of Cyprus.
While in Limassol, Richard the Lion-Heart married Berengaria of Navarre, first-born daughter of King Sancho VI of Navarre. The wedding was held on 12 May 1191 at the Chapel of St. George and it was attended by Richard's sister Joan, whom he had brought from Sicily. The marriage was celebrated with great pomp and splendor. Among other grand ceremonies was a double coronation: Richard caused himself to be crowned King of Cyprus, and Berengaria Queen of England and Queen of Cyprus as well.

Norman expeditionary ship depicted in the chronicle Le Canarien (1490)
The rapid Anglo-Norman conquest proved more important than it seemed. The island occupied a key strategic position on the maritime lanes to the Holy Land, whose occupation by the Christians could not continue without support from the sea.[34] Shortly after the conquest, Cyprus was sold to the Knights Templar and it was subsequently acquired, in 1192, by Guy de Lusignan and became a stable feudal kingdom.[34] It was only in 1489 that the Venetians acquired full control of the island, which remained a Christian stronghold until the fall of Famagusta in 1571.[33]
Canary Islands
Between 1402 and 1405, the expedition led by the Norman noble Jean de Bethencourt[35] and the Poitevine Gadifer de la Salle conquered the Canarian islands of Lanzarote, Fuerteventura and El Hierro off the Atlantic coast of Africa. Their troops were gathered in Normandy, Gascony and were later reinforced by Castilian colonists.
Bethencourt took the title of King of the Canary Islands, as vassal to Henry III of Castile. In 1418, Jean's nephew Maciot de Bethencourt sold the rights to the islands to Enrique Pérez de Guzmán, 2nd Count de Niebla.
Culture
Norman law
The customary law of Normandy was developed between the 10th and 13th centuries and survives today through the legal systems of Jersey and Guernsey in the Channel Islands. Norman customary law was transcribed in two customaries in Latin by two judges for use by them and their colleagues:[36] These are the Très ancien coutumier (Very ancient customary), authored between 1200 and 1245; and the Grand coutumier de Normandie (Great customary of Normandy, originally Summa de legibus Normanniae in curia laïcali), authored between 1235 and 1245.
Architecture

A quintessential Norman keep: the White Tower in London
Norman architecture typically stands out as a new stage in the architectural history of the regions they subdued. They spread a unique Romanesque idiom to England, Italy and Ireland, and the encastellation of these regions with keeps in their north French style fundamentally altered the military landscape. Their style was characterised by rounded arches, particularly over windows and doorways, and massive proportions.
In England, the period of Norman architecture immediately succeeds that of the Anglo-Saxon and precedes the Early Gothic. In southern Italy, the Normans incorporated elements of Islamic, Lombard, and Byzantine building techniques into their own, initiating a unique style known as Norman-Arab architecture within the Kingdom of Sicily.[3]
Visual arts
In the visual arts, the Normans did not have the rich and distinctive traditions of the cultures they conquered. However, in the early 11th century the dukes began a programme of church reform, encouraging the Cluniac reform of monasteries and patronising intellectual pursuits, especially the proliferation of scriptoria and the reconstitution of a compilation of lost illuminated manuscripts. The church was utilised by the dukes as a unifying force for their disparate duchy. The chief monasteries taking part in this "renaissance" of Norman art and scholarship were Mont-Saint-Michel, Fécamp, Jumièges, Bec, Saint-Ouen, Saint-Evroul, and Saint-Wandrille. These centres were in contact with the so-called "Winchester school", which channeled a pure Carolingian artistic tradition to Normandy. In the final decade of the 11th and first of the 12th century, Normandy experienced a golden age of illustrated manuscripts, but it was brief and the major scriptoria of Normandy ceased to function after the midpoint of the century.

A bronze lion sculpture attributed to an Italo-Norman artist. Now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art
The French Wars of Religion in the 16th century and the French Revolution in the 18th successively destroyed much of what existed in the way of the architectural and artistic remnant of this Norman creativity. The former, with their violence, caused the wanton destruction of many Norman edifices; the latter, with its assault on religion, caused the purposeful destruction of religious objects of any type, and its destabilisation of society resulted in rampant pillaging.
By far the most famous work of Norman art is the Bayeux Tapestry, which is not a tapestry but a work of embroidery. It was commissioned by Odo, the Bishop of Bayeux and first Earl of Kent, employing natives from Kent who were learned in the Nordic traditions imported in the previous half century by the Danish Vikings.
In Britain, Norman art primarily survives as stonework or metalwork, such as capitals and baptismal fonts. In southern Italy, however, Norman artwork survives plentifully in forms strongly influenced by its Greek, Lombard, and Arab forebears. Of the royal regalia preserved in Palermo, the crown is Byzantine in style and the coronation cloak is of Arab craftsmanship with Arabic inscriptions. Many churches preserve sculptured fonts, capitals, and more importantly mosaics, which were common in Norman Italy and drew heavily on the Greek heritage. Lombard Salerno was a centre of ivorywork in the 11th century and this continued under Norman domination. The intercourse between French Crusaders traveling to the Holy Land who brought with them French artefacts with which to gift the churches at which they stopped in southern Italy amongst their Norman cousins. For this reason many south Italian churches preserve works from France alongside their native pieces.
Music

An illuminated manuscript from Saint-Evroul depicting King David on the lyre (or harp) in the middle of the back of the initial 'B'
Normandy was the site of several important developments in the history of classical music in the 11th century. Fécamp Abbey and Saint-Evroul Abbey were centres of musical production and education. At Fécamp, under two Italian abbots, William of Volpiano and John of Ravenna, the system of denoting notes by letters was developed and taught. It is still the most common form of pitch representation in English- and German-speaking countries today. Also at Fécamp, the staff, around which neumes were oriented, was first developed and taught in the 11th century. Under the German abbot Isembard, La Trinité-du-Mont became a centre of musical composition.
At Saint Evroul, a tradition of singing had developed and the choir achieved fame in Normandy. Under the Norman abbot Robert de Grantmesnil, several monks of Saint-Evroul fled to southern Italy, where they were patronised by Robert Guiscard and established a Latin monastery at Sant'Eufemia. There they continued the tradition of singing.
Rulers
- List of Dukes of Normandy
- List of Counts and Dukes of Apulia and Calabria
- List of Counts of Aversa
- List of Princes of Capua
- List of Dukes of Gaeta
- List of Princes of Taranto
- List of monarchs of Sicily
- List of Princes of Antioch
- List of Officers of the Principality of Antioch
- Second House of Lusignan
- List of English Monarchs
- List of Scottish Monarchs
See also
- Norman language
Kingdom of Africa – Italo-Norman garrisons in northern Africa in the 12th century- Norsemen
- Rus' people
References
^ Chibnall 1999, p. 2: "In Normandy the conquering northmen had assimilated...the indigenous Frankish and Gallo-Roman peoples..."
^ abcd "Norman". Encyclopædia Britannica..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab "Sicilian Peoples: The Normans". L. Mendola & V. Salerno. Best of Sicily Magazine. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
^ "Norman Centuries – A Norman History Podcast by Lars Brownworth". normancenturies.com. Retrieved 20 May 2018.
^ ab "The Norman Impact". History Today Volume 36 Issue 2. History Today. 2 February 1986. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
^ abc Eleanor Searle, Predatory Kinship and the Creation of Norman Power, 840–1066 (University of California Press, Berkeley, 1988), p. 89
^ François Neveux. A Brief History of The Normans (Constable & Robbinson, Ltd, London, 2008), pp. 73. 74
^ "Claims to the Throne". Mike Ibeji. BBC. 17 February 2011. Retrieved 26 August 2015.
^ Ford, Richard; (Firm), John Murray (20 May 2018). "A Hand-book for Travellers in Spain: And Readers at Home : Describing the Country and Cities, the Natives and Their Manners, the Antiquities, Religion, Legends, Fine Arts, Literature, Sports, and Gastronomy : with Notices on Spanish History". J. Murray. Retrieved 20 May 2018 – via Google Books.
^ "Norman and Anglo-Norman Participation in the Iberian Reconquista c.1018 – c.1248 - Medievalists.net". Medievalists.net. 24 September 2008. Retrieved 20 May 2018.
^ "What Did the Normans Do for Us?". John Hudson. BBC. 12 February 2012. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
^ Hoad, TF (1993). English Etymology (paperback)|format=requires|url=(help). Oxford University Press. p. 315.
^ Dauzat, Dubois & Mitterand 1971, p. 497.
^ "Etymologie de Normand" (in French). Centre National de Ressources Textuelles et Lexicales.
^ Gunn 1975.
^ Bates Normandy Before 1066 pp. 20–21
^ ab Neveux, François (2008), The Normans, Curtis, Howard transl, Constable & Robinson, p. 5
^ Chibnall, Marjorie (2008). The Normans. Wiley-Blackwell.
^ (in Italian) The European Center for Norman Studies
^ Dupont, Jerry (2001). The Common Law Abroad: Constitutional and Legal Legacy of the British Empire. Wm. S. Hein Publishing. p. 793. ISBN 978-0-8377-3125-4.
^ Encyclopædia Britannica. "Roger II —King of Sicily". Concise.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 23 May 2007. Retrieved 21 January 2010.
^ Inturrisi, Louis (1987-04-26). "Tracing The Norman Rulers of Sicily". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-01-21.
^ Les Normands en Sicile, p. 17.
^ Lewis, p.148
^ Anna Comnena. The Alexiad, 4.8; Vranousi 1962, pp. 5–26.
^ The Normans, Marjorie Chibnall
^ Chibnall, Marjorie (2000). The Normans. Oxford: Blackwell publishing. p. 62. ISBN 978-1-4051-4965-5.
^ Flori 1999, p. 131.
^ abc Flori 1999, p. 132.
^ Flori 1999, p. 133–34.
^ Flori 1999, p. 134.
^ Flori 1999, pp. 134–36.
^ abc Flori 1999, p. 138.
^ ab Flori 1999, p. 137.
^ This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Béthencourt, Jean de". Encyclopædia Britannica. 3 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Béthencourt, Jean de". Encyclopædia Britannica. 3 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
^ "Norman customary law". Mondes-normands.caen.fr. Retrieved 20 May 2018.
Sources
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
Primary
van Houts, Elisabeth, ed. (2000), The Normans in Europe, Manchester: Manchester Medieval Sources.
Medieval History Texts in Translation, University of Leeds.
Secondary
Bates, David (1982), Normandy before 1066, London
Chalandon, Ferdinand (1907), Histoire de la domination normande en Italie et en Sicilie [History of the Norman domination in Italy & Sicily] (in French), Paris
Chibnall, Marjorie (2000), The Normans, The Peoples of Europe, Oxford.
Chibnall, M. (1999), The Debate on the Norman Conquest
Crouch, David (2003), The Normans: The History of a Dynasty, London: Hambledon.
Douglas, David (1969), The Norman Achievement, London
——— (1976), The Norman Fate, London
Dauzat, Albert; Dubois, Jean; Mitterand, Henri (1971), Larousse étymologique [Etymological Larousse] (in French), Larousse
Flori, Jean (1999), Richard Coeur de Lion: le roi-chevalier [Richard Lionheart: the king-knight], Biographie (in French), Paris: Payot, ISBN 978-2-228-89272-8
Gillingham, John (2001), The Angevin Empire, London
Gravett, Christopher; Nicolle, David (2006), The Normans: Warrior Knights and their Castles, Oxford: Osprey Publishing.
Green, Judith A (1997), The Aristocracy of Norman England, Cambridge University Press
Gunn, Peter (1975), Normandy: Landscape with Figures, London: Victor Gollancz
Harper-Bill, Christopher; van Houts, Elisabeth, eds. (2003), A Companion to the Anglo-Norman World, Boydell
Haskins, Charles H (1918), Norman Institutions
Maitland, FW (1988), Domesday Book and Beyond: Three Essays in the Early History of England (2d ed.), Cambridge University Press (feudal Saxons)
Mortimer, R (1994), Angevin England 1154–1258, Oxford
Muhlbergher, Stephen, Medieval England (Saxon social demotions)
Norwich, John Julius (1967), The Normans in the South 1016–1130, London: Longmans, Green and Co.
——— (1970), The Kingdom in the Sun 1130–1194, London: Longman Group Ltd.
Robertson, AJ, ed. (1974), Laws of the Kings of England from Edmund to Henry I, AMS (Mudrum fine)
Painter, Sidney (1953), A History of the Middle Ages 284−1500, New York
Villegas-Aristizábal, Lucas (2004), Algunas notas sobre la participación de Rogelio de Tosny en la Reconquista Ibérica [Some notes on the participation of Rogelio de Tosny in the Iberian reconquest], Estudios Humanísticos (in Spanish), III, Universidad de Leon, pp. 263–74
——— (2007), Norman and Anglo-Norman Participation in the Iberian Reconquista (PhD thesis), University of Nottingham
——— (2008), Roger of Tosny's adventures in the County of Barcelona, Nottingham Medieval Studies, 52, pp. 5–16
——— (2009), Anglo-Norman involvement in the conquest of Tortosa and Settlement of Tortosa, 1148–1180, Crusades, 8, pp. 63–129
Thompson, Kathleen (October 1987), "Montgomerys", Historical Research, 143 (143): 251–63, doi:10.1111/j.1468-2281.1987.tb00496.x
Villegas-Aristizabal, Lucas (July 2015), "Norman and Anglo-Norman Interventions in the Iberian Wars of Reconquest Before and After the First Crusade", Crusading and Pilgrimage in the Norman World, pp. 103–21
Vranousi, Era A. (1962), "Κομισκόρτης ο έξ Αρβάνων": Σχόλια εις Χωρίον της Άννης Κομνηνής (Δ' 8,4) (in Greek), Ioannina: Εταιρείας Ηπειρωτικών Μελετών
Further reading
Bates, David (2013). The Normans and Empire. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-967441-1.
- Chibnall, Marjorie (2000). The Normans. Oxford, Blackwell publishing.
ISBN 978-1-4051-4965-5.
Rowley, Trevor, ed. (2000). The Normans. The History Press.
External links
Wikisource has the text of the 1905 New International Encyclopedia article Normans. |
Editors of Encyclopædia Britannica, Norman people, Encyclopædia Britannica onlineCS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link) .
Jones, Kaye, 1066: The Impact and Legacy of the Norman Invasion of England, History in an Hour.
Hudson, John, Normans, BBC.
Salerno, V., Sicilian Peoples: The Normans, Best of Sicily Magazine.
Kelly, Patrick, The Normans: their history, arms and tactics.
"Who were the Normans?", Regia Anglorum.
of St. Quentin, Dudo, Gesta Normannorum, The orb, English translation.
Breve Chronicon Northmannicum (in Latin), Storia online.
The Normans (PDF), Jersey heritage trust, archived from the original (PDF) on 26 March 2009.
The Normans in Italy (in Italian), MondoStoria.