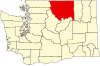
Okanogan County, Washington
Okanogan County, Washington | ||
|---|---|---|
 Okanogan County courthouse in Okanogan | ||
| ||
 Location in the U.S. state of Washington | ||
 Washington's location in the U.S. | ||
| Founded | February, 1888 | |
| Named for | Okanagan people | |
| Seat | Okanogan | |
| Largest city | Omak | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 5,315 sq mi (13,766 km2) | |
| • Land | 5,268 sq mi (13,644 km2) | |
| • Water | 47 sq mi (122 km2), 0.9% | |
| Population (est.) | ||
| • (2017) | 41,742 | |
| • Density | 7.8/sq mi (3.0/km2) | |
| Congressional district | 4th | |
| Time zone | Pacific: UTC−8/−7 | |
| Website | okanogancounty.org | |
Okanogan County /ˌoʊkəˈnɑːɡən/[1] is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington along the Canada–US border. As of the 2010 census, the population was 41,120.[2] The county seat is Okanogan,[3] while the largest city is Omak. Its area is the largest in the state.[4]
About a fifth of the county's residents live in the Greater Omak Area. The county forms a portion of the Okanogan Country. The first county seat was Ruby, which has now been a ghost town for more than 100 years.
Okanogan County was formed out of Stevens County in February 1888.[5] The name derives from the Okanagan language place name ukʷnaqín.[6] The name Okanogan (Okanagan) also refers to a part of southern British Columbia.
Contents
1 History
2 Geography
2.1 Geographic features
2.2 Major highways
2.3 Adjacent counties
2.4 National protected areas
3 Demographics
3.1 2000 census
3.2 2010 census
4 Communities
4.1 Cities
4.2 Towns
4.3 Census-designated places
4.4 Other unincorporated communities
4.5 Ghost towns
5 Politics
6 See also
7 Further reading
8 References
History
Before Europeans arrived, the Okanogan County region was home to numerous indigenous peoples that would eventually become part of three Indian reservations referred to as the Northern Okanogans or Sinkaietk, Tokoratums, Kartars and Konkonelps. They spoke in seven types of Interior Salish languages related to the Puget Sound tribes. The Okanogans experienced a favorable climate, camping in the winter, hunting bears in the spring, catching fish in the summer and hunting deer in fall. The camps consisted of teepee-like longhouses built with hides and bark. Women gathered nuts and berries. A popular destination for this was the Kettle Falls, where the Columbia River dropped some 20 feet (6.1 m).
Due to its remoteness, the Okanogan County area was one of the last in Washington settled by white people. It was an early thoroughfare used by prospectors to gain access to other communities, such as British Columbia. By the 21st century, the region specialized in agriculture, forestry and tourism. Electric producer Grand Coulee Dam was constructed between 1933 and 1942, originally with two power plants, around the Okanogan and Grant counties at the former's southern border.[7]
In July 2014, the Carlton Complex wildfire burned over 250,000 acres (390 sq mi; 1,000 km2) in Okanogan County. It destroyed over 300 homes[8] including 100 in and around Pateros[9]
Geography

Landscape near Winthrop, Washington
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 5,315 square miles (13,770 km2), of which 5,268 square miles (13,640 km2) is land and 47 square miles (120 km2) (0.9%) is water.[10] It is the largest county in the state by area, and it is larger than three states in land area.[11]
Geographic features
- Cascade Mountains
- Columbia River
- Okanogan River
North Gardner Mountain, the highest point in Okanogan County- Beaner Lake
Major highways
 U.S. Route 97
U.S. Route 97
 State Route 20
State Route 20
 State Route 153
State Route 153
Adjacent counties
Ferry County – east
Lincoln County – southeast
Grant County – south
Douglas County – south
Chelan County – southwest
Skagit County – west
Whatcom County – west
Fraser Valley Regional District, British Columbia – northwest
Okanagan-Similkameen Regional District, British Columbia – north
Kootenay Boundary Regional District, British Columbia – northeast
National protected areas
Pacific Northwest National Scenic Trail (part)
Nez Perce National Historical Park (part)- Okanogan National Forest
- Pasayten Wilderness
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1890 | 1,467 | — | |
| 1900 | 4,689 | 219.6% | |
| 1910 | 12,887 | 174.8% | |
| 1920 | 17,094 | 32.6% | |
| 1930 | 18,519 | 8.3% | |
| 1940 | 24,546 | 32.5% | |
| 1950 | 29,131 | 18.7% | |
| 1960 | 25,520 | −12.4% | |
| 1970 | 25,867 | 1.4% | |
| 1980 | 30,639 | 18.4% | |
| 1990 | 33,350 | 8.8% | |
| 2000 | 39,564 | 18.6% | |
| 2010 | 41,120 | 3.9% | |
| Est. 2017 | 41,742 | [12] | 1.5% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[13] 1790–1960[14] 1900–1990[15] 1990–2000[16] 2010–2016[2] | |||
2000 census
As of the census[17] of 2000, there were 39,564 people, 15,027 households, and 10,579 families residing in the county. The population density was 8 people per square mile (3/km²). There were 19,085 housing units at an average density of 4 per square mile (1/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 75.32% White, 0.28% Black or African American, 11.47% Native American, 0.44% Asian, 0.07% Pacific Islander, 9.58% from other races, and 2.84% from two or more races. 14.38% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 14.0% were of German, 9.5% English, 9.2% United States or American and 6.8% Irish ancestry.
There were 15,027 households out of which 33.20% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 54.40% were married couples living together, 11.00% had a female householder with no husband present, and 29.60% were non-families. 24.50% of all households were made up of individuals and 9.70% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.58 and the average family size was 3.04.
In the county, the population was spread out with 27.70% under the age of 18, 7.30% from 18 to 24, 25.50% from 25 to 44, 25.50% from 45 to 64, and 14.00% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38 years. For every 100 females there were 99.20 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 98.00 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $29,726, and the median income for a family was $35,012. Males had a median income of $29,495 versus $22,005 for females. The per capita income for the county was $14,900. About 16.00% of families and 21.30% of the population were below the poverty line, including 28.20% of those under age 18 and 10.40% of those age 65 or over.
2010 census
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 41,120 people, 16,519 households, and 10,914 families residing in the county.[18] The population density was 7.8 inhabitants per square mile (3.0/km2). There were 22,245 housing units at an average density of 4.2 per square mile (1.6/km2).[19] The racial makeup of the county was 73.9% white, 11.4% American Indian, 0.6% Asian, 0.4% black or African American, 0.1% Pacific islander, 10.1% from other races, and 3.5% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 17.6% of the population.[18] In terms of ancestry, 21.4% were German, 12.4% were Irish, 12.2% were English, and 3.6% were American.[20]
Of the 16,519 households, 29.4% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 49.7% were married couples living together, 10.7% had a female householder with no husband present, 33.9% were non-families, and 28.0% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.45 and the average family size was 2.96. The median age was 42.9 years.[18]
The median income for a household in the county was $38,551 and the median income for a family was $48,418. Males had a median income of $37,960 versus $29,032 for females. The per capita income for the county was $20,093. About 14.7% of families and 19.5% of the population were below the poverty line, including 27.3% of those under age 18 and 9.2% of those age 65 or over.[21]
Communities

Landscape near Okanogan, Washington
Cities
- Brewster
Okanogan (county seat)- Omak
- Oroville
- Pateros
- Tonasket
Towns
- Conconully
Coulee Dam (partial)- Elmer City
- Nespelem
- Riverside
- Twisp
- Winthrop
Census-designated places
- Disautel
- Loomis
- Malott
- Methow
- Nespelem Community
- North Omak
Other unincorporated communities
- Aeneas
- Azwell
- Carlton
Ellisford (aka Ellisforde)- Havillah
- Mazama
- Monse
- Nighthawk
- Rocky Butte
- Synarep
- Wauconda
Ghost towns
- Bodie
- Bolster
- Chesaw
- Molson
- Ruby
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
2016 | 54.7% 9,610 | 35.9% 6,298 | 9.4% 1,648 |
2012 | 54.2% 9,221 | 41.8% 7,108 | 4.0% 674 |
2008 | 51.8% 8,798 | 44.8% 7,613 | 3.4% 576 |
2004 | 59.0% 9,636 | 38.6% 6,309 | 2.4% 397 |
2000 | 63.4% 9,384 | 29.3% 4,335 | 7.3% 1,079 |
1996 | 45.1% 5,890 | 36.8% 4,810 | 18.2% 2,375 |
1992 | 32.7% 4,265 | 38.5% 5,015 | 28.8% 3,753 |
1988 | 49.9% 5,856 | 48.0% 5,630 | 2.2% 254 |
1984 | 57.3% 7,476 | 40.8% 5,330 | 1.9% 253 |
1980 | 51.7% 6,460 | 37.1% 4,634 | 11.2% 1,399 |
1976 | 47.1% 5,455 | 47.8% 5,543 | 5.2% 597 |
1972 | 56.1% 5,796 | 37.1% 3,835 | 6.8% 703 |
1968 | 45.2% 4,490 | 44.1% 4,379 | 10.7% 1,066 |
1964 | 37.5% 3,931 | 62.5% 6,554 | 0.1% 10 |
1960 | 48.3% 5,169 | 51.5% 5,507 | 0.2% 22 |
1956 | 50.7% 5,448 | 49.3% 5,298 | 0.1% 8 |
1952 | 55.6% 6,085 | 44.0% 4,817 | 0.4% 48 |
1948 | 41.1% 4,083 | 56.8% 5,644 | 2.1% 208 |
1944 | 46.6% 4,084 | 53.0% 4,642 | 0.4% 38 |
1940 | 44.0% 4,244 | 55.5% 5,362 | 0.5% 49 |
1936 | 27.3% 2,367 | 64.9% 5,622 | 7.8% 678 |
1932 | 32.8% 2,277 | 57.1% 3,969 | 10.1% 701 |
1928 | 64.9% 3,245 | 34.4% 1,722 | 0.7% 36 |
1924 | 50.4% 2,531 | 14.4% 721 | 35.2% 1,769 |
1920 | 55.0% 2,784 | 24.9% 1,260 | 20.1% 1,020 |
1916 | 35.6% 1,896 | 54.8% 2,924 | 9.6% 514 |
1912 | 19.0% 804 | 34.5% 1,461 | 46.6% 1,974[23] |
1908 | 49.2% 1,368 | 38.7% 1,074 | 12.1% 337 |
1904 | 66.6% 1,192 | 24.3% 435 | 9.1% 162 |
1900 | 38.1% 457 | 59.5% 714 | 2.4% 29 |
1896 | 22.7% 284 | 76.0% 950 | 1.3% 16 |
1892 | 50.0% 577 | 36.9% 425 | 13.1% 151 |
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Okanogan County, Washington. |
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Okanogan County, Washington
- Okanogan Conservation District
Further reading
An illustrated history of Stevens, Ferry, Okanogan and Chelan counties, State of Washington. Western Historical Pub. Co. 1904..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
Available online through the Washington State Library's Classics in Washington History collection
 | Fraser Valley Regional District | Regional District of Okanagan-Similkameen | Regional District of Kootenay Boundary |
| |||
Whatcom County | |||||||
Skagit County | Ferry County | ||||||
Chelan County | Douglas County Grant County | Lincoln County |
References
^ "Washington Placenames Pronunciation". Washington County Highpoint Trip Reports. Missing or empty|url=(help);|access-date=requires|url=(help)
^ ab "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 15 July 2011. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 31 May 2011. Retrieved 7 June 2011.
^ Wilma, David (21 January 2006). "Okanogan County — Thumbnail History". HistoryLink.org.
^ "Washington State Archives – Central Regional Branch: Guide to Holdings: Okanogan County". Retrieved 31 December 2007.
^ Bright, William (2004). Native American placenames of the United States. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 346. ISBN 978-0-8061-3598-4. Retrieved 16 September 2011.
^ Thumbnail History. HistoryLink. Retrieved 17 February 2013.
^ "Fire's updated toll: 300 homes, 'horrifying' devastation". Seattle Times. 26 July 2014. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
^ Geranios, Nicholas K.; Johnson, Gene (19 July 2014). "Damage from Washington Wildfires 'Hard to Believe'". The Associated Press. Boston.com. Archived from the original on 19 July 2014.
^ "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. 22 August 2012. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
^ Rhode Island has 1,545 sq. mi, and Delaware has 2,489 sq. mi. Connecticut has 5,543 sq. mi. total, but only 4,842 sq. mi. of land area, and thus is considered smaller than Okanogan County in this regard.
^ "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved 4 April 2018.
^ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 12 May 2015. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
^ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
^ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
^ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
^ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 11 September 2013. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
^ abc "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
^ "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 – County". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
^ "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006–2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
^ "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006–2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
^ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 10 April 2018.
^ The leading "other" candidate, Progressive Theodore Roosevelt, received 1,088 votes, while Socialist candidate Eugene Debs received 827 votes, Prohibition candidate Eugene Chafin received 38 votes, and Socialist Labor candidate Arthur Reimer received 21 votes.
Coordinates: 48°33′N 119°45′W / 48.55°N 119.75°W / 48.55; -119.75