Music written in all major and/or minor keys

Multi tool use

Title page of the first book of J.S. Bach's The Well-Tempered Clavier, which covers all 24 major and minor keys.
There is a long tradition in classical music of writing music in sets of pieces that cover all the major and minor keys of the chromatic scale. These sets typically consist of 24 numbers, one for each of the major and minor keys (sets that comprise all the enharmonic variants include 30 numbers).
Well-known examples include Johann Sebastian Bach's The Well-Tempered Clavier and Frédéric Chopin's 24 Preludes, Op. 28. Such sets are often organized as preludes and fugues or designated as preludes or études. Some composers have restricted their sets to cover only the 12 major keys or the 12 minor keys; or only the flat keys (Franz Liszt's Transcendental Études) or the sharp keys (Sergei Lyapunov's Op. 11 set). In yet another type, a single piece may progressively modulate through a set of tonalities, as occurs in Ludwig van Beethoven's Two Preludes through all twelve major keys, Op. 39.
The bulk of works of this type have been written for piano solo, but there also exist sets for piano 4-hands; two pianos; organ; guitar; two guitars; flute; recorder; oboe; violin solo; violin and piano; cello solo; cello and piano; voice and piano; and string quartet. There are examples of attempts to write full sets that, for one reason or another, were never completed (Josef Rheinberger's organ sonatas, Dmitri Shostakovich's string quartets, César Franck's L'Organiste).
Contents
1 Sets that cover all 24 keys
1.1 Most well-known sets
1.2 Composers who wrote multiple sets
2 Variants
2.1 Single pieces that modulate through many keys
2.2 Works covering all eight church modes
2.3 Other sets of 24 pieces
3 History
3.1 Bach and his precursors
3.2 After Bach
4 Keys
4.1 Order of keys in published works
5 Notes
6 References
7 External links
Sets that cover all 24 keys
Most well-known sets
Some of the best-known examples of works covering all 24 major and minor keys are:
Johann Sebastian Bach: The Well-Tempered Clavier, Books I and II (1722 and 1742) – two separate sets of 24 preludes and fugues, together known as "the 48".
Frédéric Chopin: 24 Preludes, Op. 28 (1835–39)
Charles-Valentin Alkan: 25 Preludes, Op. 31 (1847) – 24 etudes in all the major and minor keys, Op. 35 and 39 (1848 and 1857)
Alexander Scriabin: 24 Preludes, Op. 11 (1893–95) – All told, Scriabin wrote a total of 90 preludes for piano (50 in major keys, 31 in minor keys, and 9 in indeterminate keys). These contained only one complete set of preludes in all 24 major and minor keys, but he seems to have started another set (spread over 4 opus numbers) before the key relationships broke down.
Sergei Rachmaninoff: 24 Preludes, Opp. 3/2, 23, and 32 (1892, 1901–03, and 1910) – it seems that Rachmaninoff did not originally set out to write a set of works in all 24 keys
Paul Hindemith: Ludus Tonalis (1942) – twelve keys
Dmitri Shostakovich: 24 Preludes and Fugues, Op. 87 (1950–51) – Shostakovich also wrote a separate set of 24 Preludes, Op. 34 in 1933.
Franz Liszt: Transcendental Études, S. 139 (1826–52) – It covers the natural and flat keys (the keys with flat signatures) only. Liszt originally planned to write the full suite of 24 études, but apparently abandoned this plan. In 1897–1905, Sergei Lyapunov wrote his 12 Études d'exécution transcendante, Op. 11, which covers the remaining sharp keys and is dedicated to Liszt's memory.[1]
Composers who wrote multiple sets

Picture of Niels Viggo Bentzon, who wrote 14 complete sets of 24 Preludes and Fugues.
A number of composers have not been content with just one set of works covering all the keys of the scale. For instance, Niels Viggo Bentzon wrote no fewer than 14 complete sets of 24 Preludes and Fugues, a total of 336 pieces in this genre alone.[2][3] Others who have written more than one set include:
Charles-Valentin Alkan: 25 Preludes; Esquisses; 24 Études (published as separate sets of major-key and minor-key études) – Alkan seems to have also started a fourth set: the 11 grands préludes et un transcription du Messie de Hændel, Op. 66, are a set of 12 pieces that cover all the keys that have one to six flats (although Alkan replaces G♭ major with its enharmonic equivalent using sharps, F♯ major). However, this set was never completed.
Lera Auerbach: 24 Preludes (piano); 24 Preludes (violin and piano); 24 Preludes (cello and piano)
Johann Sebastian Bach: The Well-Tempered Clavier, Books I and II (1722 and 1742) – Though separated by 20 years, they are usually considered a single work and referred to as "the 48".
David Cope: 48 Preludes and Fugues
Carl Czerny: At least three sets, piano exercises (Opp. 152, 380) and 24 preludes and fugues ("Der Pianist im klassischen Style: 48 Präludien und Fugen in allen 24 Dur- und Moll-Tonarten als Vorstudien des volkommenen Vortrags aller klassischen Tonwerke"[a], Op. 856)
Johann Nepomuk Hummel: 24 Preludes; 24 Études
Friedrich Kalkbrenner: 24 Études; 24 Preludes
Nikolai Kapustin: 24 Preludes in Jazz Style; 24 Preludes and Fugues
Joseph Christoph Kessler: 24 Études; 24 Preludes
Craig Sellar Lang: Two books of 24 preludes and fugues
Trygve Madsen: 24 Preludes Op. 20; 24 Preludes and Fugues Op. 101
Jaan Rääts: 24 Marginalia; 24 Estonian Preludes
Igor Rekhin (b. 1941 in Tambov, Russia): 24 Preludes and Fugues for guitar; 24 Caprices for solo cello
Josef Rheinberger: 24 Fughettas, Op. 123[4] – He also intended to compose 24 organ sonatas, but died having completed only 20.
Christian Heinrich Rinck: 30 Preludes; Exercises in all the keys
Dmitri Shostakovich: 24 Preludes, Op. 34; 24 Preludes and Fugues, Op. 87 – He also set out to write 24 string quartets all in different keys, but completed only 15 of them.
Sir Charles Villiers Stanford: 2 sets of 24 Preludes, Opp. 163, 179
Louis Vierne: 24 Pièces en style libre; 24 Pièces de fantaisie
Vsevolod Zaderatsky: 24 Preludes; 24 Preludes and Fugues (written in prison, without a piano, on telegraph forms)
Variants
Single pieces that modulate through many keys
Ludwig van Beethoven wrote 2 Preludes through all 12 Major Keys, Op. 39 for piano (1789).[b] These two preludes each progressively traverse the 12 major keys. In Prelude No. 1, each key occupies from 2 to 26 bars. The keys of C♯ and D♭, which are enharmonically equivalent, are both represented. C major both opens and closes the set. In Prelude No. 2, the cycle of keys appears twice; in the first cycle, the number of bars per key ranges from 1 to 8; in the second half, after C every new key signature lasts for only one bar; the cycle concludes with 15 bars of C major. There is no evidence that Beethoven intended to write similar sets in the 12 minor keys.
Giovanni Battista Vitali (1632–1692) included in Artificii musicali, Op. 13 (1689) a passacaglia which modulates through eight major keys (out of twelve) from E♭ major to E major through the cycle of fifths.
The eighth fugue from Reicha's 36 Fugues.
Fugue No. 8 from Anton Reicha's Trente six Fugues pour le Piano-Forté composées d'après un nouveau systême (subtitled Cercle harmonique) modulates through all keys.
The rondo theme of Darius Milhaud's Le bœuf sur le toit is played fifteen times in all 12 major keys (twice in A major and thrice in the tonic, C major). It also passes through every minor key, with the exceptions of E minor and B minor.
Works covering all eight church modes
Around 1704, Johann Pachelbel completed his 95 Magnificat Fugues, which covered all eight of the church modes.
Charles-Valentin Alkan composed Petits préludes sur les huit gammes du plain-chant, for organ (1859, no opus number), a sequence of eight organ preludes covering each of the church modes.
Other sets of 24 pieces
Not all sets of 24 pieces belong in this category. For example, there was no intention in Niccolò Paganini's 24 Caprices for solo violin, Claude Debussy's 24 Préludes for piano, or Pavel Zemek Novak's 24 Preludes and Fugues for piano[5] to cover all the keys. (Paganini may not have been aware of Pierre Rode's 24 Caprices for violin, which did span the 24 keys and were written almost as the same time as Paganini's.)
Chopin's 24 Études, Opp. 10 & 25 might have originally been planned to be in all 24 keys. In fact, apart from Nos. 7 and 8, the first series (Op. 10) is made of couples of études in a major key and its parallel minor (the major key either preceding the minor key or following it) with none of the tonalities occurring twice (except for C major, which appears in No. 1 and then in the only couple which is not major-minor, i.e. Nos. 7 and 8). But in the second series (Op. 25) this tonal scheme gets more and more loose. It is still possible to see connections on a tonal basis between the couples of études in Op. 25, but they are not based on one principle (e.g. Nos. 3 and 4 in F major – A minor, two tonalities which Chopin likes to put together very often, as in his second Ballade).
One might suppose that Chopin considered writing the études in all the tonalities but eventually came to the conclusion that it wasn't practical and turned back to it later, for the 24 Preludes, Op. 28. The fact that the first étude of Op. 10 is made of arpeggios in C major draws a connection to Bach's first book of The Well-Tempered Clavier and makes it clear that Chopin had the tradition on his mind.[original research?]
History
Bach and his precursors
Johann Sebastian Bach's The Well-Tempered Clavier, two complete sets of 24 Preludes and Fugues written for keyboard in 1722 and 1742, and often known as "the 48", is generally considered the greatest example of music traversing all 24 keys. Many later composers clearly modelled their sets on Bach's, including the order of the keys.
It was long believed that Bach had taken the title The Well-Tempered Clavier from a similarly-named set of 24 Preludes and Fugues in all the keys, for which a manuscript dated 1689 was found in the library of the Brussels Conservatoire. It was later shown that this was the work of a composer who was not even born by 1689: Bernhard Christian Weber (1712–1758). In fact, the work was written in 1745–50 in imitation of Bach's example.[6][7] While Bach can safely claim the title The Well-Tempered Clavier, he was not the earliest composer to write sets of pieces in all the keys:
As early as 1567, Giacomo Gorzanis (c.1520–c.1577) wrote a cycle of 24 passamezzo–saltarello pairs.[citation needed] In 1584, Vincenzo Galilei, father of Galileo Galilei, wrote a Codex of pieces illustrating the use of all 24 major and minor keys.[8][citation needed]
In 1640, Angelo Michele Bartolotti wrote Libro primo di chitarra spagnola, a cycle of passacaglias that moves through all 24 major and minor keys according to the circle of fifths.[9] Also in 1640, Antonio Carbonchi wrote Sonate di chitarra spagnola con intavolatura franzese for guitar.[10]
In 1702, Johann Caspar Ferdinand Fischer wrote a cycle of 20 organ pieces all in different keys in his Ariadne musica. These included E major as well as E in Phrygian mode and again in Dorian mode, but not E minor per se. They also excluded C♯/D♭ major, D♯/E♭ minor, F♯/G♭ major, G♯/A♭ minor, and A♯/B♭ minor. Bach modelled the sequence of his 48 Preludes on Fischer's example.[3]
In 1735, between Bach's two sets, Johann Christian Schickhardt wrote his L'alphabet de la musique, Op. 30, which contained 24 sonatas for flute, violin, or recorder in all keys.[11] In 1749, the year before Bach's death, Johann Gottlieb Goldberg, the inspiration for J.S. Bach's Goldberg Variations, wrote his own 24 polonaises for keyboard, one in each of the major and minor keys.[12] Other examples include works by John Wilson (1595–1674), Daniel Croner (1682), Christoph Graupner (1718), Johann Mattheson (1719), Friedrich Suppig (1722), and Johann David Heinichen (1683–1729).
After Bach
The following is an incomplete list of works of this type that have been written since the death of J.S. Bach. (Legend: 5C = circle of fifths)
| Composer |
Work |
Instrument |
Date |
Order |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Étienne Ozi |
Nouvelle méthode de basson |
bassoon |
1787 |
Also, for two bassoons; or bassoon and cello or double bass[13] |
|
Johann Christian Kittel |
16 Preludes in all the keys |
organ |
? |
These preludes span C to G, major and minor. Kittel evidently intended to write 24 preludes, in honour of his teacher J.S. Bach, but the work was left unfinished.[14] |
|
Lev Gurilyov |
24 Préludes et une Fugue |
piano |
pub. 1810 |
5C[c] |
First mentioned in a MA thesis by Matthew J. Roy, 2012.[15] Further comment on style and importance in an article by Wendelin Bitzan.[16] |
Muzio Clementi |
Préludes et exercices dans tous les tons majeurs et mineurs |
piano |
1811 |
[d] | These were appended to the 5th edition of Clementi's Introduction to the Art of Playing on the Piano Forte[17] There is one prelude and exercise for each key, and the set concludes with a "Grande Exercice" that progressively modulates through all the keys but in a somewhat different order than the foregoing; further, the "Grande Exercice" uses G♭ major where the individual pieces use F♯ major.[18] |
Philip Seydler (1765–1819) |
XXIV grands Caprices pour une Flûte |
flute |
1810–12 |
5C[e] |
[19] |
Johann Nepomuk Hummel |
24 Preludes, Op. 67 |
piano |
1815 |
5C[e] |
The first such collection for keyboard in which the preludes are neither paired with fugues nor serve as an introduction to a suite.[20] Some preludes are as short as five bars and unsuitable for concert performance[21] |
Pierre Rode |
24 Caprices en forme d'études |
violin solo |
pub. 1815 |
5C[e] |
[22][23][24] |
Friedrich Kalkbrenner |
24 Etüden durch alle Tonarten, Op. 20 |
piano |
1816 |
[21] | |
Charles Chaulieu |
24 petits préludes: dans les tons majeurs et mineurs, Op. 9 |
piano |
1820 |
[3][25] |
|
Christian Heinrich Rinck |
30 Préludes dans tous les tons majeurs et mineurs, Op. 55/37–66 |
organ |
before 1821 |
[f] | The 30 Préludes for organ are part of Rinck's Practical Organ School, Op. 55, a collection of 117 pieces. They contain both members of all six enharmonically-equivalent key pairs, including the extremely rare keys of A♯ minor and C♭ major[26][27] |
Christian Heinrich Rinck |
Exercices à deux parties dans tous les tons, Op. 67 |
piano |
1821 |
The set includes a piece in A♯ minor.[28] |
|
Ignaz Moscheles |
24 Études, Op. 70 |
piano |
1825–26 |
Studien für das Pianoforte, zur höhern Vollendung bereits ausgebildeter Clavierspieler, bestehend aus 24 characteristischen Tonstücken[29] |
|
Bartolomeo Campagnoli |
30 Preludes in 30 different keys |
violin |
? |
[g] | These cover all 30 keys that use up to 7 sharps or 7 flats[30] |
Friedrich Kalkbrenner |
24 Preludes, Op. 88 |
piano |
1827 |
[21] | |
Joseph Christoph Kessler |
24 Études, Op. 20 |
piano |
1827 |
5C[e] |
The 24 Études were dedicated to Hummel. |
Joseph Christoph Kessler |
24 Preludes, Op. 31 |
piano |
c. 1829 |
5C[e] |
The 24 Preludes were published in 1835[31] and dedicated to Chopin, who a decade later, dedicated the German edition of his 24 Preludes, Op. 28 to Kessler. |
Henri Herz |
Exercices et préludes, Op. 21 |
piano |
c. 1830 |
Dedicated to Hummel[32] |
|
Ignaz Moscheles |
50 Preludes, Op. 73 |
piano |
c. 1830 |
[33] | |
Johann Nepomuk Hummel |
24 Études, Op. 125 |
piano |
c. 1834 |
[34] | |
Carl Czerny |
Grand Exercise in All the Keys, major & minor, Op. 152 |
piano |
? |
||
Carl Czerny |
Grand Exercise in 3rds in all the 24 Keys, Op. 380 |
piano |
1836 |
||
Louise Farrenc |
30 Études dans tous les tons majeurs et mineurs, Op. 26 |
piano |
1837–38 |
[35] | |
Frédéric Chopin |
24 Preludes, Op. 28 |
piano |
1835–39 |
5C[e] |
Dedicated to Camille Pleyel (French edition) and Kessler (German edition) |
Edward Wolff (1816–1880) |
24 Études en forme de Préludes, Op. 20 |
piano |
? |
Wolff was a friend of Chopin's.[36] |
|
Ferdinand David |
Bunte Reihe, Op. 30 |
violin and piano |
c. 1840 |
Published in 1851.[37] The set was arranged by Franz Liszt for solo piano in 1850 (S. 484)[38] |
|
August Klengel |
Les Avant-coureurs, 24 canons |
piano |
1841 |
This was either "patterned after Bach"[39] or "a kind of preparation" for Bach's 48.[40] After Klengel's death, Hauptmann edited and published Klengel's 48 Canons and Fugues, writing "he expressed his own thoughts in the way in which Bach would have done had he lived at the present day"[41] |
|
Stefano Golinelli |
24 Preludes, Op. 23 |
piano |
1845 |
[42] | |
Caspar Kummer |
24 Études mélodiques, Op. 110 |
flute solo |
1846 |
5C[e] |
[43] Étude No. 13 is shown in 2 versions, F♯ major and G♭ major; No. 14 as D♯ minor and E♭ minor |
Charles-Valentin Alkan |
25 Preludes in all major and minor keys, Op. 31 |
piano |
1847 |
The sequence of keys moves alternately up a fourth and down a third. The 24 keys conclude with a final Prayer in C major.[44][45] |
|
Charles-Valentin Alkan |
12 Études in all the major keys, Op. 35 |
piano |
1848 |
5C[h] |
These were complemented by the 12 minor key études, Op. 39 (1857) |
Anton Bernhard Fürstenau |
26 Uebungen (Exercises), Op.107 |
flute solo |
? |
[46] | |
Franz Liszt |
12 Transcendental Études, S. 139 |
piano |
1826–52 |
These covered the neutral and flat keys only. Liszt originally planned to write the full suite of 24 études but apparently abandoned this plan. See Sergei Lyapunov below. |
|
William Sterndale Bennett |
30 Preludes and Lessons, Op. 33 |
piano |
1851–53 |
5C[e] |
Includes major and minor keys with 7 sharps or flats: C♯ major, A♯ minor, C♭ major, A♭ minor. |
Stephen Heller |
24 Preludes, Op. 81 |
piano |
1853 |
5C[e] |
[47] |
Charles-Valentin Alkan |
12 Études in all the minor keys, Op. 39 |
piano |
1857 |
5C[i] |
These complete the sequence that was started with the 12 Études in all the major keys, Op. 35. Études 4–7 comprise the Symphony for Solo Piano, and Études 8–10 make up the Concerto for Solo Piano. |
Carl Czerny |
The Pianist in the Classical Style, 24 Preludes and Fugues, Op. 856 |
piano |
1857 |
5C |
|
Giuseppe Concone (1801–61) |
24 Brilliant Preludes, Op. 37 |
piano |
? |
[j] | [48] |
Heinrich Wilhelm Stolze (1801–1868) |
24 Fugues with preludes |
organ |
1861 |
Pupil of Johann Christian Kittel. The collection was published as part 4 of his organ method and is entitled The Well-Tempered Organ in reference to Bach. |
|
Charles-Valentin Alkan |
Esquisses, Op. 63, 49 short pieces |
piano |
1861 |
Consists of 49 pieces in 4 books, which cover all the major and minor keys twice and end with a final Laus Deo in C major. |
|
Adolf Jensen |
25 Études, Op. 32 |
piano |
1866 |
5C[e] + 1 |
This set employs the circle of fifths for the first 24 preludes, and concludes with an additional prelude in C major |
Ferdinand David |
Dur und Moll: 25 Etüden, Capricen und Charakterstücke in allen Tonarten, Op. 39 |
violin solo, or violin and piano |
? |
[49][50] |
|
Ferruccio Busoni |
24 Preludes, Op. 37, BV. 181 |
piano |
May 1881 |
5C[e] |
Busoni had just turned 15 when he wrote this work. It has been recorded by Daniele Petralia,[51]Geoffrey Douglas Madge,[52] and Trevor Barnard.[53][54][55] |
Adolf von Henselt |
Préambules dans tous les tons |
piano |
1884 |
[56] | |
Sebastian Lee |
30 Präludien in allen Tonarten, Op. 122 |
cello solo |
1885 |
[57] | |
Richard Hofmann |
32 Special-Etüden, Op. 52 |
piano |
1886 |
[58] | |
Felix Blumenfeld |
24 Preludes, Op. 17 |
piano |
1892 |
5C[e] |
Philip Thomson made the world premiere recording in 1999[59] |
José Antonio Santesteban |
24 Preludes, Op. 84 |
piano |
1892 |
[60] | |
Anton Arensky |
24 Morceaux caractéristiques, Op. 36 |
piano |
1894 |
[k] | [61] |
Alexander Scriabin |
24 Preludes, Op. 11 |
piano |
1893–95 |
5C[e] |
Scriabin chose G♭ over F♯. He seems to have set out to write a further set of 24 preludes, and the 23 preludes of Opp. 13, 15, 16 and 17 (containing 6, 5, 5 and 7 preludes respectively) contain evidence of this, but he obviously moved away from his original idea as the key sequence breaks down.[62] |
Max Reger |
111 Canons in all major and minor tonalities |
piano |
1895 |
[63] | |
August Winding |
Preludes in all the keys: A Cycle, Op. 26 |
piano |
? |
[l] | The work is in 25 parts: 24 preludes, ordered by ascending fourths (increasing flats, decreasing sharps), and a final Postludium in C major. It is dedicated to Isidor Seiss. |
Richard Hofmann |
50 leichte, melodische Studien in der ersten Lage u. in allen Tonarten, Op. 107 |
piano |
1899 |
[58] | |
40 melodische Studien in allen Lagen u. Tonarten, Op. 108 |
|||||
Johan Adam Krygell |
Moll und Dur, 24 preludes and fugues |
organ |
1893 |
[64] All minor keys followed by all major keys |
|
Josef Rheinberger |
20 sonatas |
organ |
Rheinberger set out to write 24 organ sonatas, one in each key. He completed 20 of these before his death in 1901.[65] |
||
César Cui |
25 Preludes, Op. 64 |
piano |
1903 |
[m] | [66] Cui's order of keys is unique in that each major key is followed by the minor of its mediant (e.g. C major to E minor). It includes a 25th prelude in C major.[67] |
Sergei Lyapunov |
12 Études d'exécution transcendante, Op. 11 |
piano |
1897–1905 |
This set complements Franz Liszt's set of 12 Transcendental Études from 1826–52 (which was written in neutral and flat keys only) by employing the remaining sharp keys. It is dedicated to Liszt's memory.[1] |
|
Jean-Henri Ravina |
100 Préludes dans tous les tons majeurs et mineurs, Op. 110 |
piano |
? |
[68] | |
Reinhold Glière |
25 Preludes, Op. 30 |
piano |
1907 |
[n] | [69] |
Selim Palmgren |
24 Preludes, Op. 17 |
piano |
1907 |
[o] | |
Emil Sjögren |
Legends: Religious Moods (Swedish: Legender: religiösa stämningar) Op. 46 |
organ |
1907 |
Based on fragments of his famous improvisations in St. John's Church, Stockholm. Divided into two volumes: the first follows the first half of the circle of fifths completely from C major to G♯ minor; in the second volume, the order instead is from F major to E♭ minor. |
|
Richard Hofmann |
Elementar-Studien für Violine, op. 129 |
violin solo |
1909 |
[58] | |
Ludvig Schytte |
Melodische Vortragsstudien in allen Tonarten, Op. 159 |
piano |
1909 |
[70] | |
Hans Sitt |
Dur und Moll: 28 leichte melodische Etüden für Violine (erste Lage) zur Befestigung der Intonation in allen Tonarten, Op. 107 |
violin solo |
1909 |
[71] | |
Sergei Rachmaninoff |
24 Preludes, Opp. 3/2, 23, 32 |
piano |
1892–1910 |
[p] | The Prelude in C♯ minor, Op. 3/2, was part of a collection of pieces, and there is no evidence Rachmaninoff had at that stage planned to write 24 preludes traversing all the keys. Between 1901 and 1903, he wrote 10 Preludes, Op. 23, and in 1910, he completed the 24 with his 13 Preludes, Op. 32.[72] |
Blas María de Colomer |
24 Préludes mélodiques |
piano |
1910 |
5C[e] |
[73] |
Hans Huber |
24 Preludes and Fugues, Op. 100 |
piano 4-hands |
[3] Many sources inexplicably say there were only 12 pieces in the set, while at the same time listing 24 |
||
Louis Vierne |
Vingt-quatre Pièces en style libre, Op. 31 |
organ |
1913 |
[74] | |
Georg Schumann |
Durch Dur und Moll, Op. 61 |
piano |
1916 |
[n] | [75] |
Walter Niemann |
24 Preludes, Op. 55 |
piano |
1918 |
[76] | |
Charles Villiers Stanford |
24 Preludes, Set I, Op. 163 |
piano |
1918 |
Set I has been recorded by Peter Jacobs.[77][78] |
|
Charles Villiers Stanford |
24 Preludes, Set II, Op. 179 |
piano |
1920 |
Set II was completed in December 1920, not in 1921 as many sources report.[79] |
|
Alexander Wunderer |
24 Etüden in allen Tonarten |
oboe solo |
pub. 1924 |
[n] | [80] The 11th Etüde bears a striking similarity to the 11th variation of Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov's Variations on a Theme of Glinka, for oboe and military band.[81] |
Gustav Struempl (1855–1927) |
24 Preludes, Op. 16 |
piano |
? |
[82] | |
Samuel Maykapar |
Biriulki (Spillikins), Op. 28, 26 pieces |
piano |
1926 |
Cycle of 26 children pieces (with program titles) in all 24 major and minor keys (including two times in C major and A minor) in a special order of 3 sets: Set I: 8 pieces (1–8) in the fifths circle order from C major to F♯ minor Set II: 8 pieces (9–16) in the fifths circle order from C major to C minor Set III: 10 pieces (17–26) in the fifths circle order from E major to G♯ minor (17–20), than from A♭ major to B♭ minor (21–24), than the rest 2 pieces in F♯ major and E♭ minor (25–26)[clarification needed] |
|
Louis Vierne |
Pièces de fantaisie, 4 books, Opp. 51, 53–55 |
organ |
1926–27 |
[q] | [74] |
Manuel Ponce |
24 Preludes |
guitar |
c. 1929 |
Twelve of these were published by Andrés Segovia in 1930, but the remainder had to wait for the guitarist Miguel Alcazar to reconstruct them from Ponce's manuscripts before being published in 1981.[83][84] |
|
François Demierre (1893–1976) |
24 Préludes dans tous les tons majeurs et mineurs[85] |
piano |
1932 |
Swiss-French organist and teacher; his first wife was the sister of Ernest Ansermet.[86] |
|
Dmitri Shostakovich |
24 Preludes, Op. 34 |
piano |
1932–33 |
5C[e] |
[87] See also 24 Preludes and Fugues, Op. 87 (1950–51). |
Valery Zhelobinsky |
24 Preludes, Op. 20 |
piano |
1934 |
[n] | Zhelobinsky uses Bach's sequence of keys, but Prelude No. 23, although it is effectively in B♭ minor, has a key signature with 6 flats, as if it were written in E♭ minor (like Prelude No. 8). Most C♮'s in this prelude are arrived at via the use of accidentals, while C♭, which would have required accidentals had the true key signature with only 5 flats been used.[88] |
Vsevolod Zaderatsky |
24 Preludes |
piano |
1934 |
[89] | |
Boris Goltz |
24 Preludes, Op. 2 |
piano |
1934–35 |
[90] Goltz used the key order of Chopin [91] |
|
Charles Koechlin |
Fifteen Vocalises in all major keys, Op. 152 |
voice and piano |
Aug–Sep 1935 |
[92] | |
Charles Koechlin |
Fifteen Vocalises in all minor keys, Op. 154 |
voice and piano |
Oct. 1935 |
[92] | |
Viktor Kosenko |
Twenty-four Pieces for Children, Op. 25 |
Piano |
1936 |
5C[e] |
Erroneously published in 1938 as Op. 15, but later corrected by Musichna Ukraina. |
Vsevolod Zaderatsky |
24 Preludes and Fugues |
piano |
1937–38 |
[93] | |
Algernon Ashton |
24 string quartets |
string quartet |
? |
The set was lost, possibly destroyed in WWII bombing.[94] Ashton also wrote 8 piano sonatas,[94] all in different keys,[95] and it may be that he planned to complete a cycle of 24 of them as well. One source says he wrote 24 Preludes and Fugues,[96] but this is not corroborated. |
|
Roger Sacheverell Coke |
24 Preludes, Op. 33 and Op. 34 |
piano |
1938-41 |
5C[e] |
Two sets, Op. 33 containing eleven, and Op. 34 thirteen.[97][98] |
David Diamond |
52 Preludes and Fugues |
piano |
1939–42 |
[3][96] The first recording that Leonard Bernstein ever made included some of these pieces.[99] |
|
Joseph Jongen |
Vingt-quatre petits préludes pour piano dans tous les tons, Op. 116[100] |
piano |
1941 |
[101] At least some of them exist in a version for organ.[102] |
|
Paul Hindemith |
Ludus Tonalis, 25 movements |
piano |
1942 |
[r] | The work consists of a prelude, 11 interludes, and a postlude, each separated by 12 fugues[3] |
Dmitry Kabalevsky |
24 Preludes, Op. 38 |
piano |
1943–44 |
5C[e] |
|
Julius Weismann |
Der Fugenbaum (The Fugue Tree), 24 Preludes and Fugues in all the keys, Op. 150 |
piano |
1946 |
[96] | |
Matvei Gozenpud |
24 Preludes, Op. 53 |
piano |
1947 |
[103] | |
Craig Sellar Lang |
A miniature 48; two books of short preludes & fugues in all keys, Op. 64 |
piano |
1949 |
[3] | |
York Bowen |
24 Preludes, Op. 102 |
piano |
1938–50 |
[n] | |
Dmitri Shostakovich |
24 Preludes and Fugues, Op. 87 |
piano |
1950–51 |
5C[e] |
See also 24 Preludes, Op. 34 (1932–33). In both these cases, Shostakovich adhered to Chopin's order of keys, although he was greatly influenced by Bach's The Well-Tempered Clavier and even quoted parts of that work in Op. 87. |
Franciszek Zachara |
New Well-Tempered Clavicord for the Piano |
piano |
1950s |
24 sets of preludes and fugues in all major and minor keys, with an additional 25th prelude and fugue (on a theme from Ernő Dohnányi) added at the end. |
|
Hans Gál |
24 Preludes, Op. 83 |
piano |
1959–60 |
Written during a fortnight's hospital stay, as a birthday present to himself; FP October 1960, composer, Edinburgh Society of Musicians[104]. |
|
Gara Garayev |
24 Preludes |
piano |
1951–63 |
5C[e] |
[105][106] |
Mario Castelnuovo-Tedesco |
Les Guitares bien tempérées (The Well-Tempered Guitars), 24 préludes et fugues, Op. 199 |
2 guitars |
1962 |
[s] | Described as "the longest and most important cycle of works for two guitars ever composed", the 200-page score was written between 8 March and 3 June 1962, in response to performances by the popular husband-wife duo Ida Presti and Alexandre Lagoya[107] |
Gunnar de Frumerie |
Circulus Quintus Op. 62, 24 piano pieces |
piano |
1965 |
Some have names which suggest the character of the piece such as "Siciliano", "Tarantella", or "Gavotte". As in the case of Emil Sjögren's Legends for organ, the collection is divided in two volumes, where the first has the pieces ordered in a perfect half-circle of fifths from C major to G♯ minor, and the second volume is ordered in a half-circle of fifths backwards, i.e. starting with F major and ending with E♭ minor. |
|
Richard Cumming |
24 Preludes |
piano |
1966–69 |
Commissioned by John Browning, who stipulated they should be "as hard as possible", gave the world premiere in 1969 and recorded them[108][109][110] |
|
Rodion Shchedrin |
24 Preludes and Fugues, in 2 volumes |
piano |
1964–70 |
5C[e] |
Shchedrin premiered Vol. I in Moscow in 1965 and the complete cycle in 1971. Dedicated to the memory of his father.[111] |
Dmitri Shostakovich |
15 string quartets |
string quartet |
1938–74 |
Shostakovich planned to write 24 string quartets, one each in a different key, but completed only 15 before his death.[112] |
|
Alan Bush |
24 Preludes, Op. 84 |
piano |
1977 |
Composer gave the first performance at the Wigmore Hall on 30 October 1977.[113] |
|
Hans Gál |
24 Fugues, Op. 108 |
piano |
1979–80 |
Written as a 90th birthday present to himself.[114] |
|
Hiroshi Hara (1933–2002) |
24 Preludes & Fugues |
piano |
1981 |
[3] | |
Jaan Rääts |
24 Marginalia, Op. 68 |
2 pianos |
1982 |
[115] | |
Alexander Iakovtchouk (b. 1952) |
24 Preludes and Fugues |
piano |
1983 |
[3] | |
Anthony Burgess |
The Bad-Tempered Electronic Keyboard |
piano |
November–December 1985 |
24 preludes and fugues + a closing "Finale: Natale", written for the 300th anniversary of the birth of Johann Sebastian Bach |
|
Igor Rekhin (b. 1941) |
24 Preludes and Fugues[116][117][118] |
guitar |
1985–90 |
[n] | |
Nikolai Kapustin |
24 Preludes in Jazz Style, Op. 53 |
piano |
1988 |
5C[e] |
[119] |
Jaan Rääts |
24 Estonian Preludes, Op. 80 |
piano |
1988 |
[115] | |
Igor Rekhin (b. 1941) |
24 Caprices[120][121] |
cello solo |
1991 |
[n] | |
David Cope |
The Well-Tempered Disklavier, 48 preludes and fugues |
piano |
1991 |
[3] | |
Sergei Slonimsky |
24 Preludes and Fugues |
piano |
1994 |
Inspired to create this cycle after listening to Glenn Gould's recording of The Well-Tempered Clavier on New Year's Eve, 1993. The cycle was dedicated to the memory of A. N. Dolzhansky. It follows Bach's key organization, ascending in chromatic order from C major to B minor.[111] |
|
Trygve Madsen |
24 Preludes and Fugues, Op. 101 |
piano |
1995–96 |
[3] | |
Howard Blake |
Lifestyle, Op. 489: 24 pieces |
Piano |
1996 |
[122] | [123] |
Nikolai Kapustin |
24 Preludes and Fugues, Op. 82 |
piano |
1997 |
The major keys tour the circle of fifths in the flat direction (beginning with C major and ending with G major), while the minor keys tour in the same mode but begin at the other side of the circle (starting with G♯ minor and ending with E♭ minor). This has the effect of juxtaposing very unrelated keys, and spacing relative majors and minors as far apart from one another as possible.[124] |
|
Ron Weidberg |
Voyage to the End of the Millennium: 24 Preludes and Fugues |
piano |
1997–98 |
[125] | |
Lera Auerbach |
24 Preludes, Op. 41 |
piano |
1999 |
5C[e] |
[83][126] |
| 24 Preludes, Op. 46 |
violin and piano |
||||
| 24 Preludes, Op. 47 |
cello and piano |
||||
Niels Viggo Bentzon |
Det temperede klaver, 14 sets each containing 24 Preludes and Fugues |
piano |
? |
Opp. 157, 379, 400, 409, 428, 470, 530, 532, 541, 542, 546, 554, 633, 638[2][3] |
|
Henry Martin (b. 1950) |
24 Preludes and Fugues |
piano |
1990–2000 |
[3] | |
John Ramsden Williamson (b. 1929) |
Palindromic Preludes (at least 8 sets of 12), New Preludes |
piano |
1993–2000 |
These sets generally consist of 12 major or minor keys[127][128][129][130] |
|
Daniel Padrón (b. 1966) |
24 Nocturnes |
piano |
c. 2002 |
[131] | |
Rob Peters |
24 Preludes, Op. 119 |
organ |
2003 |
[132] | |
Wim Zwaag (b. 1960) |
24 Preludes |
piano |
2004 |
Premiered in April 2007 by Paul Komen at the Bethaniënklooster, Amsterdam[133] |
|
Jeroen van Veen |
24 Minimal Preludes, 2 Books |
piano |
1999–2006 |
5C[e] |
Book I, 1999–2003; Book II, 2004–06 [134] |
Mark Alburger |
Standards: 24 Preludes and Fugues, Op. 162 |
piano |
2008 |
[3] | |
Marc-André Hamelin |
Twelve Etudes in All the Minor Keys |
piano |
1986–2008 |
5C[t] |
Each etude has a title. |
Michelle Gorrell |
Well-Tempered Licks & Grooves: 24 Preludes & Fugues in Jazz Styles |
piano |
2010 |
[3] | |
Leslie Howard |
24 Classical Preludes for Piano, Op. 25 |
piano |
? |
Each prelude is written in the style of a different composer |
|
Shuwen Zhang (b. 1991) |
The 24 Chinese Solar Terms |
piano or harpsichord |
2011–2012 |
[u] | |
Lawrence Chandler |
The Tuning of the World |
string quartet |
2012 |
||
Steven O'Brien |
24 Preludes, Op. 2 |
piano |
2012 |
[135] | |
Michael Brough (b. 1960) |
25 Picture-Preludes for Piano, Op. 19 |
piano |
2013–14 |
All the major and minor keys and a central piece in no (open) key |
Keys
Even though there can only be 24 keys,[v] each note can be represented by several enharmonic note names[w] and so each key can be represented by several enharmonic key names.[x]
In theory,[y] there are 31 possible note names[z] and, taking each as the tonic of one major and one minor key, 62 key names. But 32 of those keys have uncommon signatures which contain double flats or double sharps, so in practice the choice of key name is restricted to the 30 keys whose signatures have no double flats or double sharps. Keys with 6 flats and 6 sharps,[aa] with 7 flats and 5 sharps[ab] and with 5 flats and 7 sharps[ac] are enharmonic to one another. Composers will, in most (though not all) cases, choose only one key from each enharmonic pair. But there are also cases of sets covering all 30 keys, which, in other words, include all enharmonic variants.
The table below outlines the choices made in the various collections listed here. The keys are in the order that J.S. Bach used.
Key |
Key signature |
Comments |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
C major |
No sharps or flats |
|
| 2 |
C minor |
3 flats |
|
| 3 |
Either C♯ major |
7 sharps |
Bach and Alkan chose C♯ major, but most composers have preferred D♭ major |
| or D♭ major |
5 flats |
||
| 4 |
C♯ minor |
4 sharps |
|
| 5 |
D major |
2 sharps |
|
| 6 |
D minor |
1 flat |
|
| 7 |
E♭ major |
3 flats |
|
| 8 |
Either D♯ minor |
6 sharps |
Most composers of sets of 24 pieces have chosen E♭ minor over D♯ minor. Bach, Lyapunov and Ponce used D♯, but most composers have preferred E♭. The first use of D♯ minor was in Bach's The Well-Tempered Clavier, in Fugue No. 8 from Book 1 (although its corresponding Prelude was written in E♭ minor), while D♯ minor was used for both the Prelude and the Fugue in Book 2. Another is in Lyapunov's Étude d'execution transcendante No. 2, subtitled "Ronde des Fantômes" |
| or E♭ minor |
6 flats |
||
| 9 |
E major |
4 sharps |
|
| 10 |
E minor |
1 sharp |
|
| 11 |
F major |
1 flat |
|
| 12 |
F minor |
4 flats |
|
| 13 |
Either F♯ major |
6 sharps |
F♯ major was the choice of Bach, Hummel, Chopin, Heller, Busoni, Lyapunov, Arensky, Blumenfeld, Ponce and Shostakovich. G♭ major was preferred by Alkan, Rachmaninoff, Scriabin, Shchedrin and Winding. |
| or G♭ major |
6 flats |
||
| 14 |
F♯ minor |
3 sharps |
|
| 15 |
G major |
1 sharp |
|
| 16 |
G minor |
2 flats |
|
| 17 |
A♭ major |
4 flats |
|
| 18 |
Either G♯ minor |
5 sharps |
Alkan wrote a piece in A♭ minor, and Brahms a fugue in this key, but most composers have preferred G♯ minor. |
| or A♭ minor |
7 flats |
||
| 19 |
A major |
3 sharps |
|
| 20 |
A minor |
No sharps or flats |
|
| 21 |
B♭ major |
2 flats |
|
| 22 |
Either B♭ minor |
5 flats |
No well-known sets of 24 pieces include A♯ minor. Two examples are from Bartolomeo Campagnoli's 30 Preludes for violin, and Christian Heinrich Rinck's 30 Préludes from his Practical Organ School, Op. 55, published before 1821.[26] |
| or A♯ minor |
7 sharps |
||
| 23 |
Either B major |
5 sharps |
No well-known sets of 24 pieces include C♭ major. While C♭ major is sometimes used in compositions (particularly for the harp, which is especially suited to this key), it is not generally considered one of the standard keys because it is enharmonically equivalent to B major. With its tonic note C♭ being in fact a white key, and its parallel minor having 10 flats, its usage is generally undesirable. It is very rare for a set of pieces covering all the keys to include a piece in C♭ major. C♭ major does appear in Campagnoli's and Rinck's works mentioned above, along with A♯ minor, but those collections include both members of all six enharmonically equivalent pairs.[136] |
| or C♭ major |
7 flats |
||
| 24 |
B minor |
2 sharps |
Order of keys in published works
The circle of fifths, whereby each major key is followed by its relative minor key, is a commonly used schema. Angelo Michele Bartolotti used this approach as early as 1640, and it was also adopted by such later composers as Rode, Hummel, Chopin, Heller, Busoni, Scriabin, Shostakovich, Kabalevsky and Kapustin.
In J.S. Bach's The Well-Tempered Clavier and some other earlier sets, major keys were followed by their parallel minor keys. The Bach order was adopted by Arensky, Glière, York Bowen and others.
Other composers derived their own schemas based on certain logical rationales. For example, in Alkan’s 25 Preludes, Op. 31, the sequence of keys moves alternately up a fourth and down a third.
Yet others used no systematic ordering. Cui, Palmgren, Rachmaninoff and Castelnuovo-Tedesco's works are examples of this.
Notes
^ The number is 48 as preludes and fugues are counted separately
^ C, G, D, A, E, B, F♯, C♯, D♭, A♭, E♭, B♭, F
^ Arranged in a circle of fifths with major keys preceding the minor keys: C, G, D, A etc.; a, e, b ... d.
^ Préludes et exercices: C, a, F, d, G, e, B♭, g, D, b, E♭, c, A, f♯, A♭, f, E, c♯, D♭, b♭, B, g♯, F♯, e♭; Grande Exercice: C, a, F, d, B♭, g, E♭, c, A♭, f, D♭, b♭, G♭, e♭, B, g♯, E, c♯, A, f♯, D, b, G, e
^ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwx Arranged in a circle of fifths, as alternating major and relative minor keys: C, a, G, e, D, b, A, f♯, E, c♯, B, g♯, F♯, e♭, D♭, b♭, A♭, f, E♭, c, B♭, g, F, d. Alexander Scriabin, Rodion Shchedrin et al. chose G♭ over F♯, but this does not affect the essential integrity of the scheme.
^ C, a, G, e, D, b, A, f♯, E, c♯, B, g♯, F♯, d♯, C♯, a♯, F, d, B♭, g, E♭, c, A♭, f, D♭, b♭, G♭, e♭, C♭, a♭
^ C, a, G, e, D, b, A, f♯, E, c♯, B, g♯, F♯, d♯, C♯, a♯, C♭, a♭, G♭, e♭, D♭, b♭, A♭, f, E♭, c, B♭, g, F, d
^ A, D, G, C, F, B♭, E♭, A♭, C♯, G♭, B, E
^ a, d, g, c, f, b♭, e♭, g♯, c♯, f♯, b, e
^ C, a, F, d, B♭, g, E♭, c, A♭, f, D♭, b♭, G♭, e♭, B, a♭ (the prelude is headed "A♭ minor or G♯ minor"), E, c♯, A, f♯, D, b, G, e
^ C, c, D♭, c♯ leading to D♭, D, d, E♭, e♭, E, e, F, f, F♯, f♯, G, g, A♭, g♯, A, a, B♭, b♭, B, b
^ C, a, F, d, B♭, g, E♭, c, A♭, f, D♭, b♭, G♭, e♭, B, g♯, E, c♯, A, f♯, D, b, G, e, C
^ C, e, G, b, D, f♯, A, c♯, E, g♯, B, e♭, F♯, b♭, D♭, f, A♭, c, E♭, g, B♭, d, F, a, C
^ abcdefg C, c, D♭, c♯, D, d, E♭, e♭, E, e, F, f, F♯, f♯, G, g, A♭, g♯, A, a, B♭, b♭, B, b, C; Alexander Wunderer and York Bowen chose G♭ over F♯; Valery Zhelobinsky notated his B♭ minor prelude with a 6-flat key signature (ostensibly E♭ minor), using accidentals to achieve the correct tonality.
^ e, f♯, E, c♯, G, g, D, b, g♯, A♭, C, a, B, d, B♭, F, f, A, F♯, e♭, c, E♭, b♭, D♭
^ c♯, f♯, B♭, d, D, g, E♭, c, A♭, e♭, G♭, C, b♭, E, e, G, f, F, a, A, b, B, g♯, D♭
^ C, a, d, F, g, B♭, c, e, G, b, D♭, b♭, A♭, f, g♯, c♯, e♭, D, E♭, F♯, A, B, f♯, E
^ C, G, F, A, E, E♭, A♭, D, B♭, D♭, B, F♯
^ g, D, a, E, b, F♯, c♯, A♭, e♭, B♭, f, C, G, d, A, e, B, f♯, C♯, g♯, E♭, b♭, F, c
^ a, e, b; c, g, d; e♭, b♭, f; f♯, c♯, a♭. The etudes are laid out in four groups of three keys following the ascending circle of fifths separated by a minor third.
^ C, c, C♯, c♯, D, d, E♭, e♭, E, e, F, f, F♯, f♯, G, g, A♭, g♯, A, a, B♭, b♭, B, b
^ There are 12 notes in the octave. Each of them can be the tonic of one major and one minor key.
^ Note names which designate the same actual note in the 12 note octave such as G♯ and A♭.
^ Keys whose tonics are enharmonic to one another such as F♯ major and G♭ major.
^ If one restricts oneself to the note names used for the diatonic and chromatic tones of the 15 keys which use no double flats or double sharps in their signature.
^ The seven notes A, B, C, D, E, F and G can be natural, flat or sharp. All notes except C and F can be double-flatted. All notes except B and E can be double-sharped. F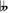 and C
and C occur only (first as chromatic tones) in keys with double flats in their key signature. B
occur only (first as chromatic tones) in keys with double flats in their key signature. B and E
and E occur only (first as chromatic tones) in keys with double sharps in their key signature.
occur only (first as chromatic tones) in keys with double sharps in their key signature.
^ G♭ major and F♯ major, E♭ minor and D♯ minor
^ C♭ major and B major, A♭ minor and G♯ minor
^ D♭ major and C♯ major, B♭ minor and A♯ minor
References
^ ab "Liszt: The complete music for solo piano, Vol. 4 – Transcendental Studies performed by Leslie Howard", Hyperion-Records.co.uk.
^ ab "Niels-Viggo Bentzon", Musicweb-international.com. Retrieved 2 February 2015
^ abcdefghijklmno "Bach cantatas, Arrangements & Transcriptions of Bach's Works: Arrangements & Works inspired by Well-Tempered Clavier BWV 847–869 & BWV 879–893 (WTC)", Bach-Cantatas.com.
^ Weyer, Martin (2010). "2". In Rudolf Faber. Handbuch Orgelmusik (in German) (2 ed.). Kassel: Bärenreiter. p. 296. ISBN 9783761822029..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ArkivMusic. Retrieved 10 April 2013
^ Grove's Dictionary of Music and Musicians, 5th ed, 1954, Vol. IX, p. 223.
^ "The Well-Tempered Clavier I", ERPmusic.com.
^ Ricercares a quattro voci by Vincenzo Galilei, 1584[dead link]
^ "Bartolotti, Angelo Michele". Archived from the original on August 20, 2011. Retrieved 2012-06-20.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
^ ""Antonio Carbonchi, Sonate di chitarra spagnola con intavolatura franzese … (1640)", Library.Appstate.edu". Archived from the original on August 20, 2011. Retrieved 2012-06-20.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
^ "L'Alphabet de la Musique", Diapason.Xentonic.org (archive from 28 January 2018, accessed 30 August 2018).
^ Goldberg, 24 Polonaises: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Ozi, Nouvelle méthode de basson: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ "Second Wind: John Brock Plays the Juget-Sinclair Organ", RavenCD.com.
^ Matthew J. Roy, The Genesis of the Soviet Prelude Set for Piano, Eastern Washington University, 2012, p. 11.
^ Wendelin Bitzan, Durch alle Tonarten: Omnitonale Präludienzyklen für Klavier, Archiv für Musikwissenschaft Vol. 73 (No. 3 / 2016), p. 12f.
^ Muzio Clementi (1752–1832): Life and Work: 2. Works", ClementiSociety.com.
^ Clementi, Préludes et exercices: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Seydler, XXIV grands Caprices pour une Flûte: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Chia-Ling Hsieh: An analytical study of York Bowen's Twenty-Four Preludes in all Major and Minor Keys, Op. 102 (Dissertation)
^ abc "Golden Fingers: News (2007)". Archived from the original on May 9, 2007. Retrieved 2012-06-20.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
^ ArkivMusic: Pierre Rode, 24 Caprices en forme d'études
^ amazon
^ archive.org
^ RIPM Journal
^ ab >IMSLP: 16 sharp preludes, Nos. 37–52
^ IMSLP: 14 flat preludes, Nos. 53–66,
^ "About Keys and Accidentals", Cisdur.de.
^ Moscheles, 24 Études, Op. 70: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ IMSLP: Campagnoli, 30 Preludes for violin
^ Maurice Hinson, Guide to the Pianist’s Repertoire
^ Herz, 24 Exercises et Préludes, Op. 21: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Moscheles, 50 Preludes, Op. 73: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ [1]
^ Free scores by Louise Farrenc at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Maurice Hinson, Guide to the Pianist's Repertoire
^ Bunte Reihe, Op.30 (David, Ferdinand): Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Hyperion Records
^ Thomas Tapper, Percy Goetschius, Essentials in Music History, p. 250
^ Grove, ed. (1900). A Dictionary of Music and Musicians, p.739.
^ Grove's Dictionary of Music and Musicians, 5th ed, 1954, Vol. IV, p. 780
^ [https://imslp.org/wiki/24_Preludes%2C_Op.23_(Golinelli%2C_Stefano)
^ Kummer, 24 Études mélodiques: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Alkan, 25 Preludes in All Major and Minor Keys, Op. 31: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Classics Online Archived 2014-07-12 at the Wayback Machine
^ Fürstenau, 26 Uebungen für die Flöte: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Heller, 24 Preludes, Op. 81: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ IMSLP: Concone, 24 Preludes, Op. 37
^ List of works by Ferdinand David: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ David, 25 Etüden, Capricen und Charakterstücke in allen Tonarten für die Violine allein oder mit Pianofortebegleitung: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ OnClassical Archived 2011-12-17 at the Wayback Machine
^ ArkivMusic
^ Classical Archives
^ Music Web International
^ Busoni, 24 Preludes, Op. 37: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Henselt: Préambules dans tous les tons. Retrieved 22 July 2016
^ List of compositions by Sebastian Lee: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ abc List of compositions by Richard Hofmann: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Ivory Classics
^ [2]
^ Arensky, 24 Morceaux caractéristiques, Op. 36: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Hyperion Records
^ Reger, 111 Canons: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Krygell, Moll und Dur: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Worcester American Guild of Organists Archived 2014-02-01 at the Wayback Machine
^ IMSLP: Cui, 25 Preludes, Op. 64
^ Matthew Roy, Preludophilia: César Cui's Op. 64
^ List of compositions by Jean Henri Ravina: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Glière, 25 Preludes, Op.30: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ List of compositions by Ludvig Schytte: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ List of compositions by Hans Sitt: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ "Rachmaninov: Preludes, Op 32", Hyperion-records.co.uk.
^ Colomer, 24 Préludes mélodiques: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ ab notredamedeparis Archived 2012-06-20 at the Wayback Machine
^ IMSLP
^ [3]
^ Bach Cantatas
^ Stanford, 24 Preludes, Op. 163: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Music Web International
^ Wunderer, 24 Etüden in allen Tonarten: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Linwood William Zoller IV, Historical Études for Oboe: 17th–20th Centuries
^ cisdur
^ ab Unsung Composers
^ Liner notes from Naxos, Ponce Guitar Works, Vol. 1, Adam Holzmann
^ Sheet Music Warehouse
^ Bibliothèque Cantonale et Universitaire – Lausanne
^ Classical Archives
^ Zhelobinsky, 24 Preludes, Op. 20: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Matthew Roy
^ Boris Goltz: Complete Works for Solo Piano at AllMusic
^ [4]
^ ab List of compositions by Charles Koechlin: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
^ Vsevolod Petrovich Zaderatsky (1891–1953) – A Lost Soviet Composer
^ ab "English Music Festival". Archived from the original on 2014-02-23. Retrieved 2012-06-20.
^ Music Web International
^ abc Fugues and Fugue Sets
^ Somm Recordings
^ Planet Hugill. Retrieved 31 October 2018
^ David Diamond: Preludes and Fugues for piano at AllMusic
^ cebedem
^ Music Web International
^ Arkiv Music
^ [5]
^ Hans Gál site
^ Toccata Classics
^ MusicWeb International
^ SoloDuo
^ Eroica
^ Sansbaton
^ ArkivMusic
^ ab Three Cycles of 24 Preludes and Fugues by Russian Composers: D. Shostakovich, R. Shchedrin and S. Slonimsky, Yun-Jin Seo 2003
^ Shostakovich: The String Quartets
^ Alan Bush Trust
^ Boosey & Hawkes
^ ab Music Web International: Jaan Rääts (b. 1932)
^ Classical Archives
^ Rekhin.narod.ru
^ WenatcheeTheHatchet
^ Naxos
^ Rekhin.narod.ru
^ Classical Archives
^ The keys are arranged in a sequence of falling fifths, starting with B minor and ending in F♯ major
^ Howard Blake website; Retrieved 12 August 2013
^ Music Web International
^ Open University: Dr Ron Weidberg
^ Lera Auerbach site Archived 2011-10-18 at the Wayback Machine
^ Classical Archives
^ Muray McLachlan site Archived 2009-01-05 at the Wayback Machine
^ Music Web International
^ iodalliance
^ Daniel Padrón site
^ IMSLP: Peters, 24 Preludes for organ
^ Wim Zwaag site
^ Jeroen van Veen site
^ [6]
^ IMSLP: Rinck, 14 flat preludes, Nos. 53–66
External links
The Short-Tempered Clavier: Preludes and Fugues in all the Major and Minor Keys Except for the Really Hard Ones, S. easy as 3.14159265 (P.D.Q. Bach)
HxRFthBFwtqh,VbCc0RC4rg7qC1U6P3LiczlNinr pL06MgRjFW54,wBfmJKm,WgF 3tzflu oqFU3 2