New Ireland Province

Multi tool use
New Ireland Province | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
 New Ireland Province in Papua New Guinea | ||
 New Ireland Province New Ireland Province in Papua New Guinea | ||
| Coordinates: 3°0′S 151°30′E / 3.000°S 151.500°E / -3.000; 151.500 | ||
| Country | Papua New Guinea | |
| Capital | Kavieng | |
| Districts | List
|
|
| Government | ||
| • Governor | Julius Chan | |
| Area | ||
| • Land | 9,557 km2 (3,690 sq mi) | |
| Population (2011 census) | ||
| • Total | 194,067 | |
| Time zone | UTC+10 (AEST) |
|
New Ireland Province, formerly New Mecklenburg (German: Neu-Mecklenburg), is the most northeastern province of Papua New Guinea.
Contents
1 Physical geography
2 Ecology
3 History
4 Human geography
5 Culture
6 Districts and LLGs
7 Provincial leaders
7.1 Premiers (1977–1995)
7.2 Governors (1995–present)
8 Members of the National Parliament
9 See also
10 References
Physical geography
The largest island of the province is New Ireland.
Also part of the province are numerous smaller islands, including Saint Matthias Group (Mussau, Emirau), New Hanover, Djaul, Tabar Group (Tabar, Tatau, Simberi), Lihir, Tanga Group (Malendok, Boang), Feni Islands (Ambitle, Babase) and Anir.
The land area of the province is around 9 560 km². The sea area within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of New Ireland Province is around 230,000 km².
Ecology
In the early days of the French Revolution while in search of a lost scientific expedition the vessel La Recherche passed by New Ireland. On board was the prominent botanist Jacques-Julien Houtou de Labillardière who noted in his journal fine stands of teak (tectona grandis) trees growing at the southern end of the island. This marks the easternmost occurrence of teak, an important timber tree which extends naturally from India to Thailand on the Asian mainland and also is present on Java in the Indonesian archipelago.
History
There have been at least three waves of migration into New Ireland over the last 40,000 years. The famous Lapita pottery culture was present around 3,300 years ago.
Chinese and South-East Asian contact appears to have been longstanding, though evidence is thin.
Dutch explorers made the first European contact in 1616. It was initially believed by Europeans to be part of New Britain, but the British explorer Philip Carteret established in 1767 that the island was physically separate, and gave it the name Nova Hibernia, Latin for 'New Ireland'.
In the 1870s and 1880s, Marquis de Rays, a French nobleman, unsuccessfully attempted to establish a French colony on the island called La Nouvelle France. He sent four ill-fated expeditions to the island, the most famous of which caused the death of 123 settlers.

German residence, Kavieng Neu-Mecklenburg pre-1914 when German New Guinea was seized by Australia.

Government House Port Moresby early 1900s before Australia took administration of British New Guinea and changed its name to Papua. For substantial exploitation of people and resources of New Guinea by Australia its personnel lived significantly less opulently than German ones.
Missionary activity did not begin until 1877, and New Ireland was colonised by Germany in 1886 under the name Neu-Mecklenburg, as part of the German partition comprising the northern half of present-day Papua New Guinea.
Blackbirding (the removal, often by force, of local young men to work on plantations in northern Australia and other Pacific islands) was widespread in New Ireland in the late 19th century especially from Lihir Island and Tanga Islands.
Australia took control in 1914, in the early stages of World War I, and renamed the island as New Ireland, after the island of Ireland. It became part of the Mandated Territory of New Guinea declared in 1921 by the League of Nations and administered by Australia.
During World War II New Ireland was occupied by Japanese forces from January 1942 until September 1945.
Australian colonial administration continued until Papua New Guinea became independent in September 1975.
Human geography
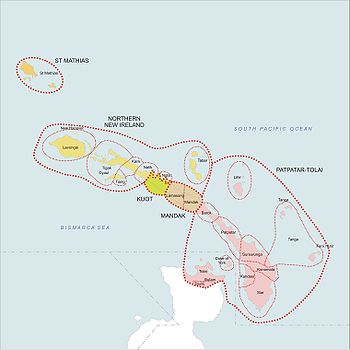
Languages of New Ireland Province
The population during the year 2000 census was 118,350 people, the vast majority of whom (about 90%) live in small rural villages. The population is very young, with a median age of 18.7 years. Over 40% of the population is under the age of 15 years, whereas only 3% is above 65 years old.[1]
The provincial capital is Kavieng, located on the northern tip of the main island. Namatanai is another small town two-thirds of the way along the island. The Boluminski Highway runs down the east coast, linking the two towns.
Around twenty languages are spoken in New Ireland, and the number of dialects and subdialects totals perhaps 45. All are in the New Ireland languages group within the Austronesian language family, except for one language isolate, Kuot.
Culture
New Ireland, like much of Papua New Guinea, has a mixture of the old and the new: traditional cultural practices ("custom") are widespread and almost universally respected, yet society is changing as a result of church activity, urbanisation, and various aspects of global contemporary culture making their mark.
Probably the most famous cultural system of New Ireland is "Malagan", a Nalik word for an ancient and revered set of practices and ceremonies practised throughout much of the main island. Malagan is also an art where the dead are remembered through the various depictions that are carved on Malagan masks. The Malagan masks have a symbolic meaning as the dead must be remembered through the masks and ceremonies. They are the practical means of capturing the spirits of recent dead relatives or clan members. During the colonial era, significant quantities of Malagan masks were collected by European administrators and can be seen in museums all over Europe.
Districts and LLGs

District map of New Ireland Province
Each province in Papua New Guinea has one or more districts, and each district has one or more Local Level Government (LLG) areas. For census purposes, the LLG areas are subdivided into wards and those into census units.[2]
| District | District Capital | LLG Name |
|---|---|---|
Kavieng District |
Kavieng |
Kavieng Urban |
Lavongai Rural | ||
Murat Rural | ||
Tikana Rural | ||
Namatanai District |
Namatanai |
Konoagil Rural |
Namatanai Rural Matalai Rural | ||
Nimamar Rural | ||
Sentral Niu Ailan Rural | ||
Tanir Rural |
Provincial leaders
The province was governed by a decentralised provincial administration, headed by a Premier, from 1977 to 1995. Following reforms taking effect that year, the national government reassumed some powers, and the role of Premier was replaced by a position of Governor, to be held by the winner of the province-wide seat in the National Parliament of Papua New Guinea.[3][4]
Premiers (1977–1995)
Premier |
Term |
|---|---|
| Robert Seeto | 1977–1986 |
| Pedi Anis | 1987–1990 |
| Demas Kavuvu | 1990–1993 |
| Samson Gila | 1993–1995 |
Governors (1995–present)
Premier |
Term |
|---|---|
| Wilson Peni | 1995–1997 |
| Paul Tohian | 1997–2002 |
| Ian Ling-Stuckey | 2002–2007 |
| Julius Chan | 2007–present |
Members of the National Parliament
The province and each district is represented by a Member of the National Parliament. There is one provincial electorate and each district is an open electorate.
Premier |
Term |
|---|---|
| New Ireland Provincial | Julius Chan |
| Kavieng Open | Ian Ling-Stuckey |
| Namatanai Open | Walter Schnaubelt |
See also
Borpop Airfield, Japanese facility during World War Two
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to New Ireland Province. |
^ (PNG Census 2000)
^ National Statistical Office of Papua New Guinea
^ May, R. J. "8. Decentralisation: Two Steps Forward, One Step Back". State and society in Papua New Guinea: the first twenty-five years. Australian National University. Retrieved 31 March 2017..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Provinces". rulers.org. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
CaJw,AAZkgW1ywYomOWPKL
