Corneal reflex
| Corneal reflex | |
|---|---|
| Medical diagnostics | |
 | |
| Purpose | examination of corneal reflex is part of some neurological test |
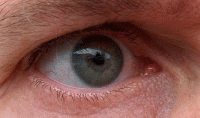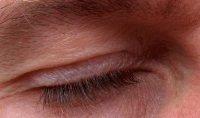
The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though could result from any peripheral stimulus. Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye). The reflex occurs at a rapid rate of 0.1 seconds. The purpose of this reflex is to protect the eyes from foreign bodies and bright lights (the latter known as the optical reflex).[1] The blink reflex also occurs when sounds greater than 40–60 dB are made.[2]
The reflex is mediated by:
- the nasociliary branch of the ophthalmic branch (V1) of the 5th cranial nerve (trigeminal nerve) sensing the stimulus on the cornea only (afferent fiber).
- the temporal and zygomatic branches of the 7th cranial nerve (Facial nerve) initiating the motor response (efferent fiber).
- the centre (nucleus) in the pons of brain stem.
Use of contact lenses may diminish or abolish the testing of this reflex.
The optical reflex, on the other hand, is slower and is mediated by the visual cortex, which resides in the occipital lobe of the brain. The reflex is absent in infants under nine months.
The examination of the corneal reflex is a part of some neurological exams, particularly when evaluating coma. Damage to the ophthalmic branch (V1) of the 5th cranial nerve results in absent corneal reflex when the affected eye is stimulated. Stimulation of one cornea normally has a consensual response, with both eyelids normally closing.
Rates
When awake, the lids spread the tear secretions over the corneal surface, on a typical basis of 2 to 10 seconds (though this may vary individually). However, blinking is not only dependent on dryness and/or irritation.[citation needed] A brain area, the globus pallidus of the basal ganglia, contains a blinking center that controls blinking. Nonetheless, the external stimuli are still involved. Blinking is linked with the extraocular muscles. Blinking is often concurrent with a shift in gaze, and it is believed that this helps the movement of the eye.[citation needed]
See also
- Reflex
- Menace reflex
References
^ "eye, human". Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD, 2009
^ Garde, M.M., & Cowey, A. (2000). "'Deaf hearing': Unacknowledged detection of auditory stimuli in a patient with cerebral deafness". Cortex 36(1), 71–80.