Crested porcupine
| Crested porcupine | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Crested porcupine in captivity | |
Conservation status | |
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] | |
Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Hystricidae |
| Genus: | Hystrix |
| Species: | H. cristata |
Binomial name | |
Hystrix cristata Linnaeus, 1758 | |
 | |
The crested porcupine (Hystrix cristata) is a species of rodent in the family Hystricidae[2]found in Italy, North Africa, and sub-Saharan Africa.
Contents
1 Physical attributes
2 Food and digestion
3 Reproduction
4 Behavior
5 Population
6 Range
6.1 Countries
6.1.1 Native
6.1.2 Possibly extirpated
7 References
8 External links
Physical attributes
@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinner{width:100%!important;max-width:none!important}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center}}

The more common name for this species is the crested porcupine. The adult crested porcupine has an average head and body length around 60 to 83 cm (24 to 33 in) long, discounting the tail, and weighs from 13 to 27 kg (29 to 60 lb).[3]
Almost the entire body is covered with bristles which are either dark brown or black and rather coarse. This mammal is recognizable by the quills that run along the head, nape, and back that can be raised into a crest, hence the name crested porcupine. Also, some sturdier quills which are about 35 cm (14 in) in length run along the sides and back half of the body. These sturdier quills are used, for the most part, for defense and are usually marked with light and dark bands which alternate; these are not firmly attached. This porcupine has a shorter tail which has rattle quills at the end. The rattle quills broaden at the terminal end and the broad portion is hollow with thin walls. When these quills are vibrated, they produce a hiss-like rattle.
The front feet of the crested porcupine have four developed and clawed digits with a regressed thumb, the rear feet have five. The paws have naked and padded soles and have a plantigrade gait. The ears are external and both the eyes and ears are very small with long vibrissae on its head. The skull is specific in many ways; first, the infraorbital foramen is greatly enlarged so portions of the masseter extend through it and attach from the frontal side surface of the snout. Second, the angular process is inflected on the lower jaw, and third, the nasal cavity is enlarged. Prominent pockets create enlarged areas of attachment for chewing muscles. Collar bones are very much reduced, and one incisor, one premolar and three molars are present in each quadrant.[4] The male's penis is directed caudally when not erect.[5]
Food and digestion
The crested porcupine is for the most part herbivorous, eating roots, bulbs, and leaves, but occasionally they do consume insects, small vertebrates, and carrion. To ingest calcium and sharpen incisors, they often gnaw on bones. These animals often travel long distances looking for food. They have high crowned teeth that grind plant tissues which are digested in the stomach, and the undigested fibers are retained in an enlarged appendix and anterior large intestine, where they are broken down by microorganisms.
Reproduction
Most of what is known about reproduction in the crested porcupine comes from individuals in captivity. Usually, female crested porcupines have one litter every year. One or two very well developed young are born in a chamber within the burrow that is usually lined with grass, after a 66-day gestation period, on average. The young weigh about 1,000 g (2.2 lb) at birth, which is about 5% of the mother's weight. They leave the den after one week. At this time, the spines begin to harden. Crested porcupines reach adult weight at one to two years and are often sexually mature just before then.[4]Breeding occurs throughout the year.[6]
Behavior
The crested porcupine is a terrestrial mammal; they very seldom climb trees, but can swim. They are nocturnal and monogamous. The crested porcupine takes care of the young for a long time and small family groups consist of the adult pair and young of various ages. In defense, when disturbed, they raise and fan their quills to make themselves look bigger. If continually bothered, the crested porcupine will stamp its feet, whirr the quills, and charge the disturber back end first trying to stab the enemy with the thicker, shorter quills. These attacks are known to have killed lions, leopards, hyenas, and even humans.[4]
Crested porcupines have been known to collect thousands of bones that they find at night. They are mostly nocturnal, and they may wander upon the skeletons of many animals. They collect these bones, and store them in an underground chamber, or cave. Sometimes, humans dig up these bones.
Population
Eight species are placed in the genus Hystrix, only two of which are found outside of Asia. Although it is favored in many parts of its range as food, its conservation status is set at least concern.
Range
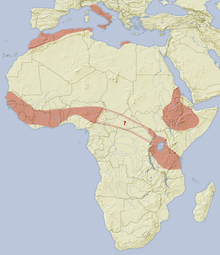
The crested porcupine is found in Italy, North Africa, and sub-Saharan Africa. In the Mediterranean, it is known from mainland Italy and the island of Sicily, Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia; they are also recorded in Libya and along the Egyptian coast. It has been recorded from sea level to 2,550 m (8,370 ft) in Moroccan Anti-Atlas. The porcupine was thought to have been introduced to Italy by the Romans, but fossil and subfossil remains suggest it was possibly present in Europe in the Upper Pleistocene.
Countries

North African crested porcupine (H. cristata) drawn by Gustav Mützel
These are the countries from which the crested porcupine is known:
Native
Algeria; Benin; Burkina Faso; Burundi; Cameroon; Central African Republic, Chad; Côte d'Ivoire; Democratic Republic of the Congo; Eritrea; Ethiopia; Gambia; Ghana; Djibouti; Guinea; Guinea-Bissau; Italy; Israel; Kenya; Liberia; Libya; Mali; Mauritania; Morocco; Nigeria; Rwanda; Senegal; Sierra Leone; Somalia; Sudan; South Sudan; Tanzania, Togo; Tunisia; Uganda[7]
Possibly extirpated
- Egypt
References
^ Grubb, P.; Amori, G.; de Smet, K. & Bertolino, S. (2008). "Hystrix cristata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2008. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 5 January 2009..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Woods, C. A.; Kilpatrick, C. W. (2005). "Hystricognathi". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. Mammal Species of the World: a Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, 3rd ed. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 1538–1600. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0.
^ van Aarde, Rudi (1984). Macdonald, D., ed. The Encyclopedia of Mammals. New York: Facts on File. pp. 704–705. ISBN 978-0-87196-871-5.
^ abc McPhee, M. 2003. "Hystrix cristata" (On-line), Animal Diversity Web. http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/accounts/information/Hystrix_cristata.html.
^ Atalar, O., and A. O. Ceribasi. "The morphology of the penis in porcupine (Hystrix cristata)." VETERINARNI MEDICINA-PRAHA- 51.2 (2006): 66.
^ Felicioli, Antonio, Antonella Grazzini, and Luciano Santini. "The mounting and copulation behaviour of the crested porcupine Hystrix cristata." Italian Journal of Zoology 64.2 (1997): 155-161.
^ Masseti, Marco; Albarella, Umberto; De Grossi Mazzorin, Jacopo (26 January 2010). "The crested porcupine, Hystrix cristata L., 1758, in Italy" (PDF). Anthropozoologica (published December 2010). 45 (2): 27–42. doi:10.5252/az2010n2a2. Retrieved 17 August 2016.
External links
Wikispecies has information related to Hystrix cristata |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hystrix cristata. |
- http://www.wildafrica.cz/images/animals/413_dikobraz-obecny.jpg
An image at the Wayback Machine (archived July 19, 2011)- http://stoneplus.cst.cmich.edu/zoogems/porc%20quills-HatchNecklace.jpg